what is the purpose of the electron transport chain in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis
We ll trace how light energy is absorbed by pigment molecules how reaction center pigments pass excited electrons to an electron transport chain and how the energetically downhill flow of electrons leads to synthesis of ATP and NADPH ATP is used by the cell as the energy for metabolic processes for cellular functions The electron transport chain is a cluster of proteins that transfer electrons through a membrane to create a gradient of protons that creates ATP adenosine triphosphate or energy that is needed in metabolic processes for cellular function
what is the purpose of the electron transport chain in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration

what is the purpose of the electron transport chain in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration
http://i.stack.imgur.com/LDVm1.jpg
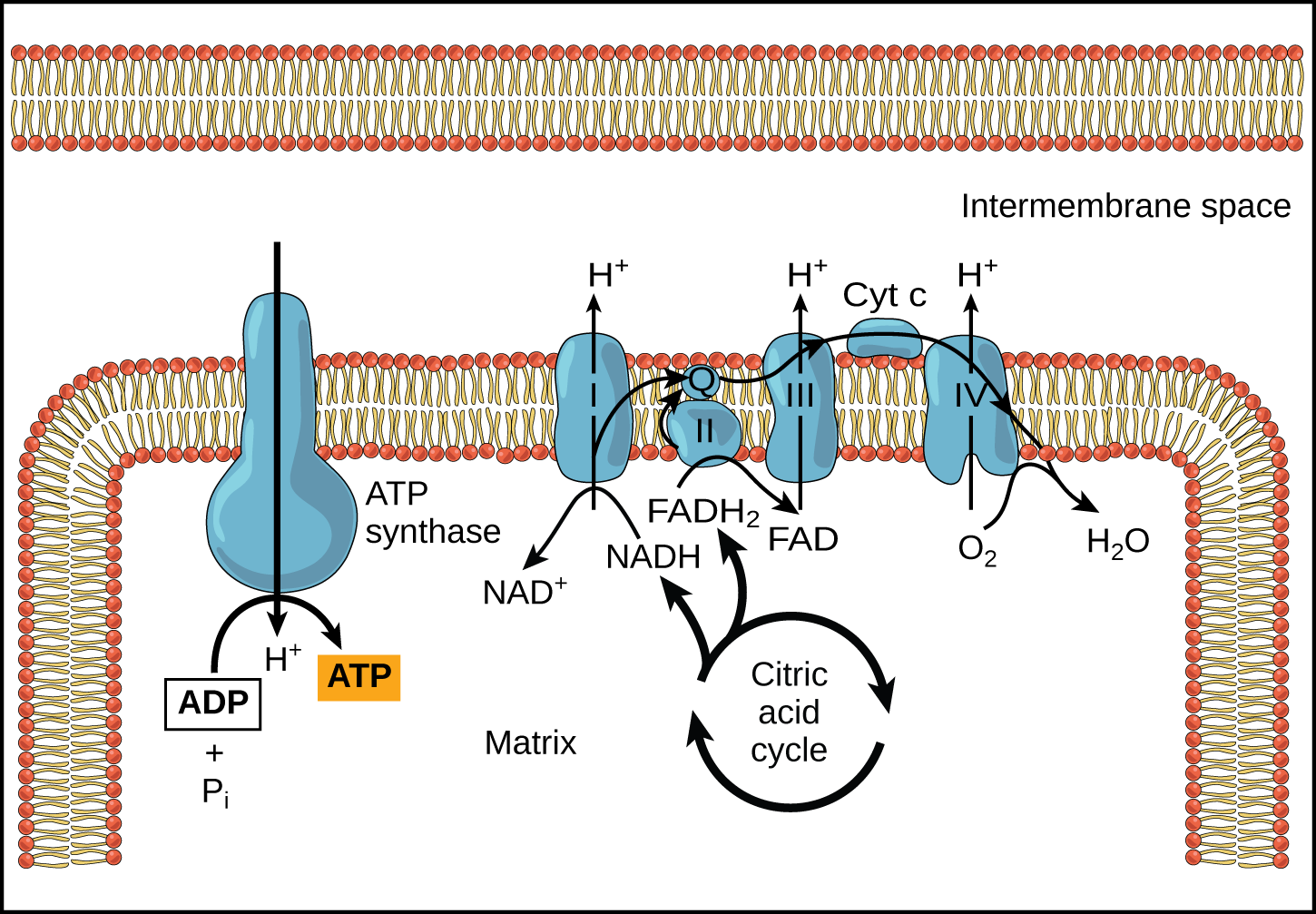
Oxidative Phosphorylation OpenStax Biology 2e
https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/3206/2018/05/03175828/Figure_07_04_03.png

