what happens when you multiply ln by ln When ln is seen automatically it is understood that its base is e The rules of logs are the same for all logarithms including the natural logarithm Hence the important natural log rules rules of ln are as follows ln mn ln m ln n ln m n ln m ln n ln m n n ln m ln a log a log e ln e 1 ln 1 0
Example 10 ln 2 6 6 ln 2 where ln means log e the natural logarithm Example 11 log 5 5 x is not equal to 2 log 5 5 x Be careful with order of operations 5 x is 5 x not 5 x log 5 5 x must first be decomposed as the log of the product log 5 5 log 5 x Justifying the logarithm properties Google Classroom Study the proofs of the logarithm properties the product rule the quotient rule and the power rule In this lesson we will prove three logarithm properties the product rule the quotient rule and the power rule Before we begin let s recall a useful fact that will help us along the way
what happens when you multiply ln by ln

what happens when you multiply ln by ln
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/86G1Ikrs_TQ/maxresdefault.jpg

E To The Power Of Ln x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/V553m9SAGgk/maxresdefault.jpg

Question Video Multiplying Vectors By Scalars Nagwa
https://media.nagwa.com/919137086838/en/thumbnail_l.jpeg
In this lesson you ll be presented with the common rules of logarithms also known as the log rules These seven 7 log rules are useful in expanding logarithms condensing logarithms and solving logarithmic equations ln x Natural Logarithm is the time to reach amount x assuming we grew continuously from 1 0 Not too bad right While the mathematicians scramble to give you the long technical explanation let s dive into the intuitive one E is About Growth The number e is about continuous growth
log b x dx x log b x 1 ln b C For example log 2 x dx x log 2 x 1 ln 2 C Logarithm approximation log 2 x n x 2 n 1 Complex logarithm For complex number z z re i x iy The complex logarithm will be n 2 1 0 1 2 Log z ln r i 2n ln x 2 y 2 From the change of base theorem log base a of b ln b ln a For example you can calculate log base 3 of 5 by calculating ln 5 ln 3 which should give approximately 1 465 Note that if your calculator also has a log key another way to calculate log base 3 of 5 is to calculate log 5 log 3
More picture related to what happens when you multiply ln by ln

How To Multiply A Fraction By A Whole Number Maths With Mum
https://i0.wp.com/www.mathswithmum.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/multiplying-a-fraction-by-a-whole-number-and-simplifying.png?resize=1024%2C768&ssl=1

Simplify Log Without Calculator Regretful Weblog Frame Store
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/72/47/78/72477858937310c00cf2ef159dba54ee.jpg
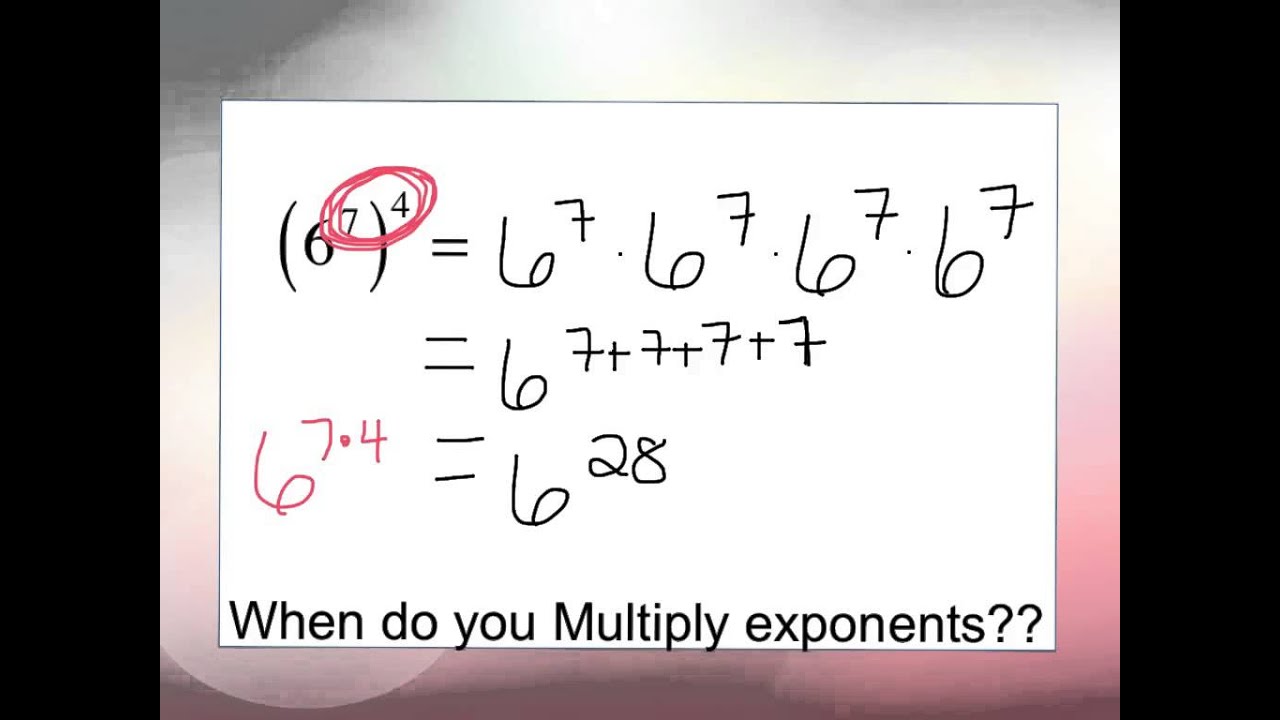
When Do You Multiply Exponents YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/UlLuJYZy8AM/maxresdefault.jpg
The associated logarithmic equation is ln y x and vice versa Product rule The product rule for logs is log a xy log ax log ay In terms of natural logarithms this same rule is ln xy ln x ln y For natural logarithms it becomes ln x y ln x ln y In other words the natural log of the multiplication of x and y is the sum of the ln of x and the ln of y Here s an example with some numbers ln 5 3 ln 5 ln 3
The natural logarithm function is defined by ln x Integral on the interval 1 x of 1 x dt t for x 0 therefore the derivative of the natural logarithm is d dx ln x 1 x The natural logarithm is one of the most useful functions in mathematics with applications throughout the physical and biological sciences Y 10 x The natural logarithm l n x is simply log base e or the inverse function of y e x Recall that the definition of an inverse function is f 1 f x x Or in plain English the inverse function undoes its original function So in the case of the natural logarithm l n e x x

