what are electron transport chain reactants The electron transport chain ETC is the biochemical process that produces most of a cell s fuel in aerobic organisms This involves the buildup of a proton motive force PMF which allows for the production of ATP the
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis An electron transport chain ETC is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons H ions across a membrane
what are electron transport chain reactants

what are electron transport chain reactants
https://d1j63owfs0b5j3.cloudfront.net/tutorial/finalImage/1033-1451937006308.png
Electron Transport Chain
https://www.vetbact.org/images/terms/large/e-transport_final-v6-eng.jpg
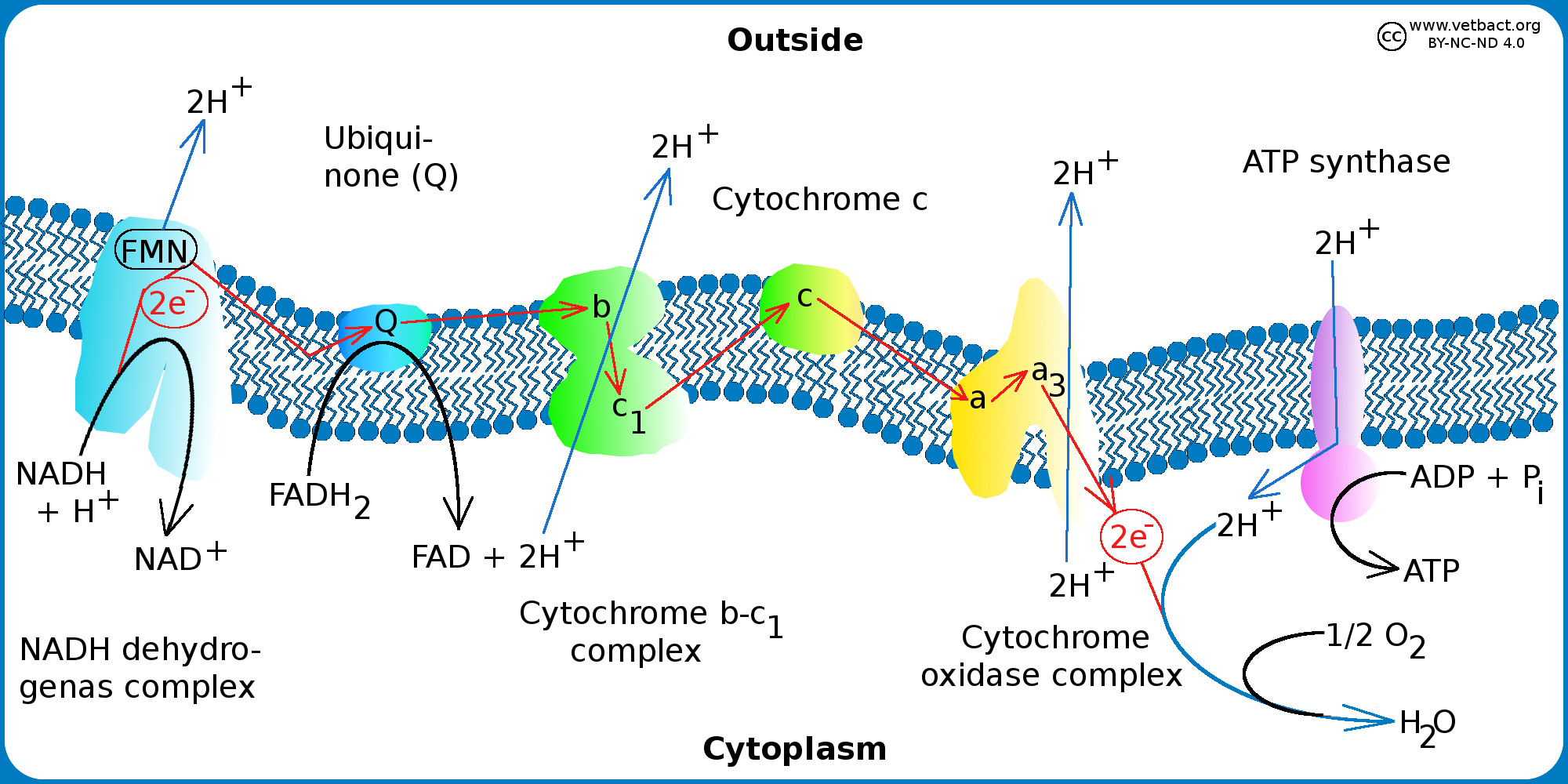
Electron Transport Chain Astonishingceiyrs
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Electron-Transport-Chain.jpg
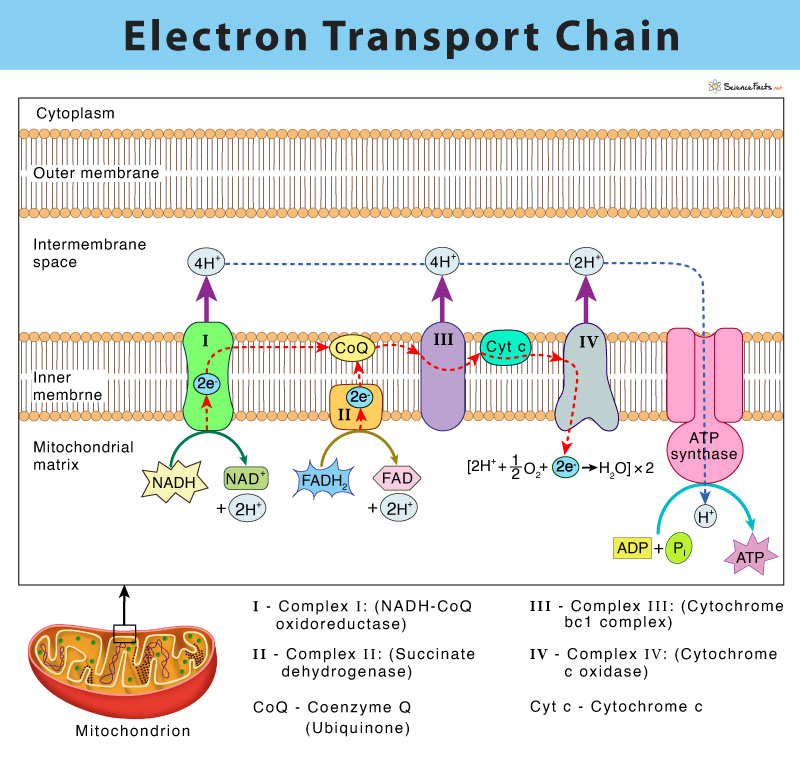
Electron transport is a series of redox reactions that resemble a relay race or bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next to the endpoint of the chain where the electrons reduce molecular