what is voltage Voltage is defined so that negatively charged objects are pulled towards higher voltages while positively charged objects are pulled towards lower voltages 15 16 Therefore the conventional current in a wire or resistor always flows from higher voltage to
Voltage is the pressure from an electrical circuit s power source that pushes charged electrons current through a conducting loop enabling them to do work such as illuminating a light In brief voltage pressure and it is measured in volts V Voltage also called potential difference electric pressure or electric tension is defined as the difference of electric potentials of two points in an electric circuit In other words the amount of energy required to move an electric charge from one point to another in an electr
what is voltage

what is voltage
https://www.freeingenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Electricity-101-v2.png

What Is Voltage
https://www.electricity-magnetism.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/what-is-voltage.png

What Is Voltage All About Voltage In Simple Words
http://www.electronicsandyou.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/voltage.jpg
Voltage is the component that applies the pressure from an electrical circuit s power source to the charged electrons enabling them to do work such as power a light Typically we measure volts by using a multimeter or voltmeter To measure voltage we have to connect to a circuit in parallel across the two points of what we want Voltage and current are the cornerstone concepts in electricity We will create our first mental models for these basic electrical quantities We will also talk about power which is what happens when voltage and current act together
Electric potential difference also known as voltage is the external work needed to bring a charge from one location to another location in an electric field Electric potential difference is the change of potential energy experienced by a test charge that has a value of 1 Voltage is also known as the electromotive force or EMF It is the potential difference between two terminals where one terminal has more electrons gathered compared to the other terminal Voltage is measured in Volts V which is the derived unit for electric potential
More picture related to what is voltage