Learn How To Condense Natural Logs Separated By Subtraction YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZlCHy2vmiOo/maxresdefault.jpg
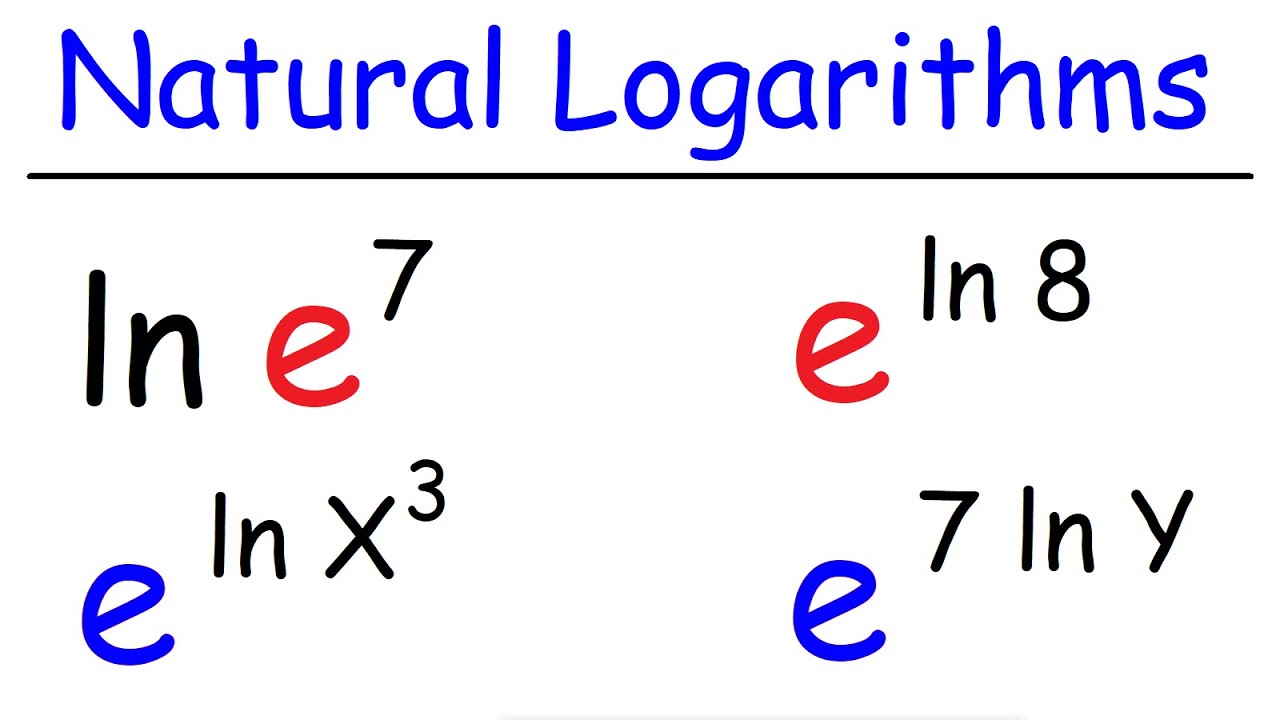
Natural Logarithms log E Ln
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/daUlTsnCNRQ/maxresdefault.jpg
what happens when you multiply ln by ln - In this lesson you ll be presented with the common rules of logarithms also known as the log rules These seven 7 log rules are useful in expanding logarithms condensing logarithms and solving logarithmic equations