what is systolic and diastolic blood pressure definition Systolic blood pressure is the first number on your reading and measures the force of blood as your heart pushes it out Diastolic blood pressure the second number is the force of blood as your
Your blood pressure numbers and what they mean Your blood pressure is recorded as two numbers Systolic blood pressure is the first number It measures the pressure your blood is pushing against your artery walls when the heart beats Diastolic blood pressure is the second number A blood pressure reading has two numbers Top number called systolic pressure The top number measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats Bottom number called diastolic pressure The bottom number measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats
what is systolic and diastolic blood pressure definition

what is systolic and diastolic blood pressure definition
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/79C6A9FS0MI/maxresdefault.jpg
Difference Between Systolic And Diastolic Blood Pressures Viva
https://vivadifferences.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Capture-13-661x420.png
5 2 What Are Systolic And Diastolic Pressures Taking Vital Signs
https://brooksidepress.org/vitalsigns/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/Blood_Pressure.jpg
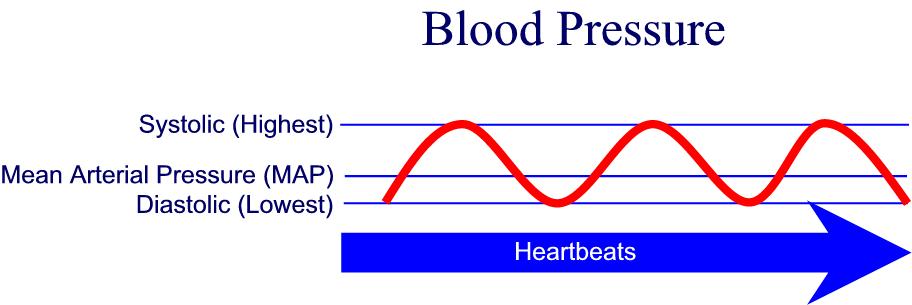
Diastolic blood pressure is the bottom number of a blood pressure reading and it measures the blood pressure applied against the artery walls when the heart is filling between beats The balance between diastolic and systolic pressure determines a person s blood pressure A blood pressure reading displays systolic and diastolic pressure
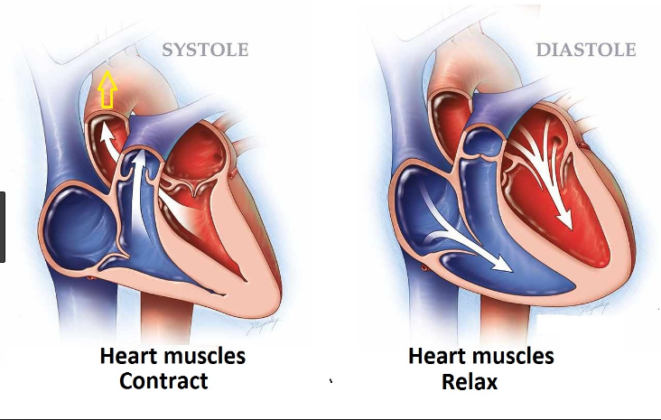
The diastolic reading or the bottom number is the pressure in the arteries when the heart rests between beats This is the time when the heart fills with blood and gets oxygen This is what Systolic blood pressure This is the pressure when the heart beats while the heart muscle is contracting squeezing and pumping oxygen rich blood into the blood vessels Diastolic blood pressure This is the pressure on the blood vessels when the heart muscle relaxes
More picture related to what is systolic and diastolic blood pressure definition
Blood Pressure Types Of Blood Pressure And Its Differences
https://cdn1.byjus.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Difference-Between-Systolic-and-Diastolic-Blood-Pressure.png

Diastolic And Systolic Blood Pressure The Differences Between Them
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/9t1uQL36y3E/maxresdefault.jpg

