domain and range of functions In creating various functions using the data we can identify different independent and dependent variables and we can analyze the data and the functions to determine the domain and range In this section we will investigate methods for determining the domain and range of functions such as these
What is the Domain and Range of a Function The domain and range of a function are the set of all the inputs and outputs a function can give respectively i e for any function y f x the domain is the set of all x values for which f x is defined the range is the set of all y values that the function f x produce In this article we will learn about the domain and range of a function how to calculate the domain and range of a function with solved examples the domain and range of a function worksheet the domain and range of a function examples domain and range of a function graph and others in detail
domain and range of functions
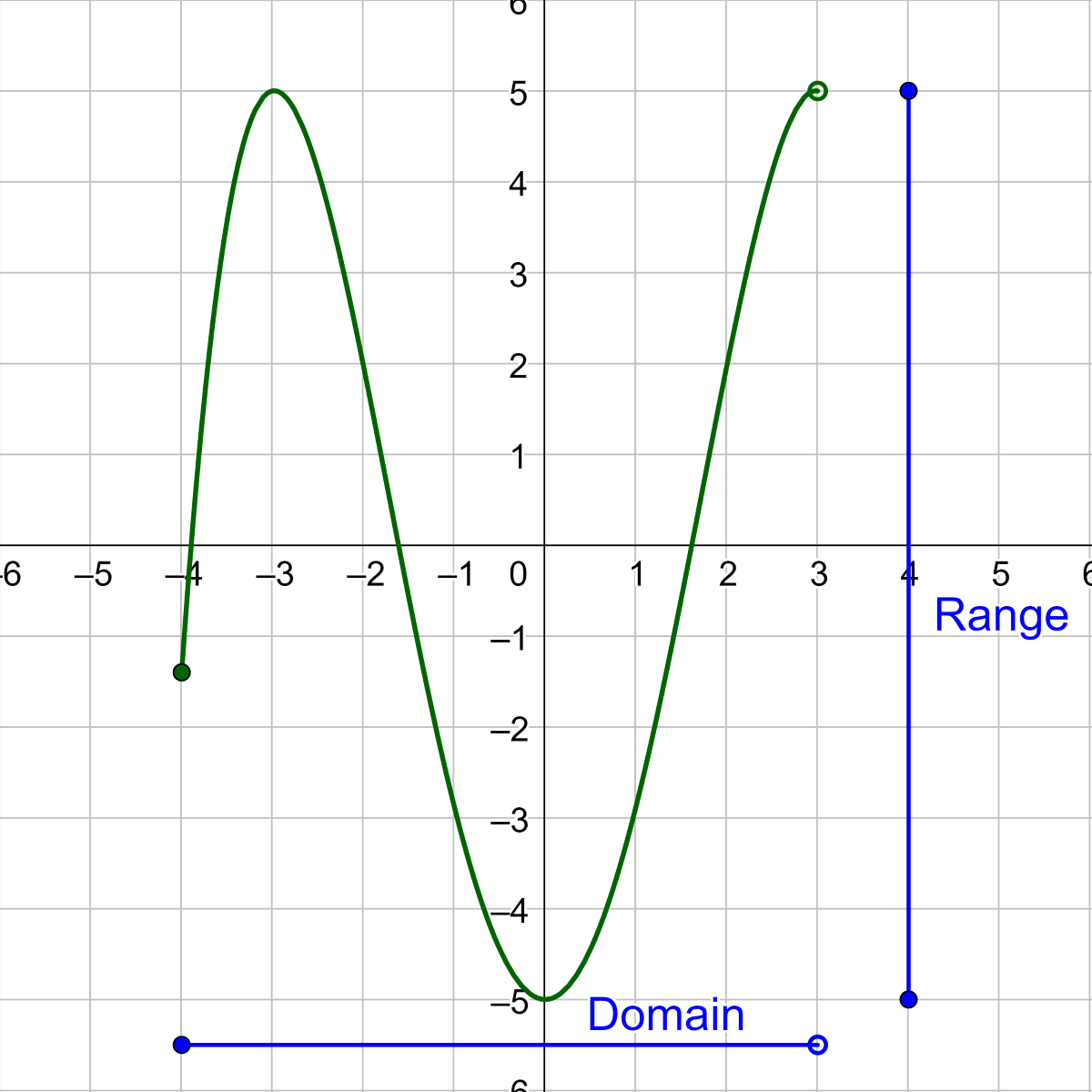
domain and range of functions
