e xy 2 e x 2 e y 2 In mathcal L 2 cdot for any X Y in mathcal L 2 random variables in a probability space mathcal F P define the inner product X cdot Y int XY rm dP E XY and get
X 2 E X2 E X 2 The variance is the mean squared deviation of a random variable from its own mean If X has high variance we can observe values of X a long way from the mean If X Theorem 2 Expectation and Independence Let X and Y be independent random variables Then the two random variables are mean independent which is defined as E XY E X E Y
e xy 2 e x 2 e y 2

e xy 2 e x 2 e y 2
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/1zqNZBQONaE/maxresdefault.jpg

If X Y 8 And Xy 5 Find X2 Y2 Brainly in
https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d0b/bc10302ae5087b3c45ab551a2be1263c.jpg
25 Y xy 2x 2y 2 dx X xy x 2y 2 dy 0 651442 X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy
https://qph.cf2.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-01f5c84ea7850793ac085a68e2582072-lq
Moreover if f alpha 0 for some alpha then we have EW E X alpha Y 2 0 which essentially means X alpha Y with probability one To prove the Cauchy Schwarz Let T denote the set of products of two elements in S Then XY is a discrete random variable taking values in the set T Now suppose I ask you what the probability of XY
Y E X and its MSE is given by MSE 2 X Cov2 X Y 2 Y 1 2 X Y 2 X Properties of MMSE linear estimate E X E X i e estimate is unbiased If X Y 0 i e X and Y Linearity of expectation implies E Q X Y E X Y Q X Y 1E U2 2E V2 This generally gives the simplest possible interpretation of Q it s a weighted sum or
More picture related to e xy 2 e x 2 e y 2

Pokemon X And Y Pok mon Fan Art 34792858 Fanpop
http://images6.fanpop.com/image/photos/34700000/Pokemon-X-and-Y-pokemon-34792858-1024-1444.png
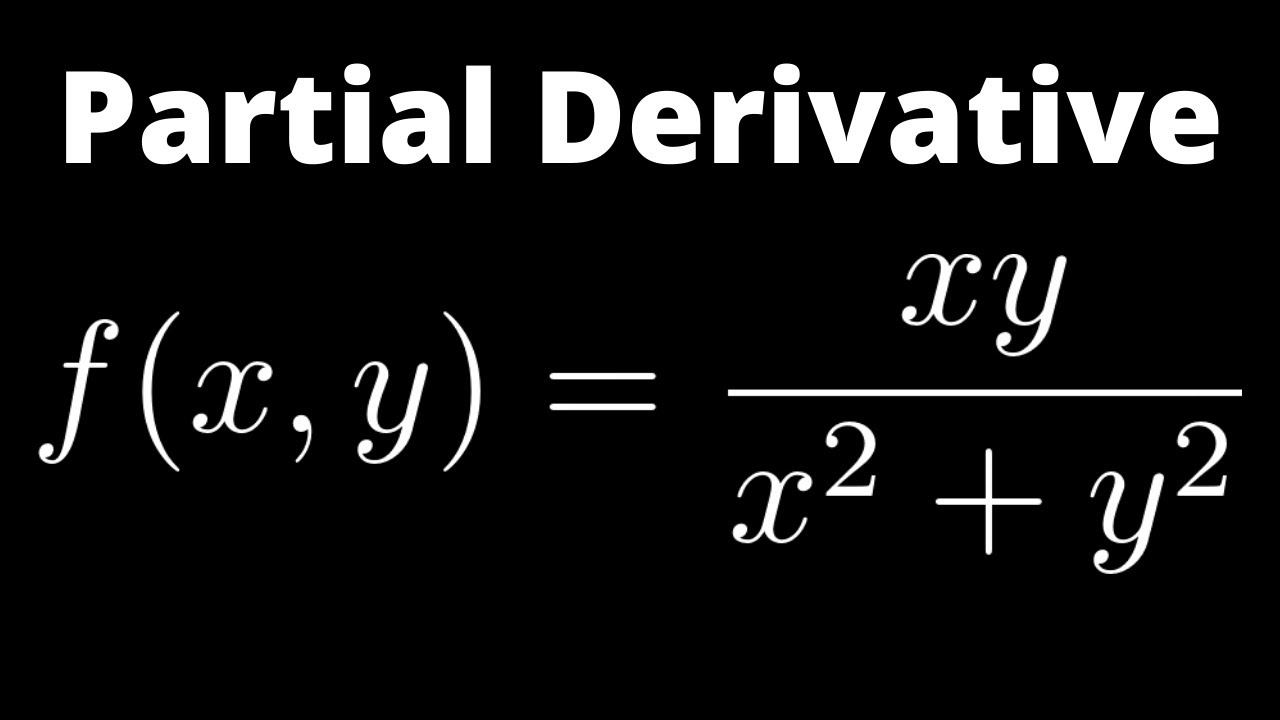
Partial Derivative Of F x Y Xy x 2 Y 2 With Quotient Rule YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/M_HDJBmv4z4/maxresdefault.jpg
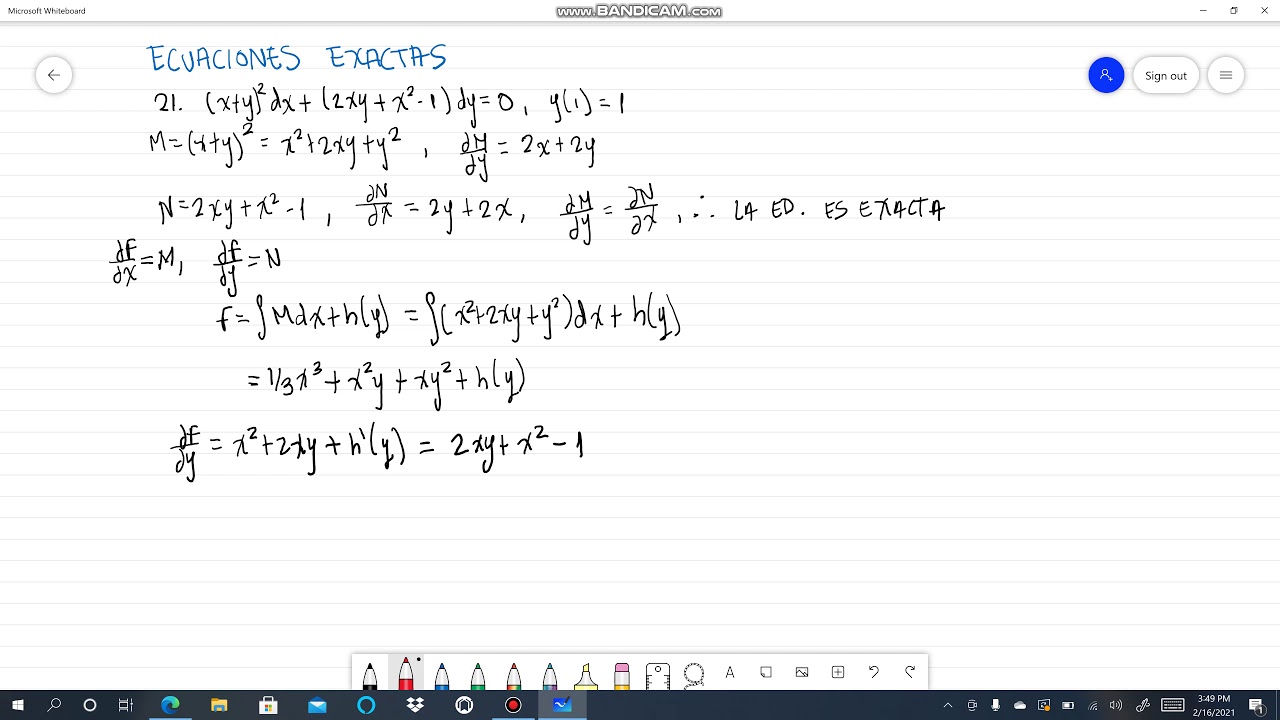
21 x y 2 Dx 2xy x 2 1 dy 0 Y 1 1 Ecuaciones Exactas Alexander
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/kaDpUkDo7SY/maxresdefault.jpg
Covariance formula E XY E X E Y or expectation of product minus product of expectations is frequently useful Note if X and Y are independent then Cov X Y 0 E XjY y def x xfXjY xjy and more generally E g X jY y def x g x fXjY xjy is de ned for any real valued function g X In particular E X2jY y is obtained when g X X2 and
Using E X 4 3 E Z 0 E X 2 E Z 2 1 and the independence of X and Z one gets indeed that E X 2Y 2 3a 2 0 1 a 2 1 2a 2 Otherwise that is under the conditions I can get the correct answer through this method E X Y 2 Var X Y E X Y 2 and noting that X Y has a Poisson distribution with mean 2 But why doesn t the first method

