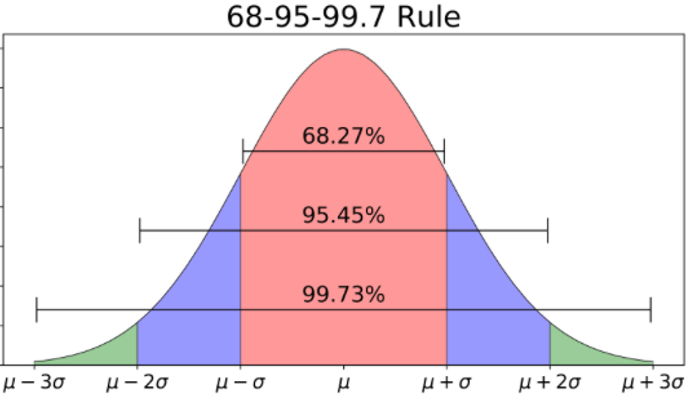
what does the 68 95 99 rule refer to The empirical rule also known as the 68 95 99 7 rule represents the percentages of values within an interval for a normal distribution That is 68 percent of data is within one standard deviation of the mean 95 percent of data is within two standard deviation of the mean and 99 7 percent of data is within three standard deviation of the mean
The 68 95 99 rule is based on the mean and standard deviation It says 68 of the population is within 1 standard deviation of the mean 95 of the population is within 2 standard deviation of the mean 99 7 of the population is within 3 The 68 95 99 rule tells us that 95 of delivery times will fall within the range of 2 standard deviations which is 5 2 3 to 7 days This leaves 5 outside of this range In other words 5 of packages will arrive either earlier than 3 days or later than 7 days
what does the 68 95 99 rule refer to
what does the 68 95 99 rule refer to
https://d20ohkaloyme4g.cloudfront.net/img/document_thumbnails/ea81f75d6aab368a598f20084e59b26a/thumb_1200_1698.png
10 Sampling Data Applications In Public Administration
https://alex-combs.github.io/data-apps-text/images/normdist.png

Explaining The 68 95 99 7 Rule For A Normal Distribution Data Science
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/b1/75/89/b1758935bcd02752e6ca6fb829ad649f.png
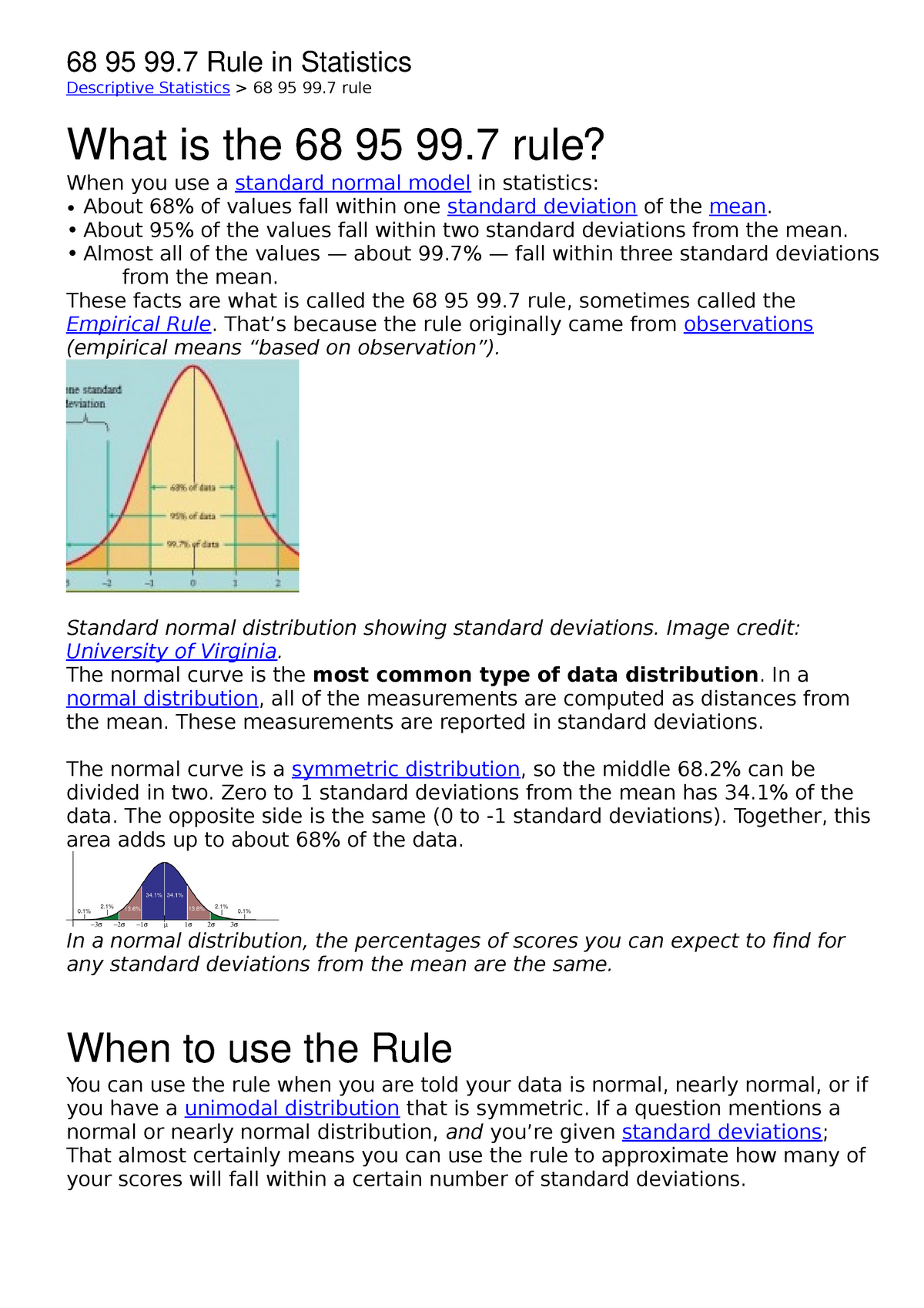
The empirical rule in statistics also known as the 68 95 99 rule states that for normal distributions 68 of observed data points will lie inside one standard deviation of the mean 95 will fall within two standard deviations and 99 7 will occur within three standard deviations The empirical rule also called the 68 95 99 7 rule is a guideline for how data is distributed in a normal distribution
Empirical Rule also known as the 68 95 99 7 rule states that in a normal distribution approximately 68 of the data falls within one standard deviation of the mean 95 within two standard deviations and 99 7 within three standard deviations The empirical rule also known as the 68 95 99 7 rule is a handy way to analyze statistical data It only work for a normal distribution bell curve however and can only produce estimates You ll need to know the mean and standard deviation of your data
More picture related to what does the 68 95 99 rule refer to
Empirical Rule Definition Formula Statistics By Jim
https://statisticsbyjim.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/empirical_rule_graph2.png

