what is the purpose of the electron transport chain at the cytoplasmic membrane The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis
The electron transport chain has two essential functions in the cell Regeneration of electron carriers Reduced electron carriers NADH and FADH 2 pass their electrons to the chain turning them back into NAD and FAD An electron transport chain ETC 1 is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons H ions across a membrane
what is the purpose of the electron transport chain at the cytoplasmic membrane

what is the purpose of the electron transport chain at the cytoplasmic membrane
https://i0.wp.com/www.agrilearner.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/maxresdefault-3-1.jpg

09 21 electron transport L Electron Transport Chain Biochemistry
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/13/ae/30/13ae30319f69aa719a3952b5b5dd87fb.jpg
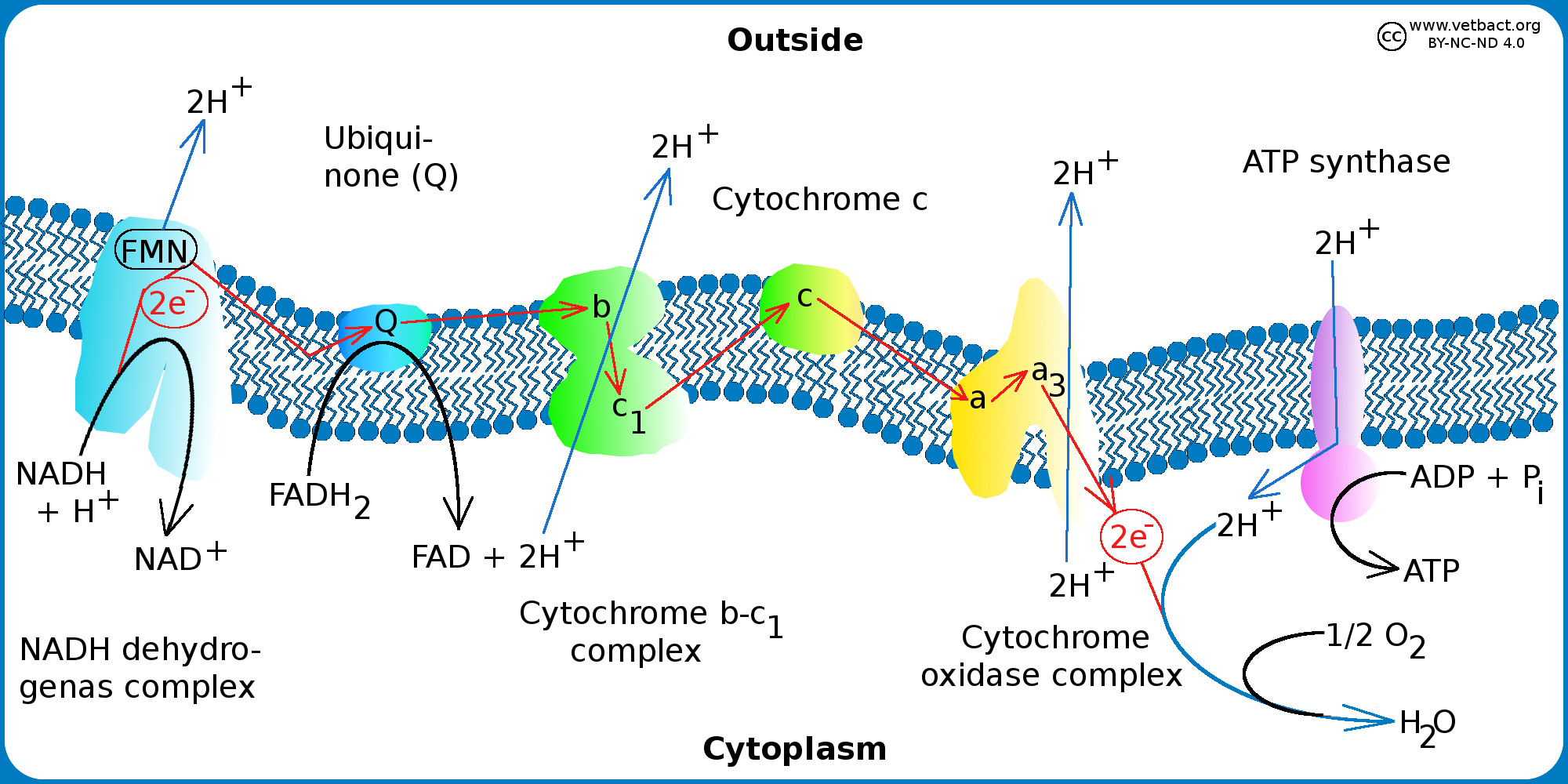
VetBact
https://www.vetbact.org/images/terms/large/e-transport_final-v6-eng.jpg