Electron Transport Chain Summary Diagrams Expii
https://d20khd7ddkh5ls.cloudfront.net/sketch0512_2.jpg
The electrons travel through the chloroplast electron transport chain to photosystem I PSI which reduces NADP to NADPH The electron transport chain moves protons across the thylakoid membrane into the lumen The light dependent reactions of photosynthesis include an electron transport chain Like the electron transport chain that functions in the mitochondrion electrons are passed between protein complexes The energy released by this process is used to transport hydrogen ions against their gradient
In plants and other photosynthetic organisms an ETC serves to oxidize NADPH a phosphorylated version of the electron carrier NADH In both cases free energy released when the redox reactions of an ETC are coupled to the active transport of protons H ions across a membrane In cellular respiration electrons from glucose move gradually through the electron transport chain towards oxygen passing to lower and lower energy states and releasing energy at each step The goal of cellular respiration is to capture this energy in the form of ATP
More picture related to what is the purpose of the electron transport chain in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration
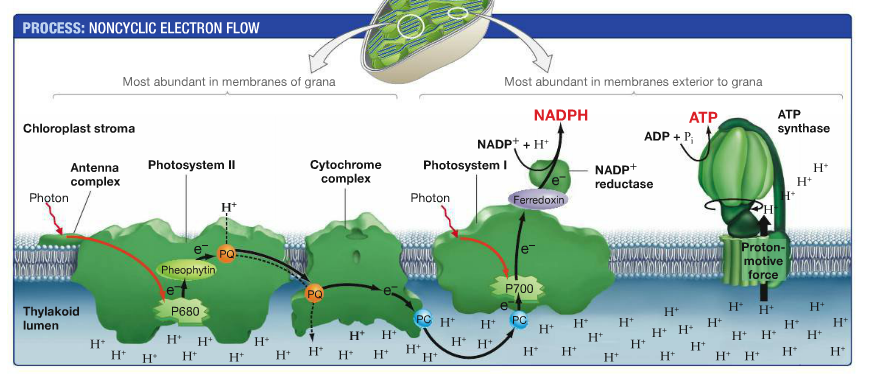
What Is The Product Of The Electron Transport Chain Of Photosynthesis
https://useruploads.socratic.org/Dg3GcK69SLGh2nUMiqWe_electrontransport.png

Electron Transport Chain Summary Diagrams Expii
https://d20khd7ddkh5ls.cloudfront.net/sketch0511.jpg
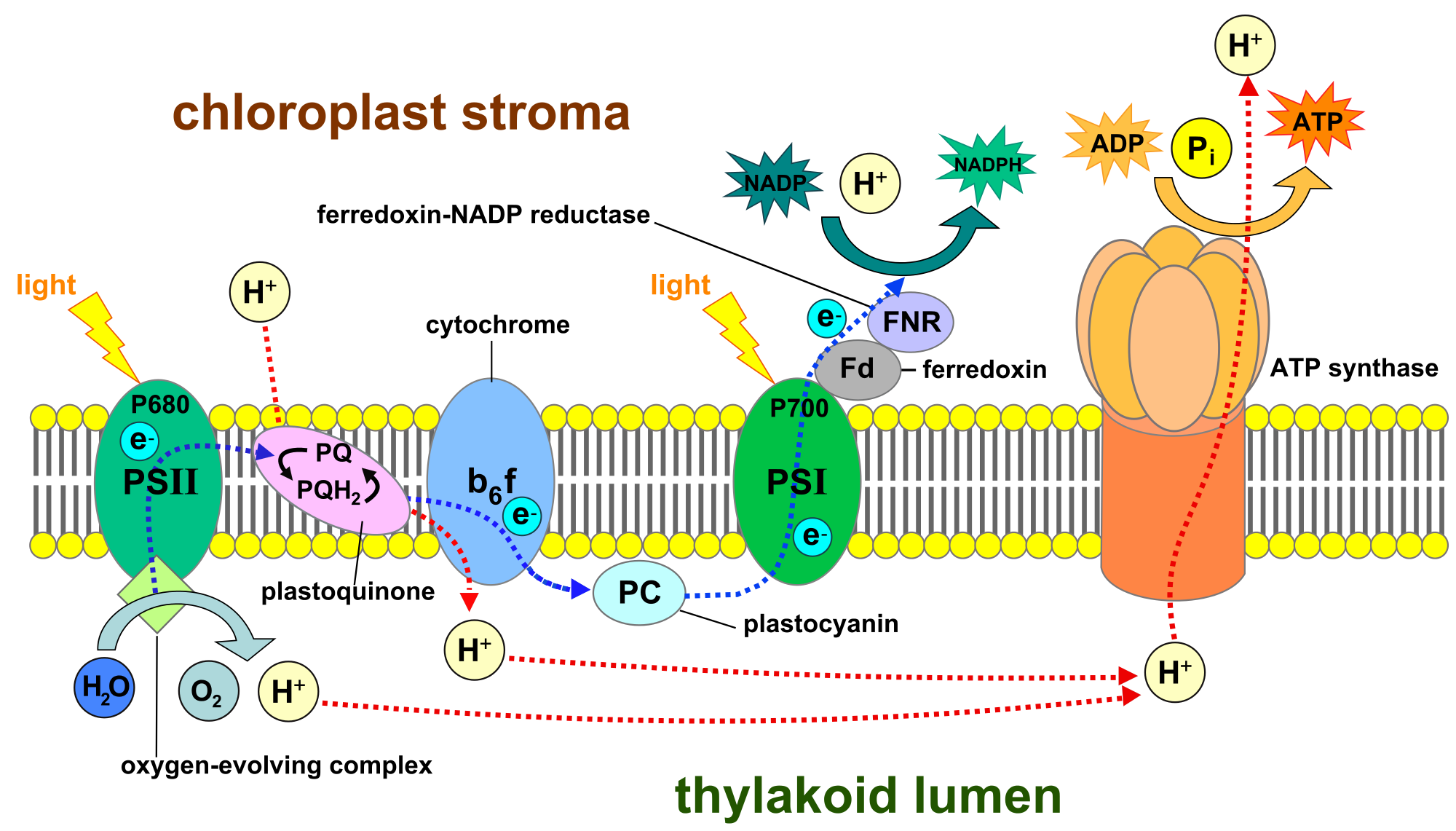
Electron Transport Respiratory Chain
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/49/Thylakoid_membrane_3.svg/2000px-Thylakoid_membrane_3.svg.png
In both cases the electron transport chain uses the energy to pump hydrogen ions across a membrane The protons pass back through ATP synthase driving the production of ATP In photosynthesis this ATP is used to construct Photosynthesis and respiration rely upon a proton gradient to produce ATP In photosynthesis the Respiratory Complex I homologue Photosynthetic Complex I PS CI is proposed to