What Is Systolic And Diastolic Blood Pressure YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZuExCx5D0cc/maxresdefault.jpg
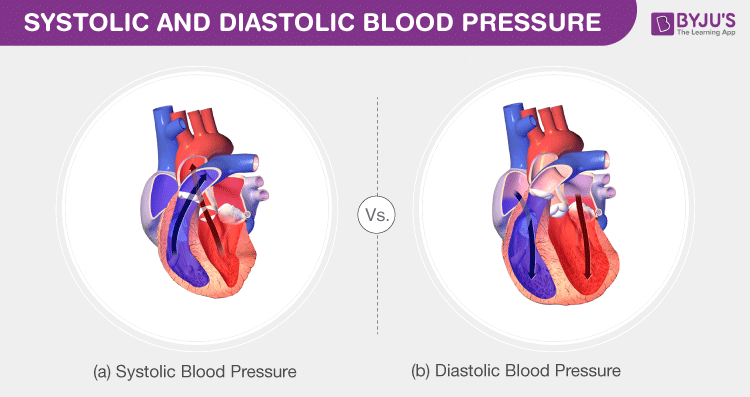
Systolic blood pressure measures the force that s exerted on your arteries when your heart squeezes and sends blood into your arteries Diastolic blood pressure measures the force that s exerted on your arteries during diastole when your heart is at rest and relaxing between beats Blood pressure BP is the pressure of circulating blood on the walls of arteries Healthcare providers use BP readings to help evaluate cardiovascular health BP is measured as a systolic pressure the top number and a
Systolic blood pressure the top first number This is the pressure in your arteries when your heart is beating and sending blood into your arteries Diastolic blood pressure the bottom second number This is the pressure in your arteries when your heart is at rest between heartbeats The systolic blood pressure the number on top is the pressure produced when the heart contracts and pushes out blood The diastolic blood pressure the number on the bottom is the pressure when the heart relaxes and fills with blood between heartbeats

What s Systolic And Diastolic Blood Pressure CBSE Class Notes Online
https://classnotes123.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/SYS-DIA-illustration.png
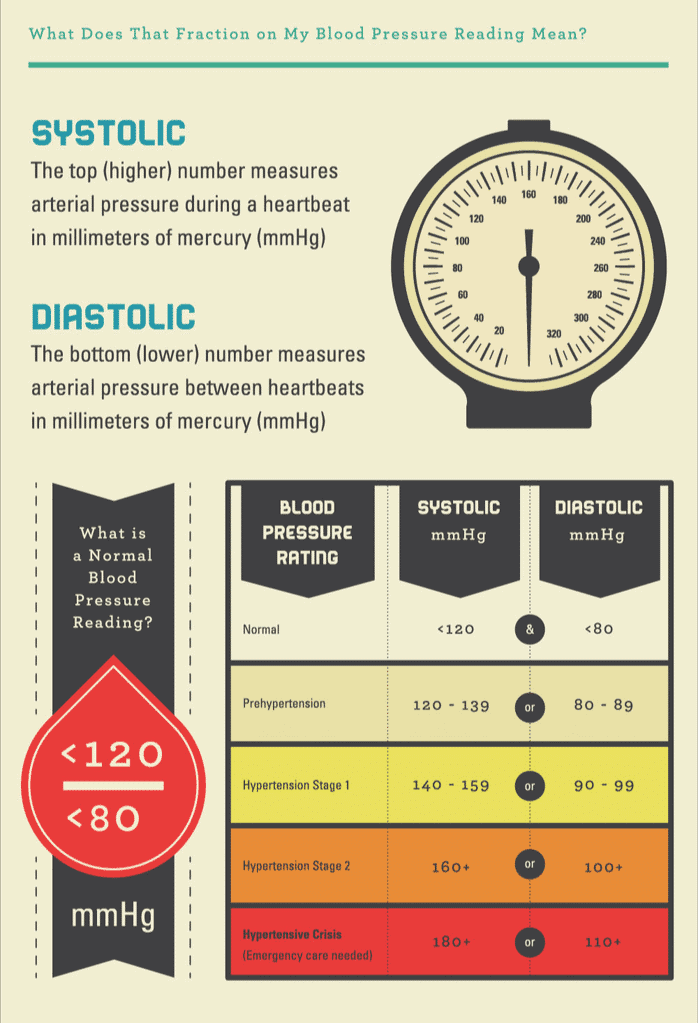
What Do Blood Pressure Readings Mean Carrington College
https://carrington.edu/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/What-does-the-fraction-mean.png
what is systolic and diastolic blood pressure definition - Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure maximum pressure during one heartbeat over diastolic pressure minimum pressure between two heartbeats in the cardiac cycle It is measured in millimeters of mercury mmHg above the surrounding atmospheric pressure or in kilopascals kPa