https://www.andrews.edu/~rwright/Precalculus-RLW/Images/01-05F04b.png
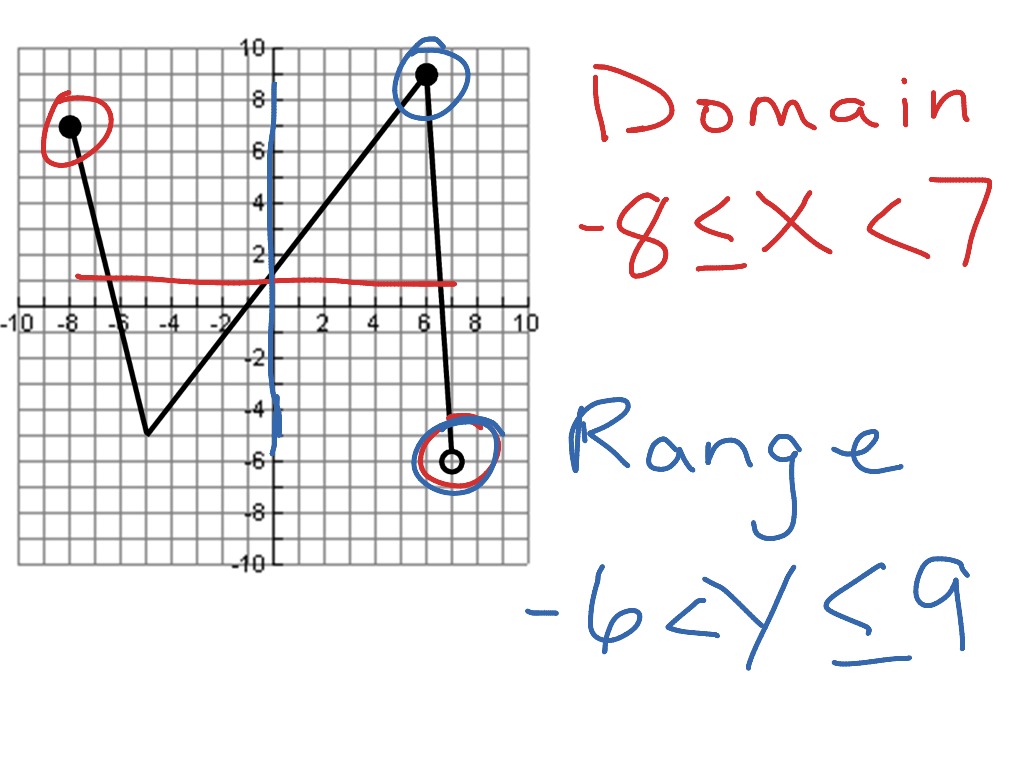
Domain And Range Math Algebra Functions F IF 1 ShowMe
https://showme0-9071.kxcdn.com/files/126931/pictures/thumbs/304206/last_thumb1347155365.jpg

Basics Of Functions And Their Graphs
http://cf.ppt-online.org/files/slide/1/1sHV8kwebfU4WXcdaGpEB5noxDTA69uNgm3Jlt/slide-17.jpg
Definition The set of values of the independent variable for which a function f x is defined is called the domain of that function For example the function is defined for all values of except 1 because at x 1 the function evaluates to which is undefined and does not lie in set of Real numbers Definition Domain and Range of a Function The domain of a function is all possible values of x that can be used as input to the function which will result in a real number as the output The range of a function is the set of
