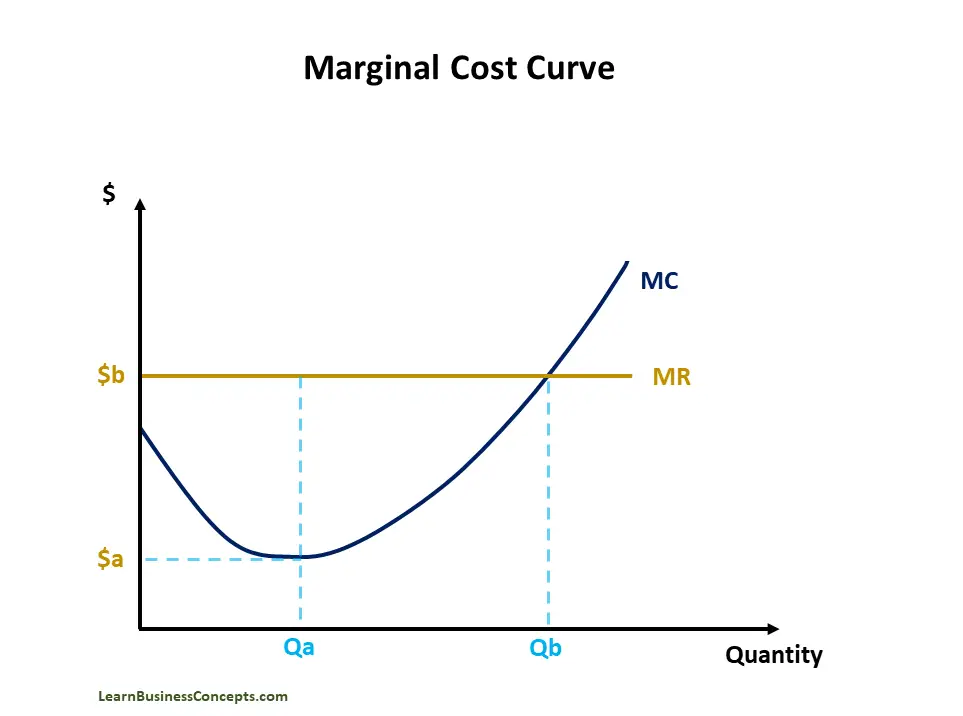
why is the marginal cost curve u shaped Short run cost curves tend to be U shaped because of diminishing returns In the short run capital is fixed After a certain point increasing extra workers leads to declining productivity
The following article will guide you to know why cost curve is U shaped The addition of fixed and Variable Cost gives us total costs which when divided by the output give us Average Costs in the short period The nature of short period Average Cost Curve is U shaped The marginal cost curve is a U shaped curve It indicates that initially when the production starts the marginal cost is comparatively high as it reflects the total cost including fixed and variable costs
why is the marginal cost curve u shaped

why is the marginal cost curve u shaped
https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perfectcompetitionsflsonline-151119125008-lva1-app6891/95/perfect-competition-sfls-online-18-638.jpg?cb=1452612519

Why Is Short Run Average Cost Curve U Shaped U Shaped Average Cost
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/2xZLEQfLSl4/maxresdefault.jpg

Measures Of Cost Average Marginal Cost Why Is Marginal Cost Curve
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/AEcT6EG1wcI/maxresdefault.jpg
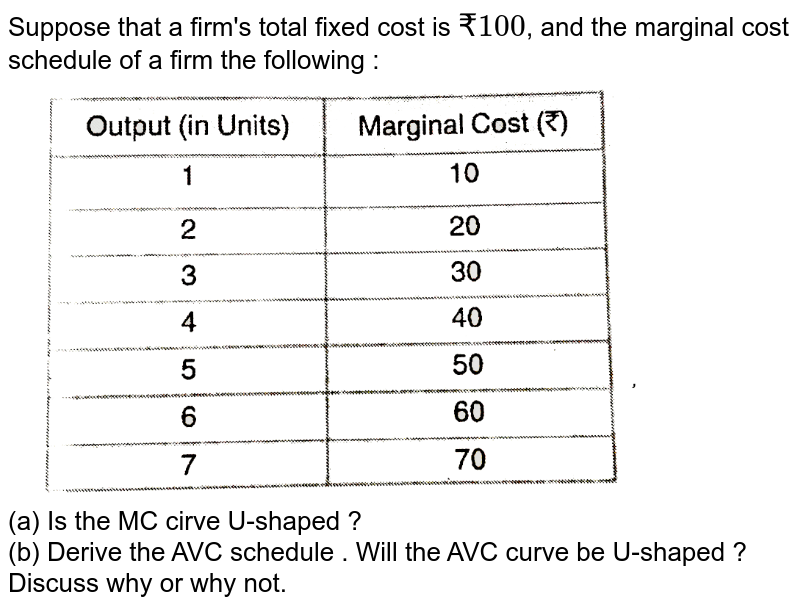
The Marginal Cost curve is U shaped because initially when a firm increases its output total costs as well as variable costs start to increase at a diminishing rate At this stage due to economies of scale and the Law of Diminishing Returns Marginal Cost falls till it In the short run the shapes of the cost curves AC AVC MC are determined by the law of diminishing marginal returns This fully explained on the page Diminishing Returns Returns to Scale Diagram The law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
The SMC curve is a U shaped curve due to the law of variable proportions In order to understand the reason behind the U shape of SMC let us divide the SMC curve UAB into three different parts according to the law of variable proportions UA The average variable cost curve lies below the average total cost curve and is typically U shaped or upward sloping Marginal cost MC is calculated by taking the change in total cost between two levels of output and dividing by the change in output
More picture related to why is the marginal cost curve u shaped

Understanding The Shape Of A Marginal Cost Curve Economics Stack Exchange
https://i.stack.imgur.com/5wQEF.png
Why Is The Cost Curve Always U Shaped Give The Reasons
https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/question-thumbnail/en_26301137.png
What Is Marginal Cost Explanation Formula Curve Examples
https://learnbusinessconcepts.com/wp-content/uploads/Marginal-Cost-Curve-Diagram.png
The average variable cost curve lies below the average total cost curve and is also typically U shaped We calculate marginal cost MC by taking the change in total cost between two levels of output and dividing by the change in output In this graph we can observe three important properties of cost curves that apply to most firms 1 The marginal cost curve eventually rises as output increases 2 the average total cost curve is U shaped and 3 the marginal cost
[desc-10] [desc-11]

Understanding Firm Short Run Cost Curves YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/OSaLDDQk0OE/maxresdefault.jpg
The Shape Of The Marginal Cost Curve YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/W5YmVFlSPZ8/maxresdefault.jpg
why is the marginal cost curve u shaped - The Marginal Cost curve is U shaped because initially when a firm increases its output total costs as well as variable costs start to increase at a diminishing rate At this stage due to economies of scale and the Law of Diminishing Returns Marginal Cost falls till it