oxygen producing water The electron transport chain ETC is a group of proteins and organic molecules found in the inner membrane of mitochondria Each chain member transfers electrons in a series of oxidation reduction redox reactions to form a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis
An electron transport chain or ETC is composed of a group of protein complexes in and around a membrane that help energetically couple a series of exergonic spontaneous red ox reactions to the endergonic pumping of protons across the membrane to generate an electrochemical gradient Electron transport is a series of redox reactions that resemble a relay race or bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next to the endpoint of the chain where the electrons reduce molecular oxygen producing water
More picture related to what are electron transport chain reactants
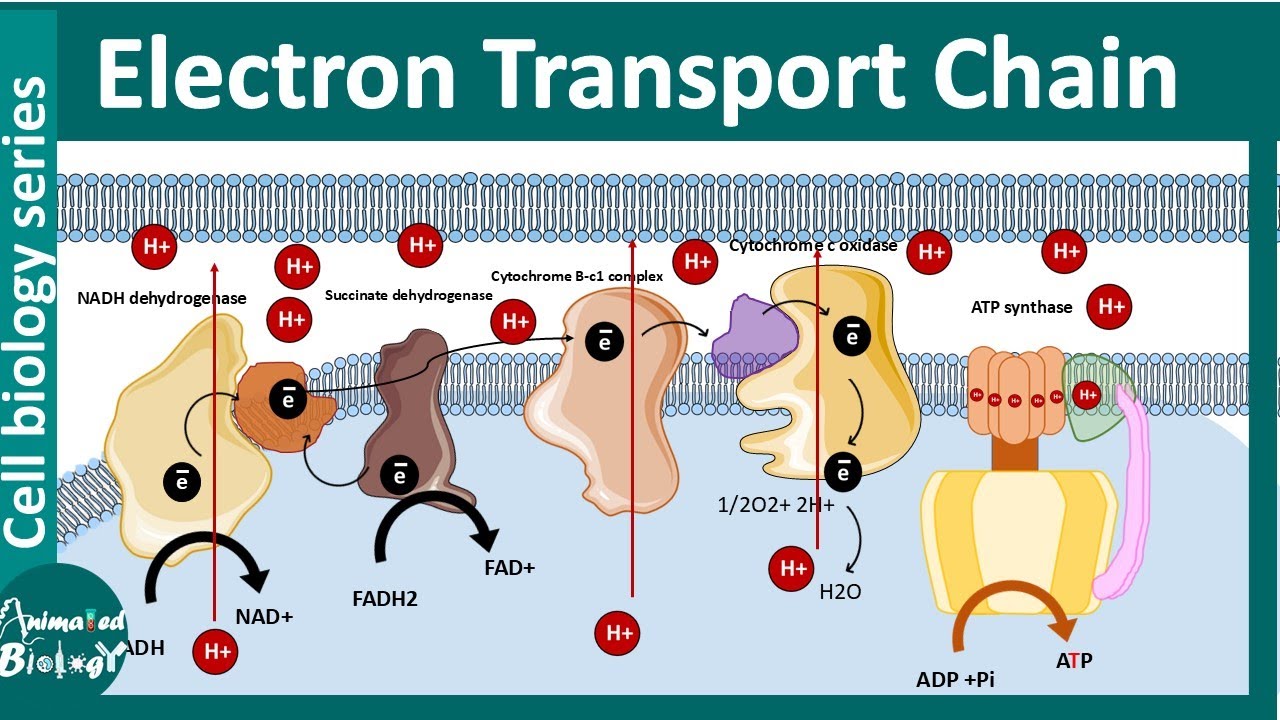
Electron Transport Chain And Oxidative Phosphorylation YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/i8CC8pmtAp4/maxresdefault.jpg

Electron Transport Chain And Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Dictionary