The domain of a function is the set of all possible inputs for the function For example the domain of f x x is all real numbers and the domain of g x 1 x is all real numbers except for x 0 We can also define special functions whose domains are more limited A function is a relation where every domain x value maps to only one range y value If you have the points 2 3 4 6 1 8 and 3 7 that relation would be a function because there is only one y value for each x X values don t repeat
More picture related to domain and range of functions
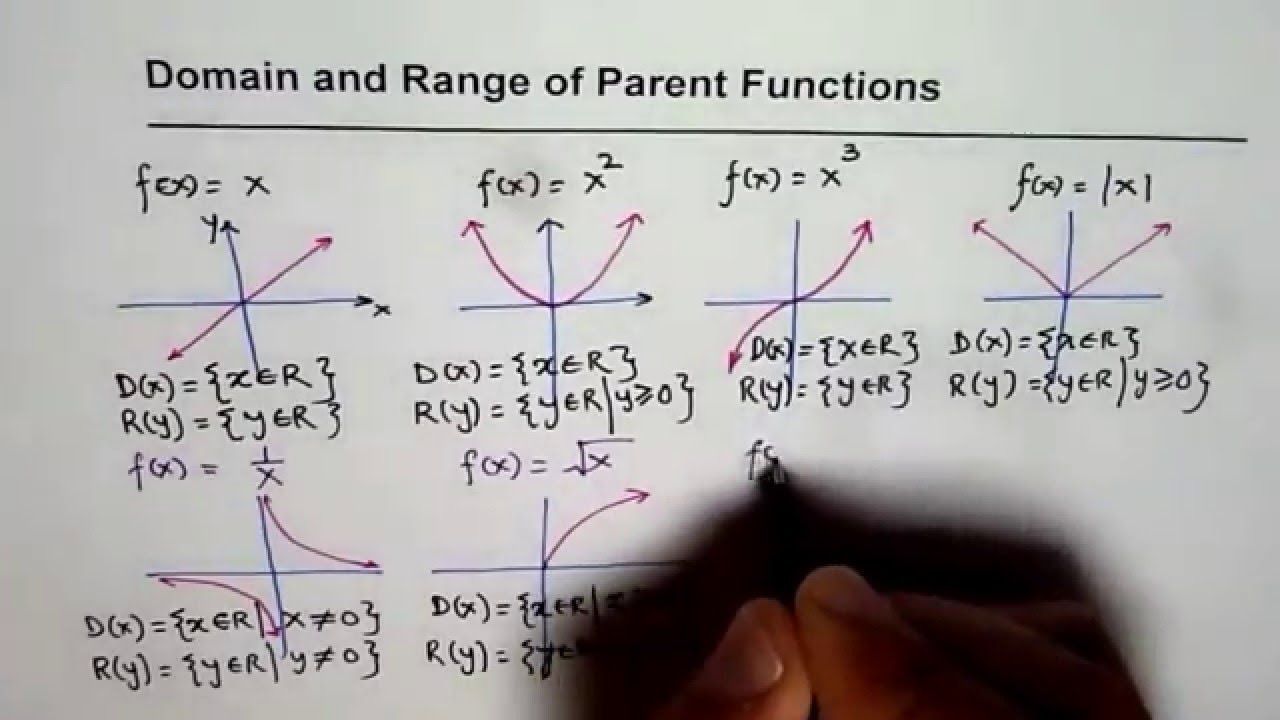
Domain And Range Of Parent Functions IB MCR3U YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/6Sy5SMWE_Ko/maxresdefault.jpg
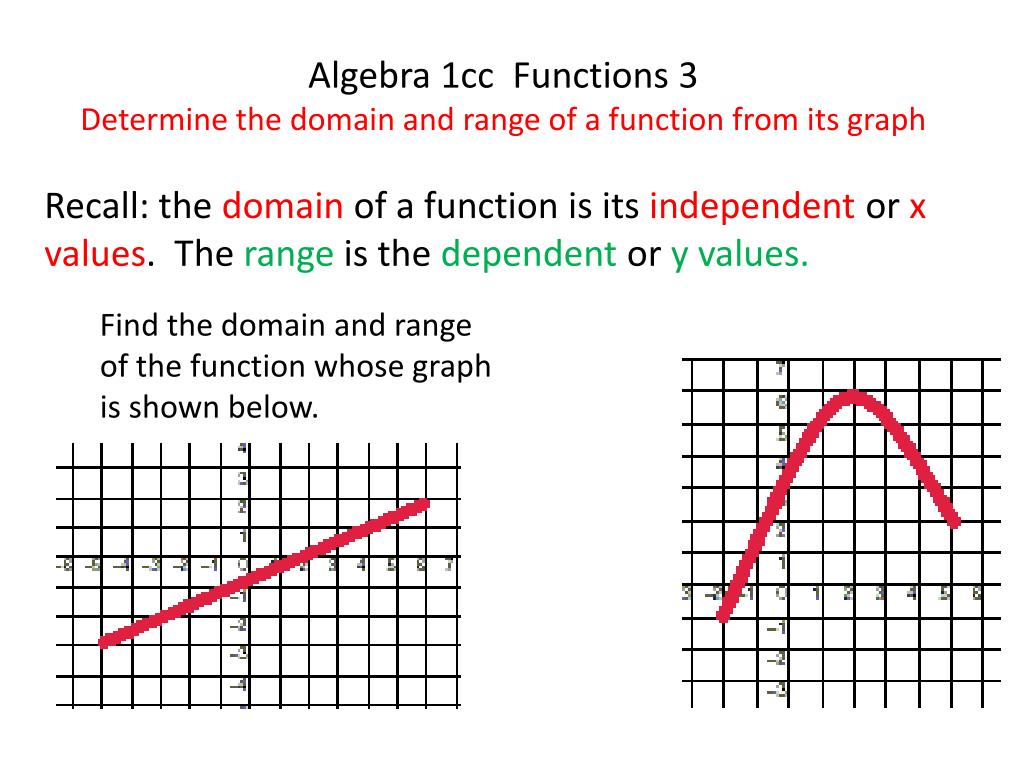
PPT Algebra 1cc Functions 3 Determine The Domain And Range Of A
https://image1.slideserve.com/2929570/algebra-1cc-functions-3-determine-the-domain-and-range-of-a-function-from-its-graph-l.jpg

What Are The Domain And Range Of A Function
http://www.quickanddirtytips.com/sites/default/files/images/5680/domain_and_range_pop_quiz_solution.png
