what is the purpose of the electron transport chain etc The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis
An electron transport chain ETC is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons H ions across a membrane All cells use an electron transport chain ETC to oxidize substrates in exergonic reactions The electron flow from reduced substrates through an ETC is like the movement of electrons between the poles of a battery In the case of the battery the electron flow releases free energy to power a motor light cell phone etc
what is the purpose of the electron transport chain etc

what is the purpose of the electron transport chain etc
https://i0.wp.com/www.agrilearner.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/maxresdefault-3-1.jpg
Electron Transport Chain Introduction Steps Examples
https://ibiologia.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/maxresdefault.jpg

Electron Transport Chain Biochemistry Medbullets Step 1
https://upload.medbullets.com/topic/102051/images/etc - complete1.jpg
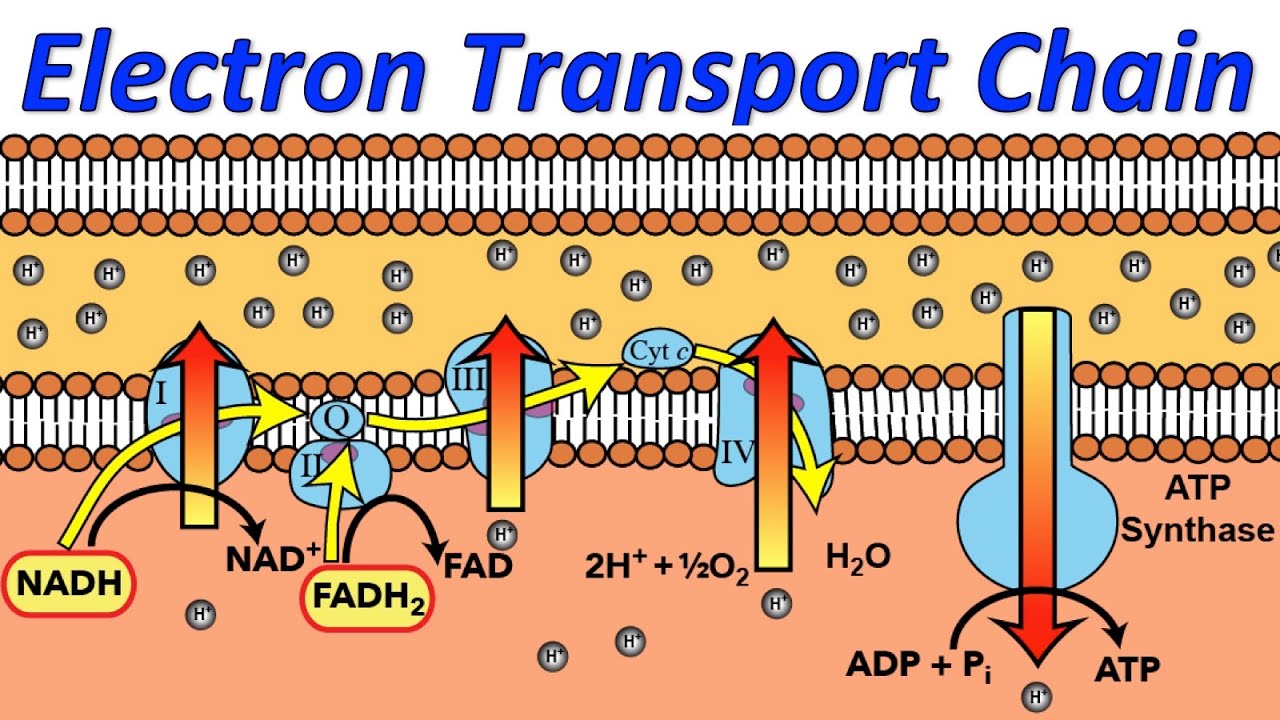
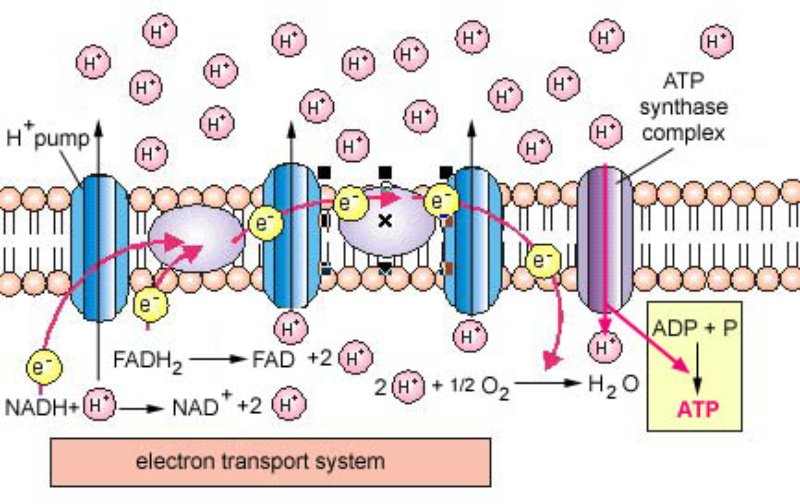
An electron transport chain or ETC is composed of a group of protein complexes in and around a membrane that help energetically couple a series of exergonic spontaneous red ox reactions to the endergonic pumping of protons across the membrane to generate an electrochemical gradient The electron transport chain aka ETC is a process in which the NADH and FADH 2 produced during glycolysis oxidation and other catabolic processes are oxidized thus releasing energy in the form of ATP The mechanism by which ATP is formed in the ETC is called chemiosmotic phosphorolation
The electron transport chain Figure 1 is the last component of aerobic respiration and is the only part of glucose metabolism that uses atmospheric oxygen Oxygen continuously diffuses into plants in animals it enters the body through the respiratory system The electron transport chain ETC is the main source of ATP production in the body and is vital for life The previous stages of respiration generate electron carrier molecules such as NADH to be used in the ETC
More picture related to what is the purpose of the electron transport chain etc

