why does sin squared cos squared 1 0 00 2 21 Does 0 999 1 Have you ever been told that sine squared plus cosine squared equals one Did your teacher explain why that s true This is the most important pythagorean id
Trigonometry Share Cite edited Jul 8 2013 at 7 57 Tobias Kienzler 6 649 1 44 86 asked Jul 8 2013 at 7 39 user22979 213 2 6 Since sin30 1 2 sin 30 1 2 and sin2 x cos2 x 1 sin 2 x cos 2 x 1 what is cos30 cos 30 Adriano Jul 8 2013 at 7 43 sin2 x cos2 x 1 sin 2 x cos 2 Note that the three identities above all involve squaring and the number 1 You can see the Pythagorean Thereom relationship clearly if you consider the unit circle where the angle is t the opposite side is sin t y the adjacent side is cos t x and the hypotenuse is 1
why does sin squared cos squared 1

why does sin squared cos squared 1
https://media.nagwa.com/574170246764/en/thumbnail_l.jpeg

Sin Square Theta Cos Square Theta 1 How To Prove YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/V1ZhicJSMUY/maxresdefault.jpg
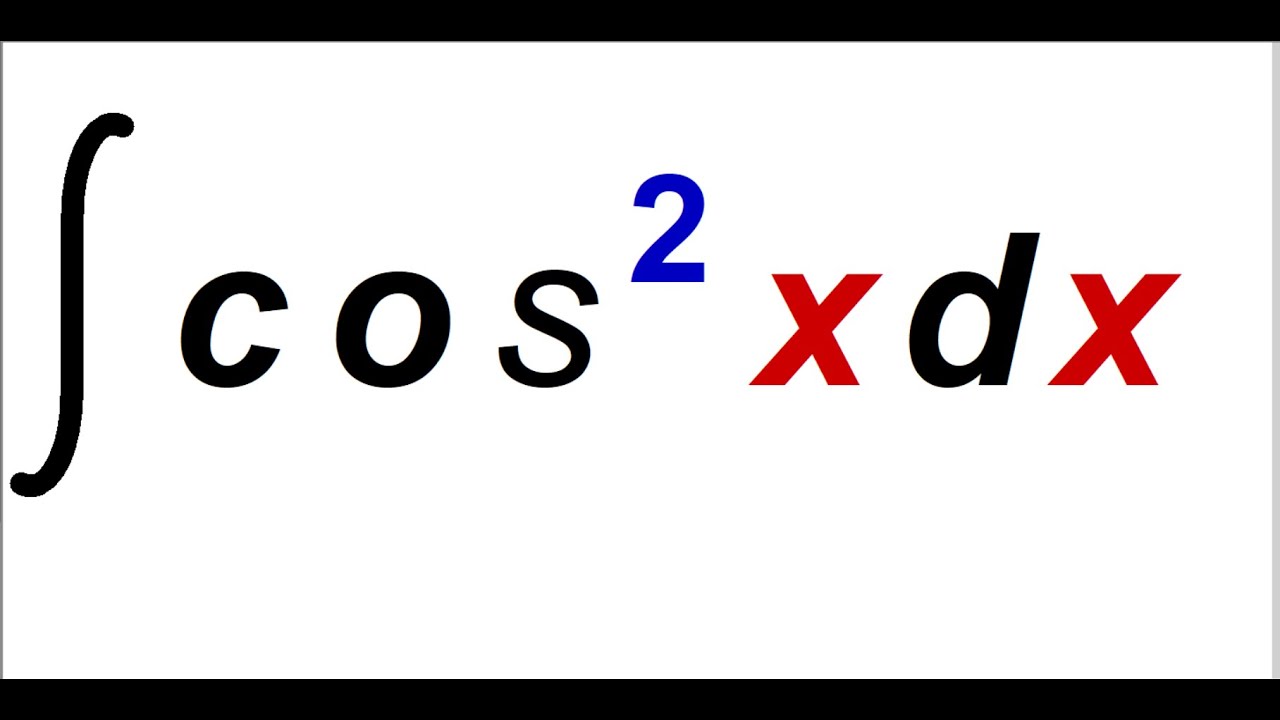
Integral Of Cosine Squared Integral Cos 2x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/rTB6z7_7Vus/maxresdefault.jpg
Well the one thing that we do know and this is the most fundamental trig identity this comes straight out of the unit circle is that cosine squared theta plus sine squared theta is equal to 1 And then if we subtract sine squared theta from both sides we get cosine squared theta is equal to 1 minus sine squared theta So we have two options Why is sin x squared plus cos x squared 1 Thinking of sine and cosine as ratios of side lengths in a right angled triangle sin x o h and cos x a h so the sin x 2 cos x 2 becomes o 2 a 2 h 2