The electrons passing through the electron transport chain gradually lose energy High energy electrons donated to the chain by either NADH or FADH 2 complete the chain as low energy electrons reduce oxygen molecules and form water Photosynthetic electron transport is the first stage of photosynthesis that produces chemically stored energy and uses solar photons to drive electron transport against a thermodynamic gradient
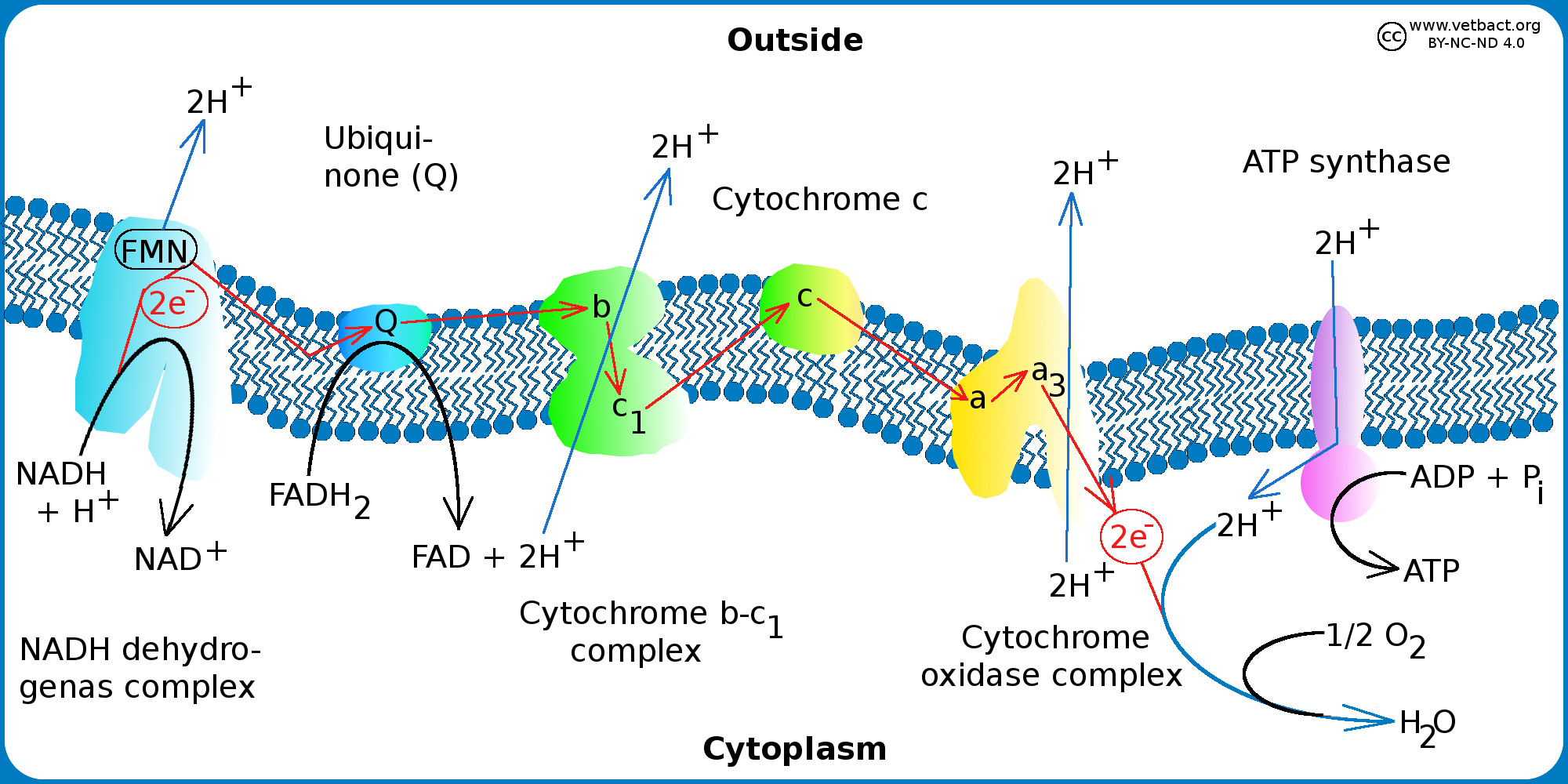
VetBact
https://www.vetbact.org/images/terms/large/e-transport_final-v6-eng.jpg
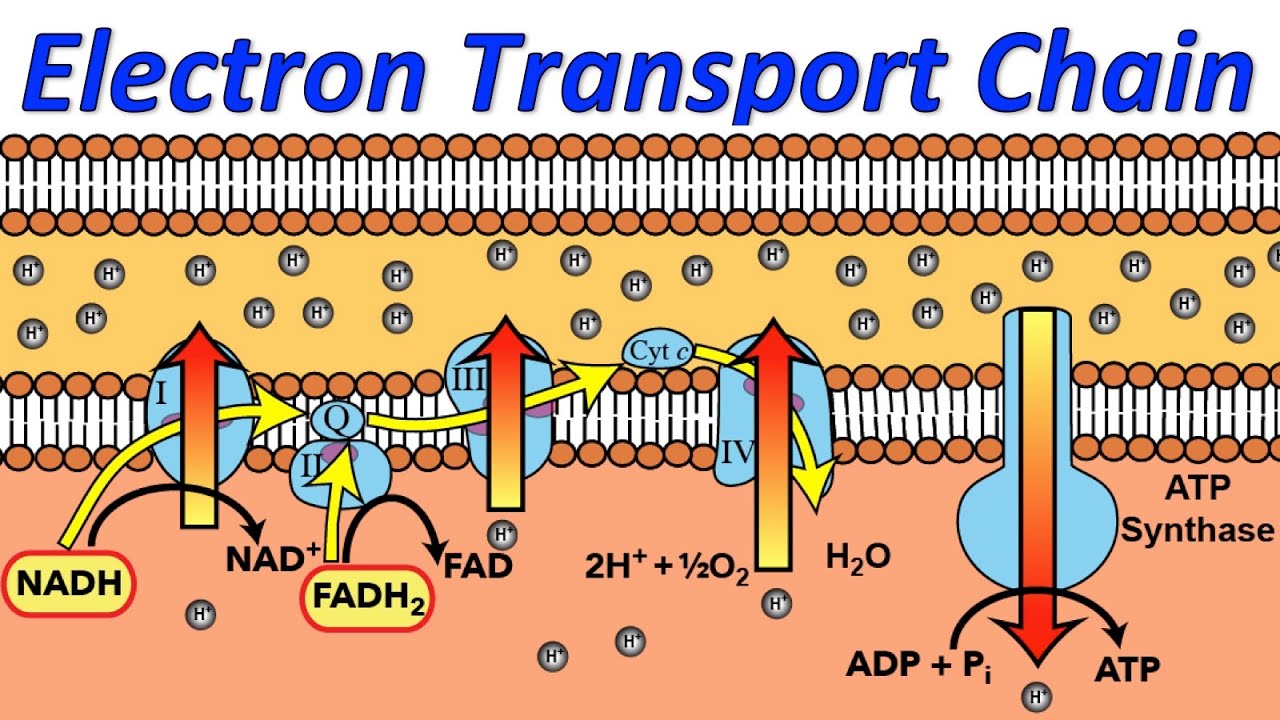
Electron Transport Chain Introduction Steps Examples
https://ibiologia.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/maxresdefault.jpg
what is the purpose of the electron transport chain in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration - There are three main steps of cellular respiration glycolysis the citric acid TCA or the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain where oxidative phosphorylation occurs The TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation require oxygen while glycolysis can occur in anaerobic conditions