The electron transport chain is a series of electron transporters embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH 2 to molecular oxygen In the process protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space and oxygen is reduced to form water The electron transport chain aka ETC is a process in which the NADH and FADH2 produced during glycolysis oxidation and other catabolic processes are oxidized thus releasing energy in the form of ATP The mechanism by which ATP is formed in the ETC is called chemiosmotic phosphorolation
In plants and other photosynthetic organisms an ETC serves to oxidize NADPH a phosphorylated version of the electron carrier NADH In both cases free energy released when the redox reactions of an ETC are coupled to the active transport of protons H ions across a membrane The ETC collects electrons from NADH or FADH 2 and transfers them through a series of electron carriers within multiprotein respiratory complexes complex I to IV to oxygen therefore generating an electrochemical gradient that can be used by the F 1 F 0 ATP synthase also named complex V in the mitochondrial inner membrane to
More picture related to what is the purpose of the electron transport chain at the cytoplasmic membrane
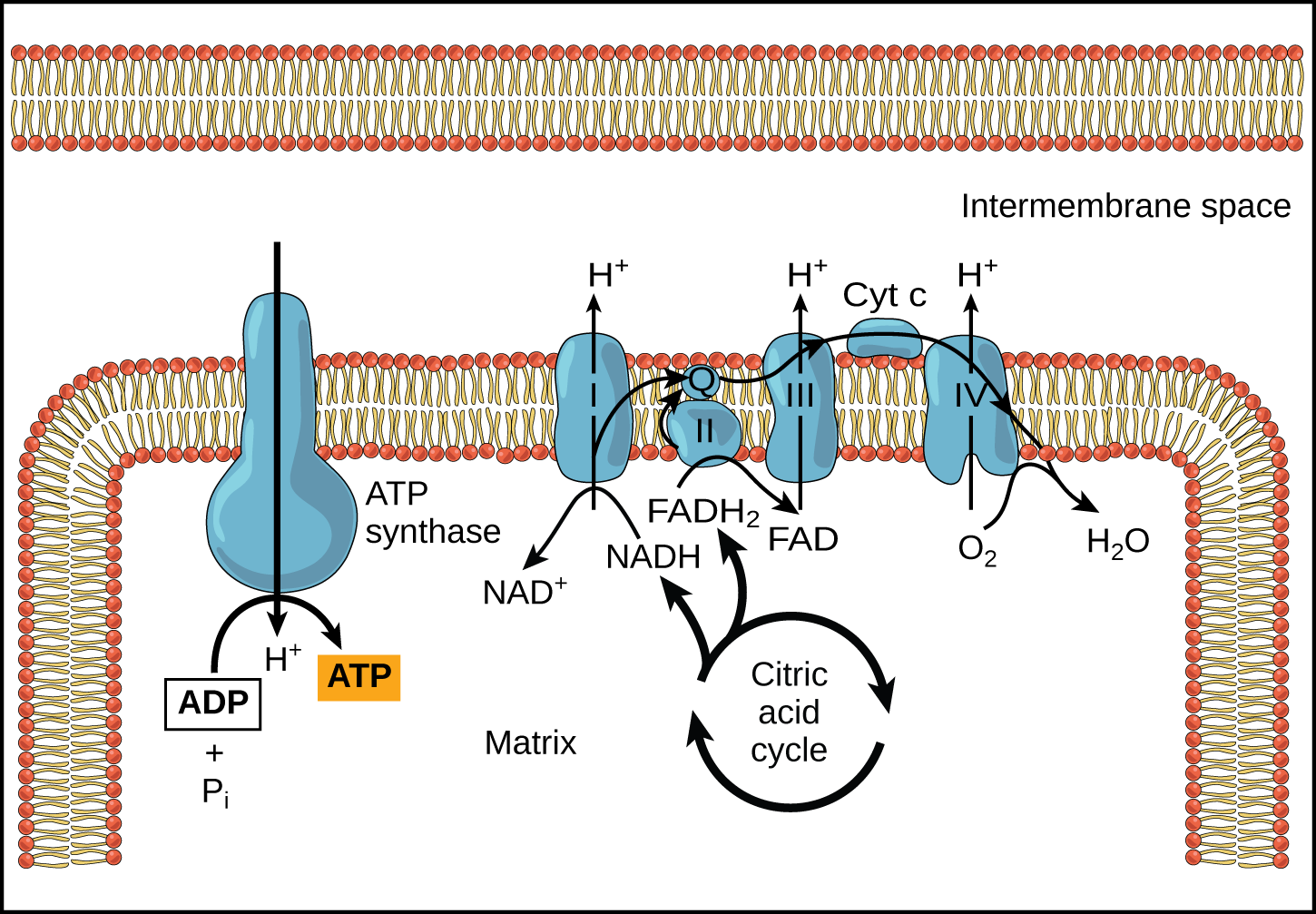
Oxidative Phosphorylation OpenStax Biology 2e
https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/3206/2018/05/03175828/Figure_07_04_03.png
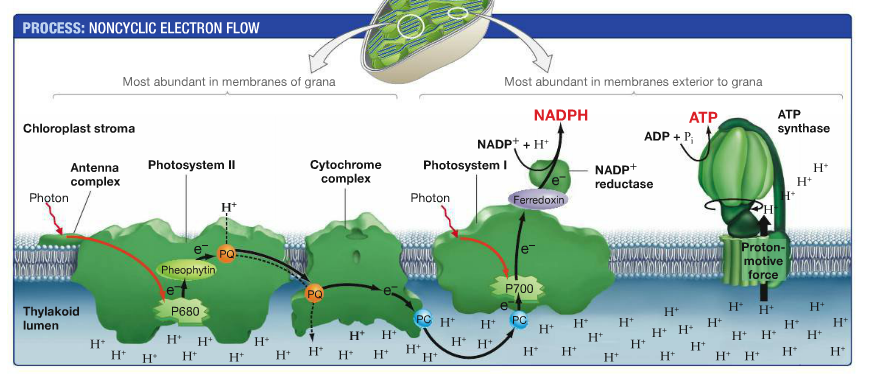
What Is The Product Of The Electron Transport Chain Of Photosynthesis
https://useruploads.socratic.org/Dg3GcK69SLGh2nUMiqWe_electrontransport.png

Oxidative Phosphorylation OpenStax Biology 2e
https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/3206/2018/05/03175821/Figure_07_04_01.jpg
The electron transport chain is comprised of a series of enzymatic reactions within the inner membrane of the mitochondria which are cell organelles that release and store energy for all Oxidative phosphorylation is made up of two closely connected components the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis In the electron transport chain electrons are passed from one molecule to another and energy released in these electron transfers is used to form an electrochemical gradient