Using the Pythagorean trig identity The Pythagorean identity tells us that no matter what the value of is sin cos is equal to 1 This follows from the Pythagorean theorem which is why it s called the Pythagorean identity We can use this identity to A2 c2 b2 c2 c2 c2 This can be simplified to a c 2 b c 2 1 a c is Opposite Hypotenuse which is sin b c is Adjacent Hypotenuse which is cos So a c 2 b c 2 1 can also be written sin 2 cos 2 1 Note sin2 means to find the sine of then square the result but
More picture related to why does sin squared cos squared 1

Prove That Sin Squared Theta Cos Squared Theta Is Equal To 1 Class
https://classofachievers.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/sin-square-theta-plus-cos-square-theta-equal-to-1.png
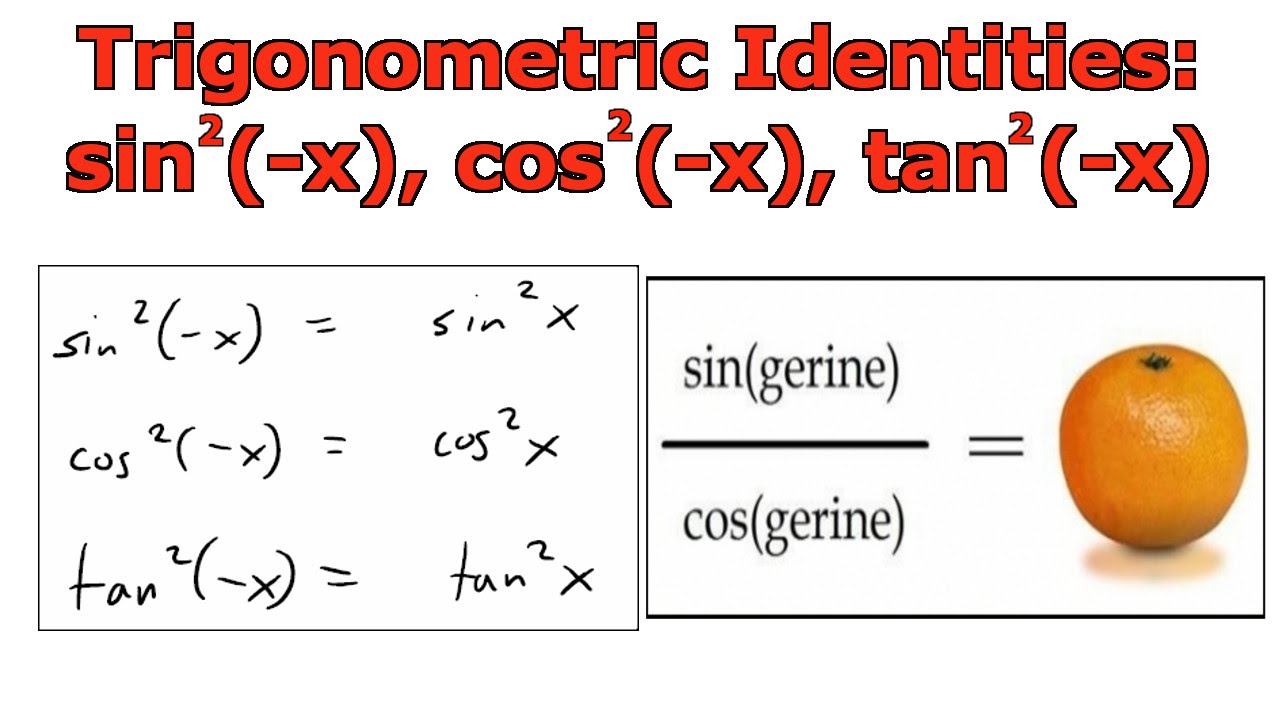
Trigonometric Identities Sin 2 x Cos 2 x Tan 2 x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/yIJsrPJENLA/maxresdefault.jpg

Cos Squared Theta Minus Sin Square Theta Equal To 1 Minus Tan Squared
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Ds8isybzqmk/maxresdefault.jpg
This is a right triangle here the hypotenuse has length one so we know that this expression squared the absolute value of cosine of theta squared plus this expression squared which is this length plus the absolute value of the sine of theta squared needs to be equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared which is the same thing which is Using the Sum and Product Formulas Conditional Identities Proving Trigonometric Identities Basic Trigonometric identities are equalities involving trigonometric functions An example of a trigonometric identity is sin 2
The Pythagorean Theorem works on right triangles If you consider the xcoordinate of a point along the unit circle to be the cosine and the ycoordinate of the point to be the sine and the distance to the origin to be 1 then the Pythagorean Theorem immediately yields the identity y2 x2 1 sin2x cos2x 1 For example the equation sin x 1 sin x 1 0 sin x 1 sin x 1 0 resembles the equation x 1 x 1 0 x 1 x 1 0 which uses the factored form of the difference of squares Using algebra makes finding a solution straightforward and familiar
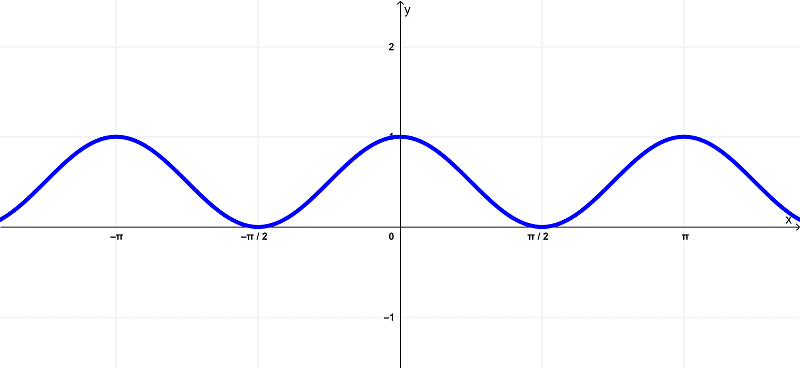
Derivative Of Cosine Squared Cos 2 x With Proof And Graphs Neurochispas
https://en.neurochispas.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/graph-of-cosine-squared-cos^2x.png
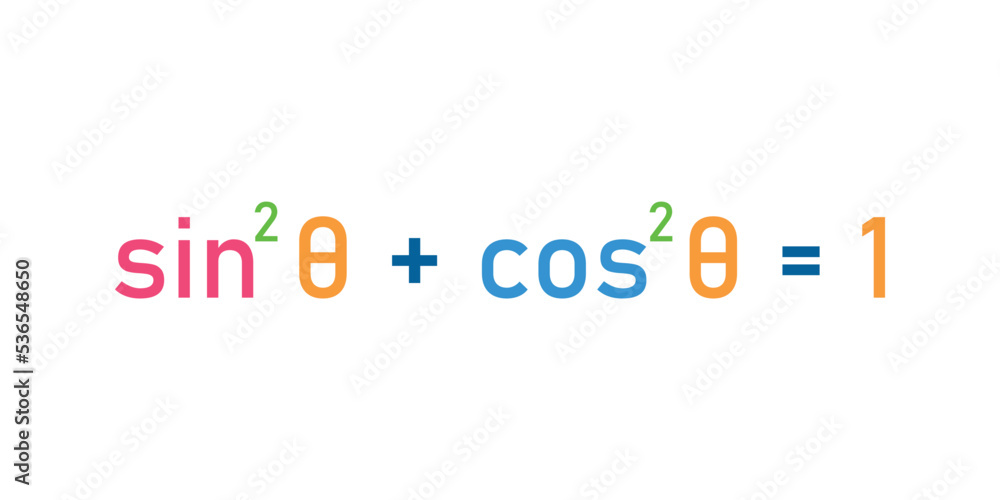
Pythagorean Identities Formulas Sine Squared Plus Cosine Squared Equal
https://as1.ftcdn.net/v2/jpg/05/36/54/86/1000_F_536548650_roWGkUGhTfSQ67AfNfZAbvZ4KE2RNNsj.jpg
why does sin squared cos squared 1 - A2 c2 b2 c2 c2 c2 This can be simplified to a c 2 b c 2 1 a c is Opposite Hypotenuse which is sin b c is Adjacent Hypotenuse which is cos So a c 2 b c 2 1 can also be written sin 2 cos 2 1 Note sin2 means to find the sine of then square the result but