68 95 99 Rule In R Finnstats
https://finnstats.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/68-95-99-Rule-in-R.jpg
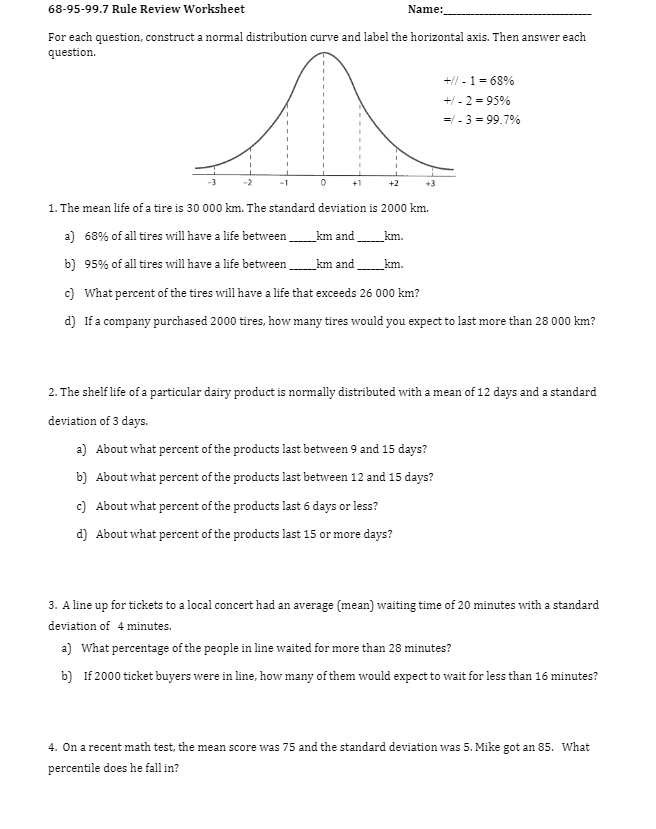
Solved 68 95 99 7 Rule Review Worksheet Name For Each Chegg
https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/0fb/0fb3e624-0e2e-4ba5-ae94-16d6aeb5167e/image
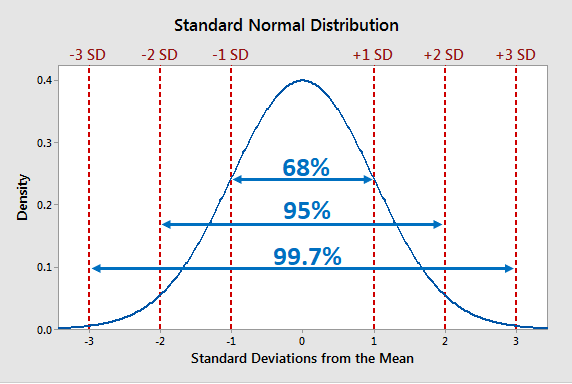
The empirical rule calculator also a 68 95 99 rule calculator is a tool for finding the ranges that are 1 standard deviation 2 standard deviations and 3 standard deviations from the mean in which you ll find 68 95 and 99 7 of The 68 95 99 7 rule also known as the empirical rule is a statistical principle that describes the distribution of data in a normal distribution It provides a general guideline for understanding the proportion of data that falls within certain standard deviation ranges from the mean
The 68 95 99 rule tells us how the data in a normal distribution will be clumped We know that roughly 68 or more accurately 68 2 of the data that is collected will be within one standard deviation from the mean The graph below illustrates it At its core the 68 95 99 7 Rule encapsulates the idea that in a normal distribution a symmetric bell shaped curve a specific percentage of data falls within certain standard

PPT The 68 95 99 7 Rule PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID
https://image1.slideserve.com/2960901/the-68-95-99-7-rule-l.jpg

68 95 99 7 Rule empirical Rule NCEA Level 2 Maths NZ Level 7 NZC
https://mathspace-production-media.mathspace.co/media/upload/images/001_Chapter_Entries/Statistics/68.png
what does the 68 95 99 rule refer to - The Empirical Rule is also known as the 68 95 99 7 Rule in correspondence with those three properties It s used to describe a population rather than a sample but you can also use it to help you decide whether a sample of data came from a normal distribution