Electron Transport Chain Summary Diagrams Expii
https://d20khd7ddkh5ls.cloudfront.net/electron_carriers_etc.png
Electron Transport Chain Labster Theory
https://labsterim.s3.amazonaws.com/CACHE/images/media/uploads/wiki/Electron_transport/9e8ca0a98d96ad5a84986d62f3a68d1d.jpg

Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained With Diagram
https://pixfeeds.com/images/41/608834/1280-electron-transport-chain-diagram.png
Renee J LeClair Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine via Virginia Tech Libraries Open Education Initiative In the production of NADH and FADH 2 2 by the TCA cycle oxidation or glycolysis is funneled directly into the electron transport chain ETC where each of these reduced coenzymes will donate two electrons to electron carriers The primary task of the last stage of cellular respiration the electron transport chain is to transfer energy from the electron carriers to even more ATP molecules the batteries which power work within the cell
The electron transport chain has two essential functions in the cell Regeneration of electron carriers Reduced electron carriers NADH and FADH 2 pass their electrons to the chain turning them back into NAD and FAD The electron transport chain ETC is a set of redox reactions that take place in the inner mitochondrial membrane or in prokaryotes the plasma membrane The transport of electrons through the ETC creates a proton gradient across the membrane which is utilized to drive ATP synthase

Electron Transport Chain ETC In Cellular Respiration Definition
https://1.bp.blogspot.com/-ovQUhHv-MSM/X41LqAhbN1I/AAAAAAAAEgA/pRiSrXw-zjIt_Bri20HU2xEqhoxqT0gqQCLcBGAsYHQ/s1601/ETC%2Band%2Bchemiosmosis.png

Electron Transport Chain ETC And ETC Inhibitors Biotechfront
https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-F1kwSsLVg8Y/XywOxxKN12I/AAAAAAAAACQ/6fzJ4CdmeyUzriaFn3S-6CBtLvKGM229ACLcBGAsYHQ/s1600/1596722883476133-0.png
what is the purpose of the electron transport chain etc - An electron transport chain or ETC is composed of a group of protein complexes in and around a membrane that help energetically couple a series of exergonic spontaneous red ox reactions to the endergonic pumping of protons across the membrane to generate an electrochemical gradient