An electron transport chain or ETC is composed of a group of protein complexes in and around a membrane that help energetically couple a series of exergonic spontaneous red ox reactions to the endergonic pumping of protons across the membrane to generate an electrochemical gradient The mitochondrial electron transport chain utilizes a series of electron transfer reactions to generate cellular ATP through oxidative phosphorylation A consequence of electron transfer is the generation of reactive oxygen species ROS which contributes to both homeostatic signaling as well as oxidative stress during pathology
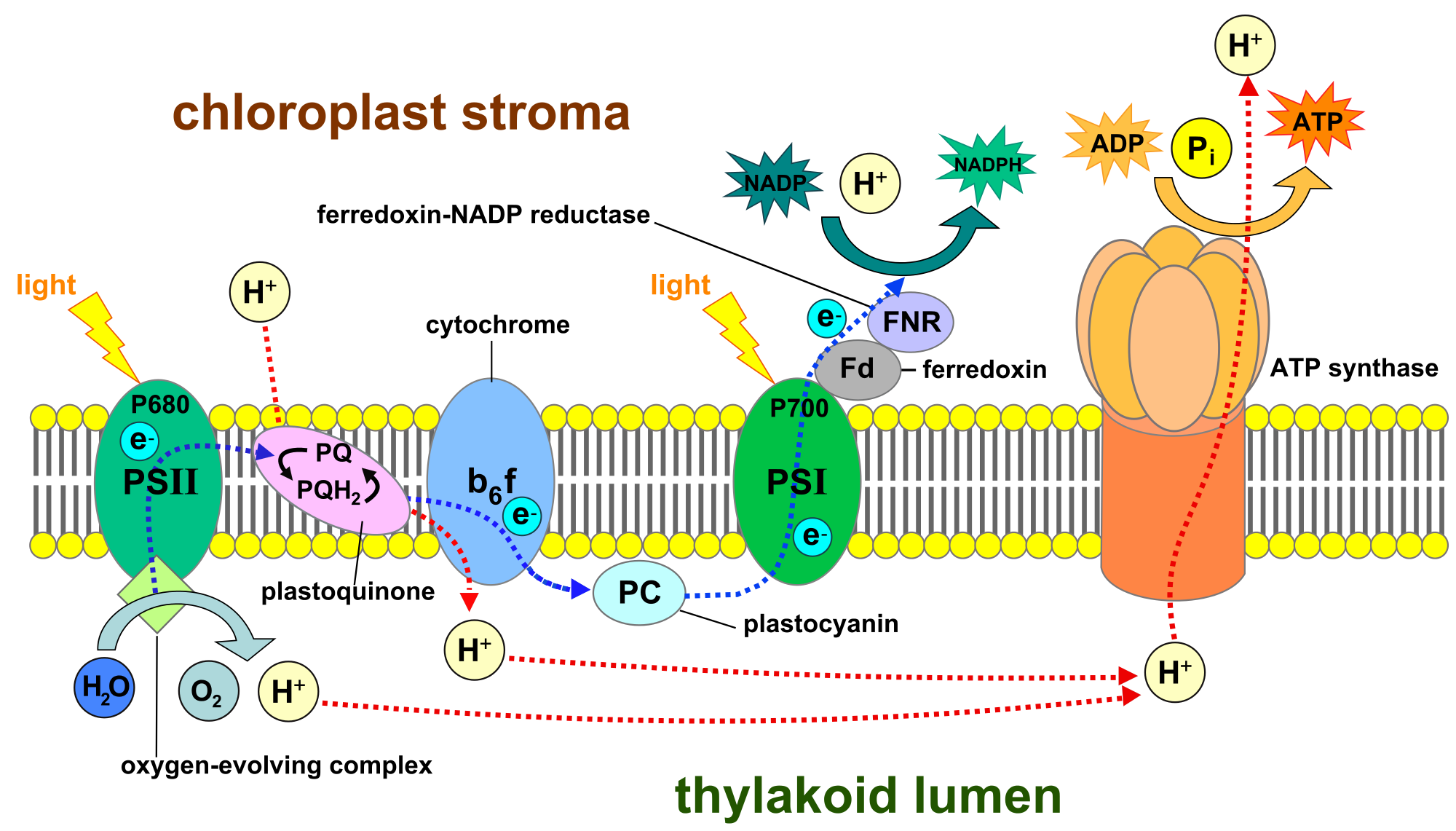
Electron Transport Respiratory Chain
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/49/Thylakoid_membrane_3.svg/2000px-Thylakoid_membrane_3.svg.png

Electron Transport Chain Summary Diagrams Expii
https://d20khd7ddkh5ls.cloudfront.net/sketch0511.jpg
what is the purpose of the electron transport chain at the cytoplasmic membrane - The electron transport chain aka ETC is a process in which the NADH and FADH2 produced during glycolysis oxidation and other catabolic processes are oxidized thus releasing energy in the form of ATP The mechanism by which ATP is formed in the ETC is called chemiosmotic phosphorolation