e vs v graph The electric field strength E has a 1 r2 relationship and the area under the graph represents change in electric potential The key features of this graph are All values of field strength are negative for a negative charge All
Components which show I V graphs that are not straight lines are non linear circuit elements The current through them is not directly proportional to the potential difference across them Electric Potential V The electric potential at a point r from a point charge is defined as The work done per unit charge against the field to move a positive point charge from infinity to that point
e vs v graph

e vs v graph
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/qO6NB92XcjE/maxresdefault.jpg

V Vs T Graphs YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/HqTXQ_ebv6Q/maxresdefault.jpg
Speedup Graph Processing By Graph Ordering Papers
https://papers-gamma.link/static/memory/previews/159.png
So the area under a graph of electric field strength against distance between two points is the potential difference between those two points For a uniform electric field E is Potential Energy and E field 1 Sketch a graph of the E field vs x from the V vs x graph shown below 2 Draw a Potential Energy graph for a particle with a 20 nC charge that moves
I V Graphs We can complete an experiment to investigate how the potential difference changes as current changes for an ohmic conductor a filament bulb and a diode We can then draw a current potential difference graph I V graph The I V graph for an ohmic conductor at constant temperature e g a resistor is very simple The current is directly proportional to the potential difference This is demonstrated by the straight
More picture related to e vs v graph
Algebrallinen Rakenne Wikipedia
https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/409a91214d63eabe46ec10ff3cbba689ab687366
Verkottuva Koulu
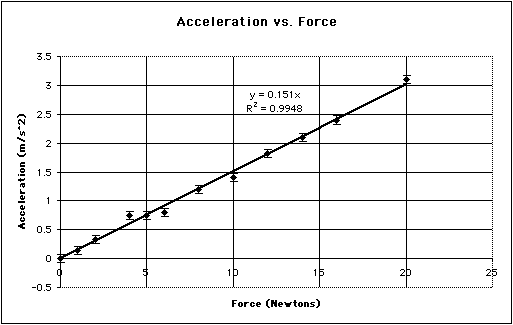
http://www.batesville.k12.in.us/physics/apphynet/Measurement/Images/f_vs_a_graph.gif

Discrete Mathematics 1 CHAPTER V GRAPH THEORY Roughly Speaking A
https://d20ohkaloyme4g.cloudfront.net/img/document_thumbnails/d3068d6b9dab314c8d16f3676ecdae20/thumb_1200_1553.png
Explore math with our beautiful free online graphing calculator Graph functions plot points visualize algebraic equations add sliders animate graphs and more The line at energy E represents the constant mechanical energy of the object whereas the kinetic and potential energies K A and U A are indicated at a particular height y A You can see how the total energy is divided between
The I V graph for an ohmic conductor at constant temperature e g a resistor is very simple The current is directly proportional to the potential difference This is How to affect electric current OCR 21st Century Current voltage graphs Electrical current depends on resistance and potential difference Different electrical components have different
V Graphy
https://lookaside.fbsbx.com/lookaside/crawler/media/?media_id=100063526062644

Figure Shows A Cyclic Process ABCA In The V T Diagram Which Of The
https://dwes9vv9u0550.cloudfront.net/images/4458184/36cc7d31-29bd-492d-b470-a500b13e2cf6.jpg
e vs v graph - Based on their basic definitions we can derive the I V curves of ideal passive components resistors capacitors and inductors using the concept of linear voltage sweeps