https://cdn-acgla.nitrocdn.com/bvIhcJyiWKFqlMsfAAXRLitDZjWdRlLX/assets/static/optimized/rev-5131b73/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/The-Electron-Transport-Chain.jpg
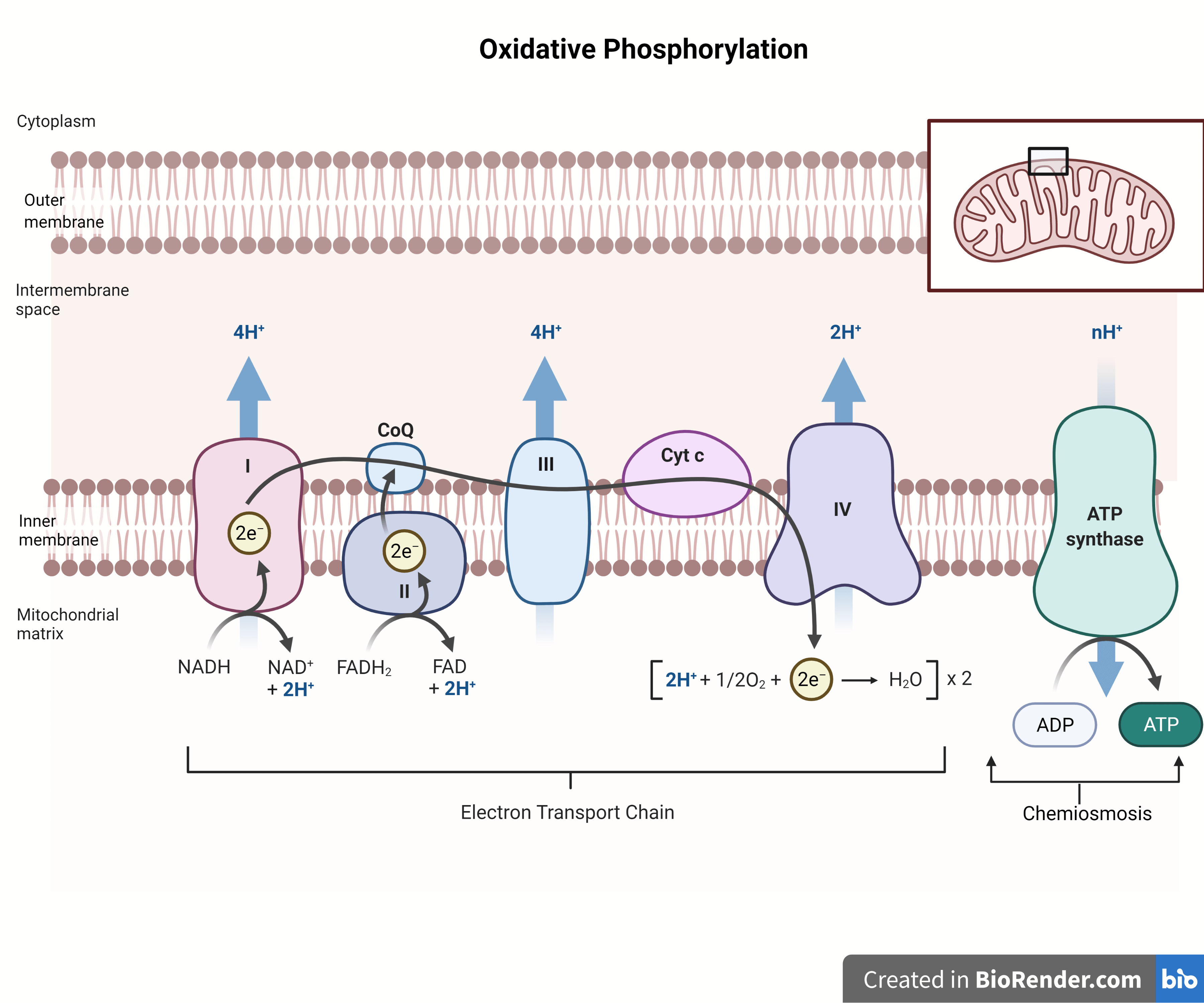
Oxidative Phosphorylation Mechanism And Regulation Microbe Online
https://microbeonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/oxidative-phosphorylation-1.png
The Electron Transport System also called the Electron Transport Chain is a chain of reactions that converts redox energy available from oxidation of NADH and FADH 2 into proton motive force which is used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex through a process called Oxidative phosphorylation is made up of two closely connected components the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis In the electron transport chain electrons are passed from one molecule to another and energy released in these electron transfers is used to form an electrochemical gradient
Electron transport chains rely on the transfer of electrons Electron transfer involves oxidation and reduction reactions which occur at the same time An oxidation reaction strips an electron from an atom in a compound and the addition of this electron to another compound is a reduction reaction All cells use an electron transport chain ETC to oxidize substrates in exergonic reactions The electron flow from reduced substrates through an ETC is like the movement of electrons between the poles of a battery In the case of the battery the electron flow releases free energy to power a motor light cell phone etc

Electron Transport Chain Summary Diagrams Expii
https://d20khd7ddkh5ls.cloudfront.net/sketch0511.jpg

Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained With Diagram
https://pixfeeds.com/images/41/608834/1280-electron-transport-chain-diagram.png
what are electron transport chain reactants - The electron transport chain ETC is a group of proteins and organic molecules found in the inner membrane of mitochondria Each chain member transfers electrons in a series of oxidation reduction redox reactions to form a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis