tangent circle theorem proof How do I prove circle theorems involving chords and tangents This type of proof can be used to prove the following circle theorems The perpendicular from the centre of a circle bisects a chord The tangent to a
How to use the tangent theorems In order to use the tangent of a circle Locate the key parts of the circle for the theorem Use other angle facts to determine the remaining angle s made Theorem 1 The tangent to the circle is perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of contact Theorem 2 If two tangents are drawn from an external point of the circle then they are of equal lengths
tangent circle theorem proof

tangent circle theorem proof
https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/68e1a2d2-8e6d-4f11-b0ad-a27752220bab/4-theorem-10.2---from-1-and-2-pq--=-pr-hence-proved-4.jpg
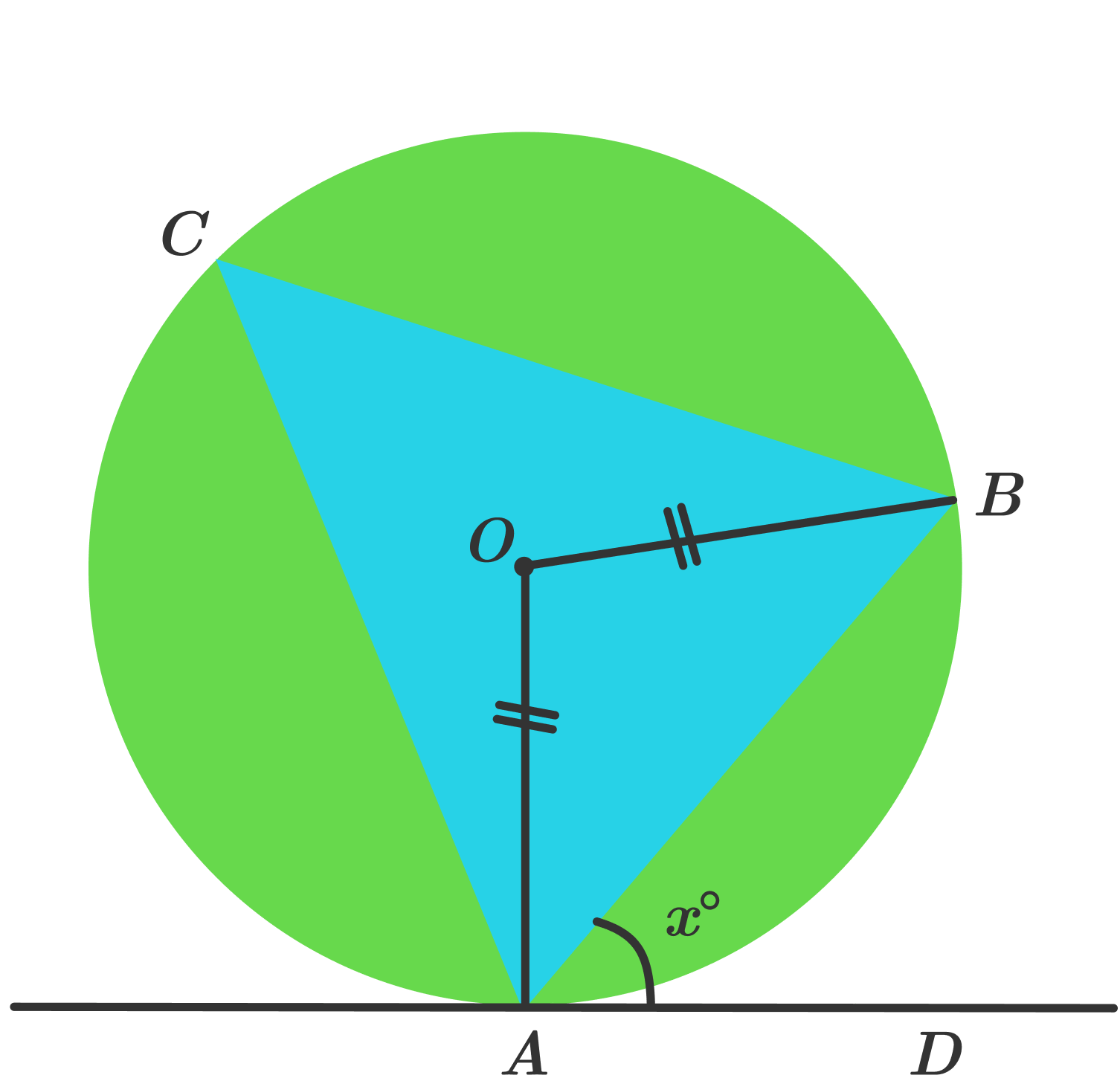
Alternate Segment Theorem Brilliant Math Science Wiki
https://brilliant-staff-media.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/tiffany-wang/8hXaIhOe42.png

Alternate Segment Theorem Brilliant Math Science Wiki
https://brilliant-staff-media.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/tiffany-wang/ZNgJ7VOr3p.png
Circle theorems Higher AQA Tangents Higher Circles have different angle properties described by different circle theorems Circle theorems are used in geometric proofs and to Learn Proof Segments tangent to circle from outside point are congruent Tangents of circles problem example 1 Tangents of circles problem example 2 Practice Segments tangent to a
How To Prove The Tangent To A Circle Theorem The Tangent to a Circle Theorem states that a line is tangent to a circle if and only if the line is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point of tangency Workout Question 1 Prove that the angle in a semi circle is always 90 Question 2 Prove that the angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference Question 3 Prove the angles
More picture related to tangent circle theorem proof

Tangent Secant Theorem Circles Class 10 Most Important Theorem For
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/m0o5sra690c/maxresdefault.jpg

Secant Of A Circle Definition Formula Properties Theorems And Examples
https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/geetha-secant-of-a-circle-04-1622097840.png
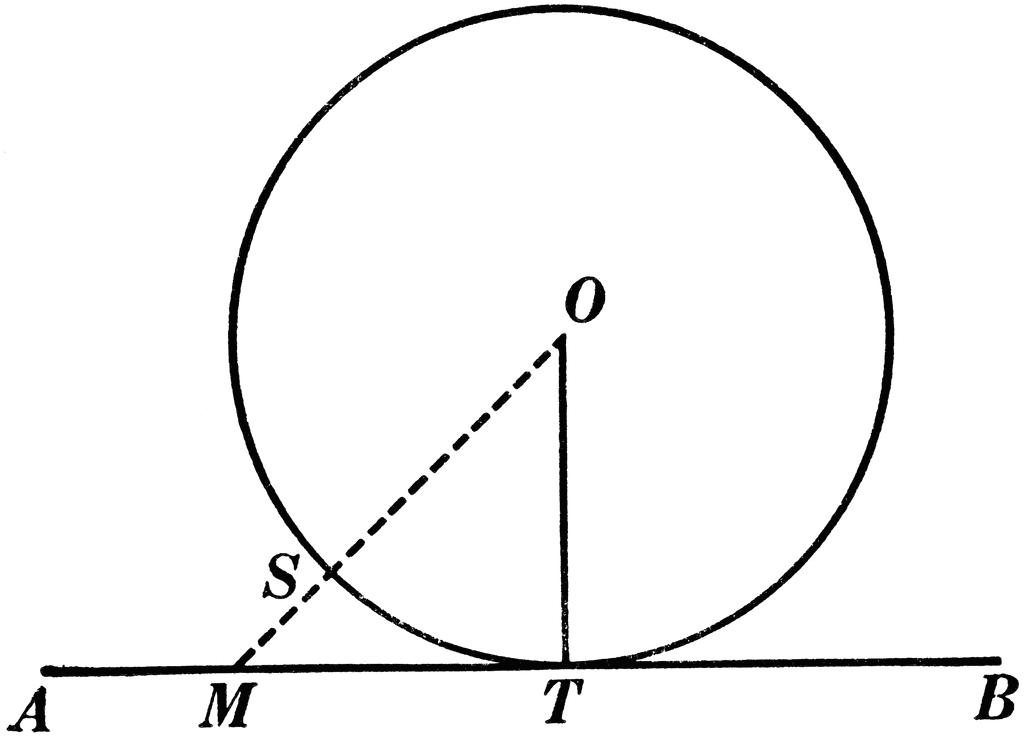
Tangent To Perpendicular Radius Circle Theorem ClipArt ETC
http://etc.usf.edu/clipart/72400/72473/72473_circles_lg.gif
Proof The angle between the tangent and the radius is 90 Angle BCO angle BAO 90 AO and OC are both radii of the circle Length AO Length OC Draw the line OB It creates two triangles Circle theorems Objectives To establish the following results and use them to prove further properties and solve problems The angle subtended at the circumference is half the angle at
In Euclidean plane geometry a tangent line to a circle is a line that touches the circle at exactly one point never entering the circle s interior Tangent lines to circles form the subject of Tangent A tangent to a circle is a line segment that touches the circle at a unique point and lies outside the circle Segment A segment of a circle is the area enclosed by a chord and arc of a
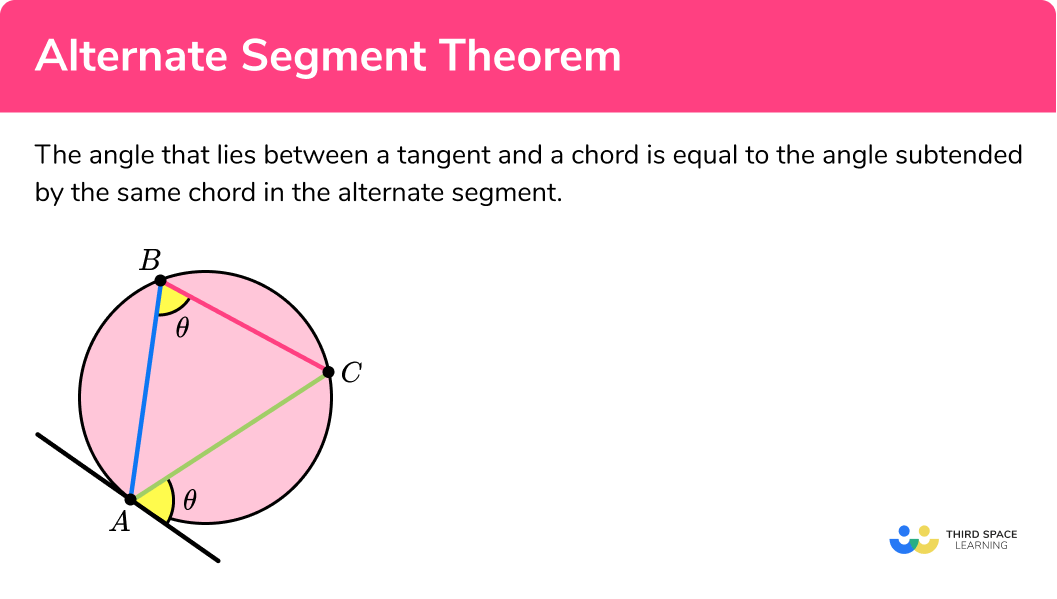
Alternate Segment Theorem GCSE Maths Steps Examples
https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Alternate-segment-theorem-what-is.png

Alternate Segment Theorem Circles Proof Solutions Cuemath
https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/geetha-alternate-segment-theorem-02-1609155060.png
tangent circle theorem proof - Identify use and prove seven circle theorems We will go through each one of them in detail The order of the following theorems does not matter Theorem 1 When a radius meets a