d dx meaning D dx is an operator you can apply it to a function to get an output d dx x 1 dy dx is the derivative of y with respect to x and y is considered to be a function If y x dy dx 1 dy dx is a function itself not an operator on a function dx is notation used in integrals It basically represents infinitely small changes in x and is
You calculate the derivative of that function so y has to be considered the output variable of the function and x is the input value The dy dx notation is useful for several things mainly related to the chain rule of derivatives Chain rule dy dx dx dz dy dz Chain rule related In the context of ODEs dy and dx are linear maps to the real numbers that act on the vector field that defines the ODE the solution is tangent to this vector field The maps dx and dy return the x and y components of the vector at a point The ratio dy dx is then just a ratio of two real numbers And since the ODE solution is tangent to the
d dx meaning

d dx meaning
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/wouMgDxvMSY/maxresdefault.jpg

Related Rates Calculus Confused About What Dx dt Dy dt And Dx dy
https://i.stack.imgur.com/CYehu.png

D 2y Dx 2 Triston has York
https://study.com/cimages/videopreview/videopreview-full/opomayuzj7.jpg
The shortest answer is that d dx means the derivative of So d dx x 2 means the derivative of x 2 A slightly more detailed answer is that d dx means the derivative with respect to x of We take derivatives of functions and functions have inputs and sometimes we need to specify which variable is the input D dx is an operator a function from a space of certain functions in x back to that space Put in a function get out a function just like everyday functions are put in a real number get out a real number So in d 2y dx 2 we are really applying the operator d dx twice to the function y
General d dx e x e x meme dx What doesn t kill you makes you stronger because of c after n integrations you will have e x polynomial of degree n 1 r mathmemes d dy dead Meme looks dank Or just f x f x dx dx Substitute f for your actual function rearrange to get dx on top then trend dx towards 0 and you get your gradient dx is delta x the difference between x1 and x2 As this trends towards a zero limit you get the gradient of a curve at a single point Reply reply
More picture related to d dx meaning

Calculus Geometrical Meaning Of Dx Dy And Dy dx Mathematics Stack
https://i.stack.imgur.com/bUj7F.png
How To Find The Derivative Of A Fraction Quora
https://qph.cf2.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-2698e131dc4aa9a354f0223b69e5b0ba
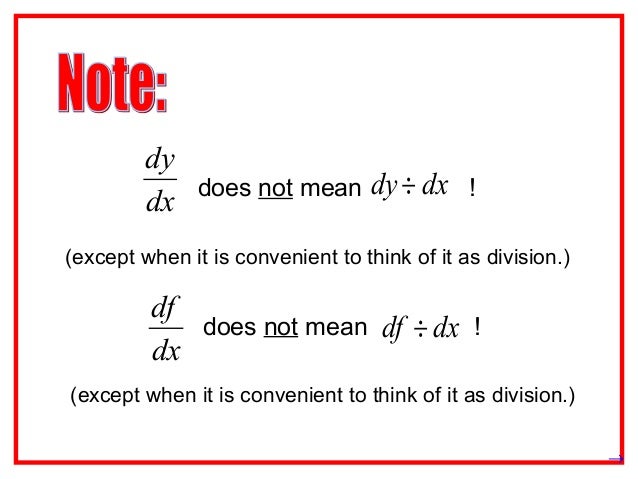
3 1 Derivative Of A Function
https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-160119184400/95/31-derivative-of-a-function-11-638.jpg?cb=1453229084
D dx is the derivative operator You take the derivative with respect to x of whatever follows it d dx y dy dx d dx x 2 2x d dt 1 2 a t 2 a t 1 2 da dt t 2 Note that the second term here goes to 0 if a is a constant and I took the derivative with respect to t this time d dx dy dx d 2 y dx 2 D anything means a small infinitesimally small change in that anything When slope was y x or y x in earlier math we were referring to a change of x and y that was sizeable dy dx means it s the rate of change of something at basically an exact point because the change in x and y are so small it s referred to as instantaneous rate of change
[desc-10] [desc-11]

Calculus Implicit Differentiation Find Dy dx Example 3 YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/O4LPMRJ0Jvk/maxresdefault.jpg

Derivatives Definition Of A Derivative Differentials Rules For
https://www.math10.com/en/university-math/definition-of-a-derivative/imgFig6.gif
d dx meaning - Or just f x f x dx dx Substitute f for your actual function rearrange to get dx on top then trend dx towards 0 and you get your gradient dx is delta x the difference between x1 and x2 As this trends towards a zero limit you get the gradient of a curve at a single point Reply reply