What Is Voltage The Engineering Mindset
https://theengineeringmindset.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/water-analogy1-700x427.png
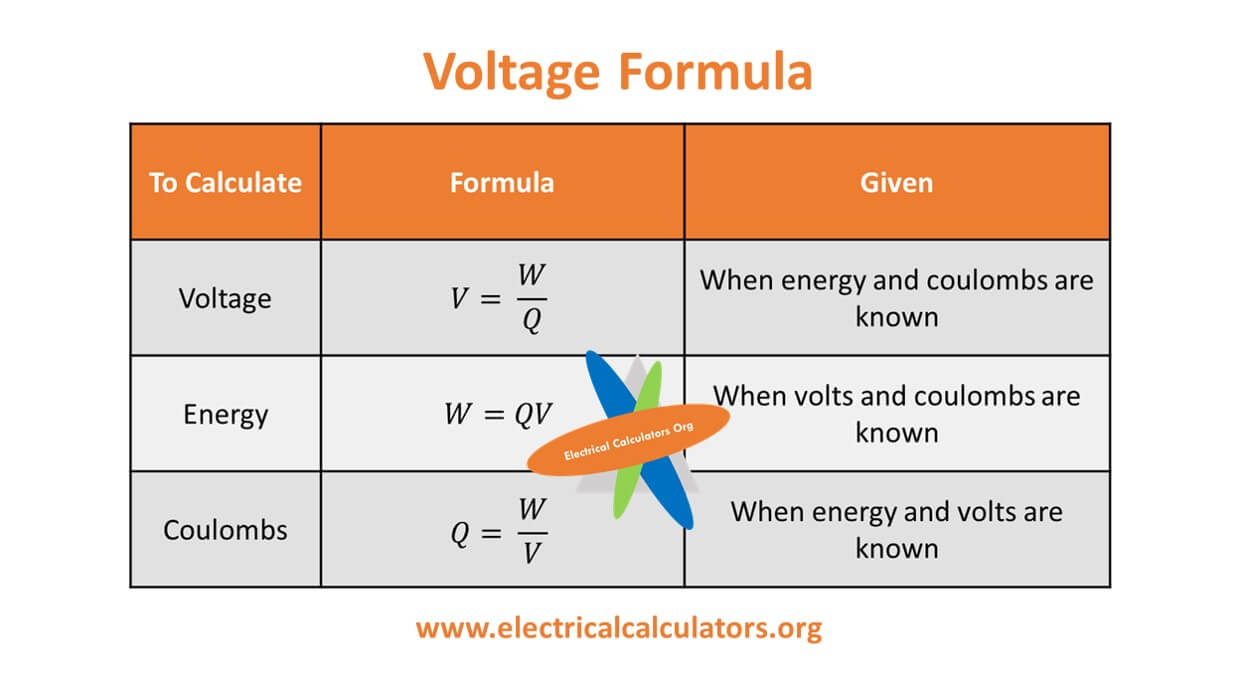
Voltage formula Electrical Calculators Org
https://www.electricalcalculators.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/voltage-formula.jpg
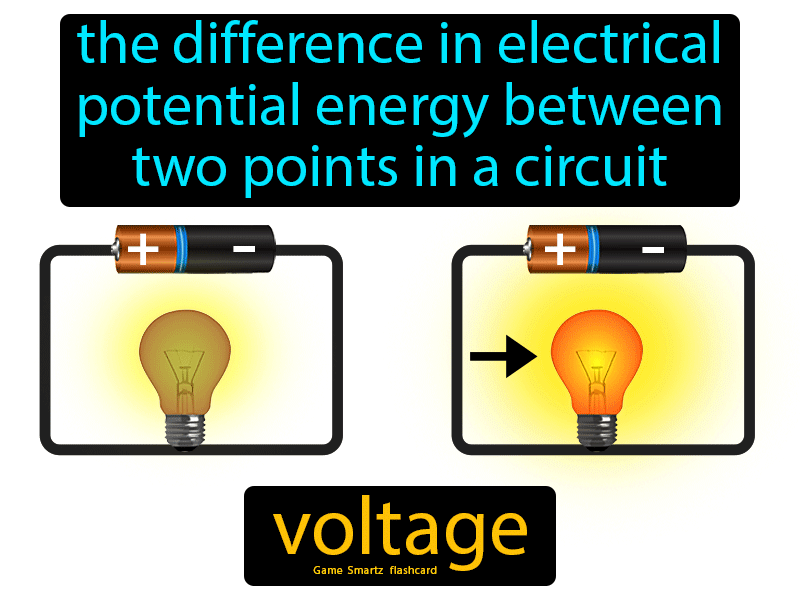
Voltage Definition Electricity Electrical Voltage Chart Lifecoach
https://gamesmartz.com/upload/subjects/science/800/voltage.png
The Definition of Voltage Defined in the context of static electricity voltage is the measure of work required to move a unit charge from one location to another against the force which tries to keep electric charges balanced Voltage is the difference in charge between two points Current is the rate at which charge is flowing Resistance is a material s tendency to resist the flow of charge current So when we talk about these values we re really describing the movement of charge and thus the behavior of electrons
[desc-10] [desc-11]
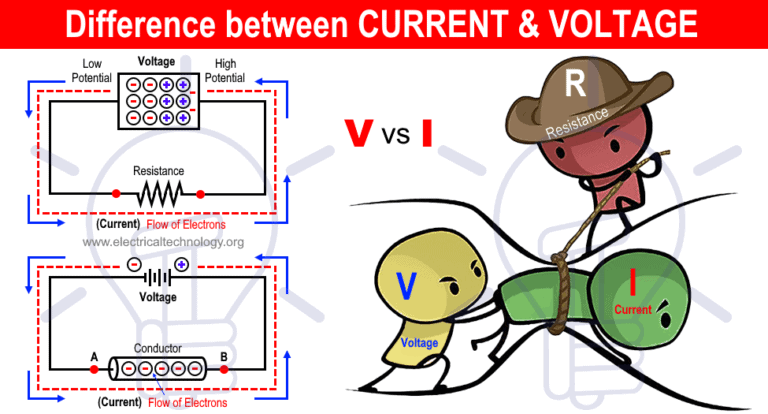
Difference Between Current And Voltage Electrical Technology
https://www.electricaltechnology.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/Difference-between-current-and-voltage-768x414.png

Understanding Vape Pens
https://theengineeringmindset.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/what-is-voltage-voltage-is-pressure-in-an-electrical-circuit.png
what is voltage - Voltage is also known as the electromotive force or EMF It is the potential difference between two terminals where one terminal has more electrons gathered compared to the other terminal Voltage is measured in Volts V which is the derived unit for electric potential