The domain and range of a function is all the possible values of the independent variable x for which y is defined The range of a function is all the possible values of the dependent variable y Simple explanation for domain and range We learn the domain of a function is the set of possible x values and the range is the resulting set of y values
[desc-10] [desc-11]

Functions Domain And Range YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TlUTMJpyJAE/maxresdefault.jpg?sqp=-oaymwEmCIAKENAF8quKqQMa8AEB-AHUBoAC4AOKAgwIABABGGUgZShlMA8=&rs=AOn4CLD65xsTGooFw7gwhn_3qIhUMlj3Eg
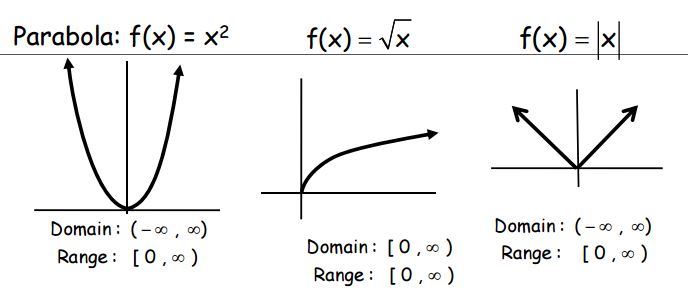
Unit 3 Parent Functions
http://manganomath.weebly.com/uploads/5/7/8/2/57822321/3105468_orig.jpg
domain and range of functions - Definition The set of values of the independent variable for which a function f x is defined is called the domain of that function For example the function is defined for all values of except 1 because at x 1 the function evaluates to which is undefined and does not lie in set of Real numbers