what is the free fall acceleration on earth With algebra we can solve for the acceleration of a free falling object The acceleration is constant and equal to the gravitational acceleration g which is 9 8 meters per square second at sea level on the Earth The weight size and shape of the object are not a factor in describing a free fall
Free Falling An object that moves because of the action of gravity alone is said to be free falling If the object falls through an atmosphere there is an additional drag force acting on the object and the physics involved with the motion of the object is more complex than in free fall Free Fall discuss ion summary practice problems resources Discussion acceleration due to gravity Want to see an object accelerate Pick something up with your hand and drop it When you release it from your hand its speed is zero On the way down its speed increases The longer it falls the faster it travels
what is the free fall acceleration on earth
what is the free fall acceleration on earth
https://qph.fs.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-ab8063b50883485eb926a38a074ca1f9

Free Fall Acceleration Due To Gravity Morgandeathedelirium
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-VE2PV7Uklw/maxresdefault.jpg

On Planet Tehar The Free fall Acceleration Is The Same As That On The
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/HWejETTBldw/maxresdefault.jpg
The acceleration of free fall often denoted as g g is defined as the acceleration experienced by an object falling freely near the Earth s surface uninhibited by any other forces like air resistance In terms of vector quantities it can be represented as g 9 81m s2 j g 9 81 m s 2 j At different points on Earth s surface the free fall acceleration ranges from 9 764 to 9 834 m s 2 32 03 to 32 26 ft s 2 depending on altitude latitude and longitude A conventional standard value is defined exactly as 9 80665 m s about 32 1740 ft s
All free falling objects on Earth accelerate downwards at a rate of 9 8 m s s often approximated as 10 m s s for back of the envelope calculations Because free falling objects are accelerating downwards at a rate of 9 8 m s s a ticker tape trace or dot diagram of its motion would depict an acceleration Recall that the acceleration of a free falling object near Earth s surface is approximately g 9 80 m s 2 g 9 80 m s 2 The force causing this acceleration is called the weight of the object and from Newton s second law it has the value mg
More picture related to what is the free fall acceleration on earth

PPT Free fall Lab PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID 6954703
https://image3.slideserve.com/6954703/acceleration-due-to-gravity-l.jpg