Solve x 3 2y 3 dx 3xy 2dy 0
https://d1hj4to4g9ba46.cloudfront.net/questions/1162929_1062909_ans_3352c9b79c1749598f1136697d0d8153.jpg
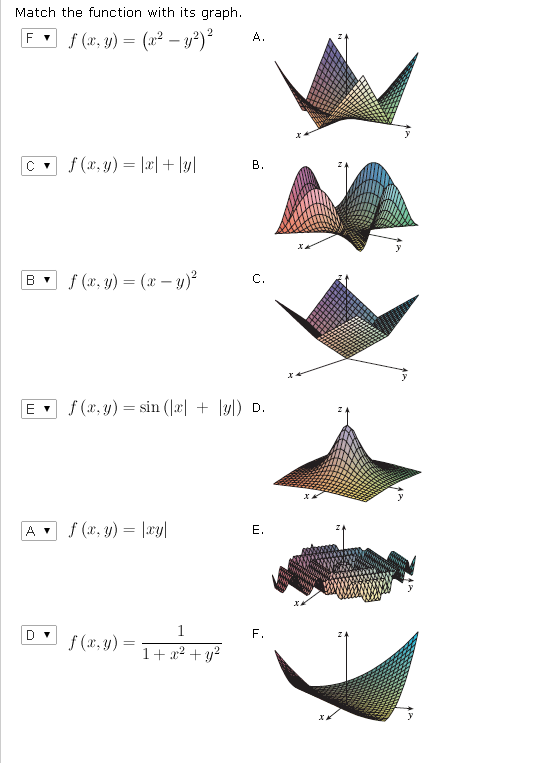
Solved Match The Function With Its Graph F x Y x 2 Chegg
https://d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media/5b7/5b71f0d5-d092-4b0d-9094-97c6b042883c/phpnLcr6p.png
e xy 2 e x 2 e y 2 - Remember that the conditional expectation of X given that Y y is given by E X Y y xi RXxiPX Y xi y Note that E X Y y depends on the value of y In other words by