Question Video Comparing The Frequency Of A Pendulum On Earth And On
https://media.nagwa.com/904164068691/en/thumbnail_l.jpeg
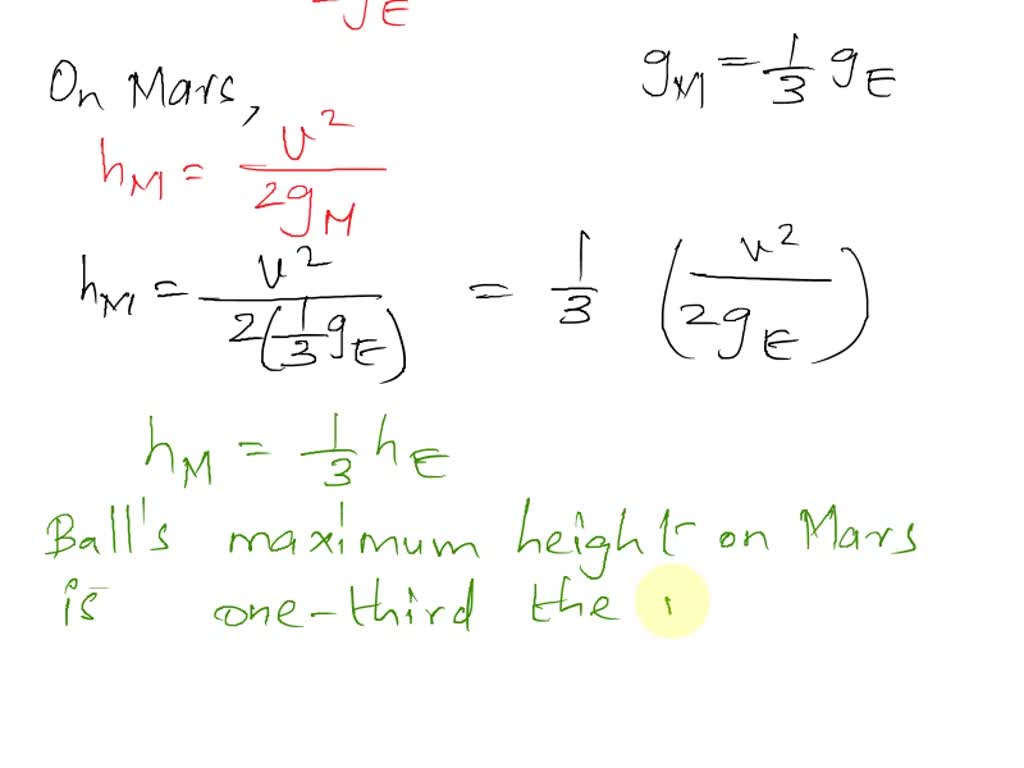
SOLVED The Free Fall Acceleration On Mars Is About One third Tha On
https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_previews/4db15891-66bf-48ab-997c-8a16a4cc1724_large.jpg
The acceleration of free falling objects is therefore called acceleration due to gravity Acceleration due to gravity is constant which means we can apply the kinematic equations to any falling object where air resistance and friction are negligible Freefall in mechanics state of a body that moves freely in any manner in the presence of gravity The planets for example are in free fall in the gravitational field of the Sun An astronaut orbiting Earth in a spacecraft experiences a condition of weightlessness because both the spacecraft and the astronaut are in free fall
Acceleration of free fall often referred to as gravity or acceleration due to gravity is the rate at which an object near the Earth s surface accelerates downward under the influence of gravity It has an approximate value of 9 8 meters per second squared m s and is denoted as g What is Acceleration of Free Fall Recall that the acceleration of a free falling object near Earth s surface is approximately g 9 80 m s 2 The force causing this acceleration is called the weight of the object and from Newton s second law it has the value mg This weight is present regardless of whether the object is in free fall
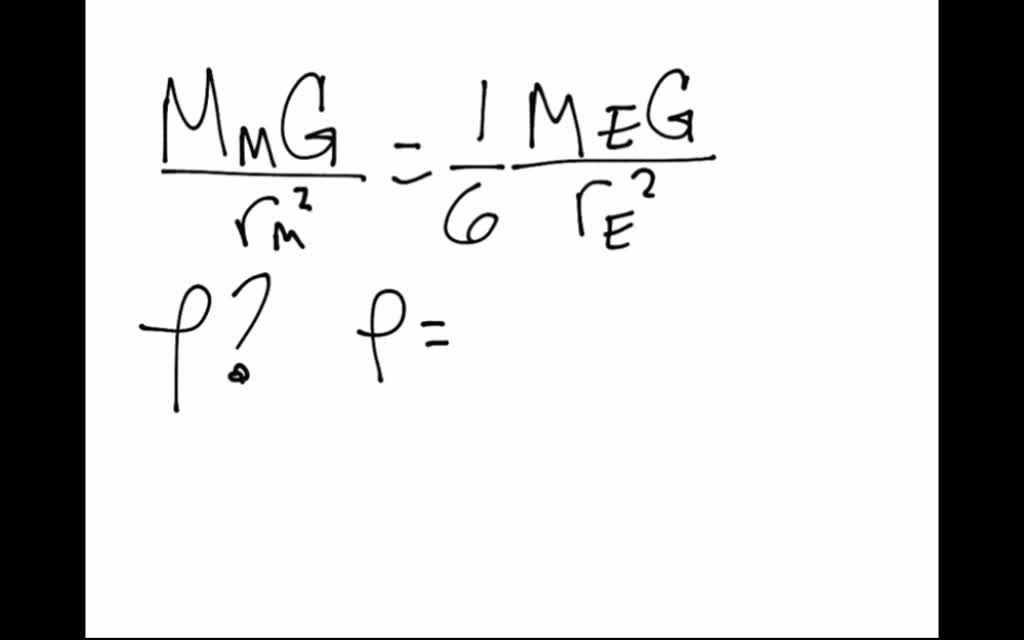
SOLVED The Free fall Acceleration On The Surface Of A Fictional Planet
https://cdn.numerade.com/previews/b866734d-d675-455f-be73-0c15e8fac7f3_large.jpg

The Free Fall Acceleration On Mars Is 3 7 M s 2 a What Length Of
https://d1hj4to4g9ba46.cloudfront.net/questions/1981917_1858118_ans_0117b4faabda495fb48d38851b2c2b05.jpg
what is the free fall acceleration on earth - All free falling objects on Earth accelerate downwards at a rate of 9 8 m s s often approximated as 10 m s s for back of the envelope calculations Because free falling objects are accelerating downwards at a rate of 9 8 m s s a ticker tape trace or dot diagram of its motion would depict an acceleration