w g graph theory In graph theory a clique kli k or kl k is a subset of vertices of an undirected graph such that every two distinct vertices in the clique are adjacent That is a clique of a graph is an induced subgraph of that is complete
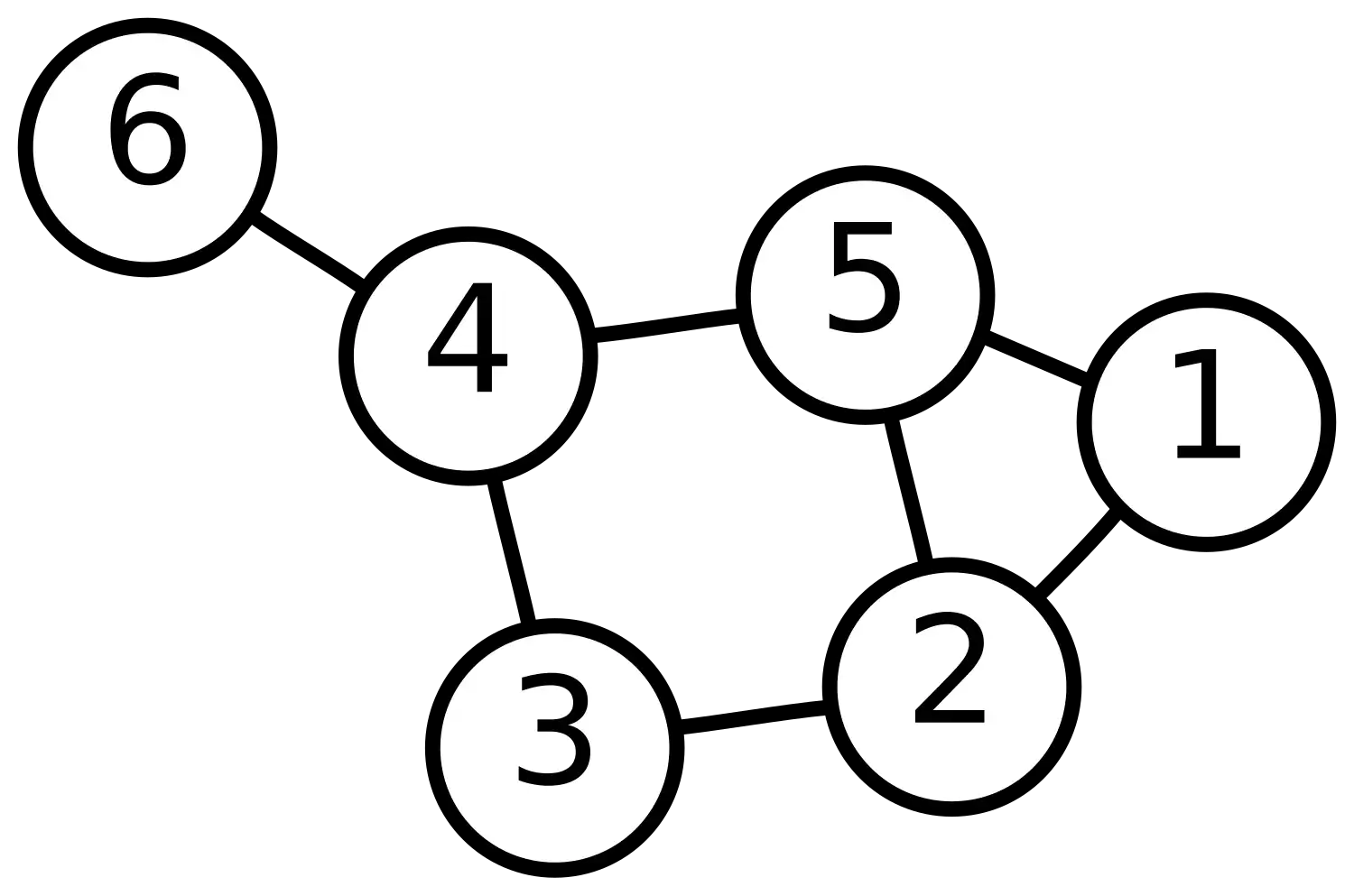
In each graph there is one dominating vertex in G 1 it is v 3 and in G 2 it is w Each graph has one vertex with degree one in G 1 it is v 4 and in G 2 it is x In both graphs the remaining two vertices are adjacent and each have the same degree We will investigate some of the basics of graph theory in this section A graph G is a collection E of distinct unordered pairs of distinct elements of a set V The elements of V are called vertices or nodes and t he pairs in E are called edges or arcs or the graph
w g graph theory
w g graph theory
https://wikiwandv2-19431.kxcdn.com/_next/image?url=https:%2F%2Fupload.wikimedia.org%2Fwikipedia%2Fcommons%2Fthumb%2F5%2F5b%2F6n-graf.svg%2F1500px-6n-graf.svg.png&w=1920&q=50

Graph Theory
https://d1xuqjt1wg0fxw.cloudfront.net/b0c25e10-1539-11ec-b157-fdcc127717ef.jpg

Graph Theory Buy Graph Theory Online At Low Price In India On Snapdeal
https://n3.sdlcdn.com/imgs/b/m/x/Graph-Theory-SDL558248438-1-0b570.jpg
Whitman College See Section 4 5 to review some basic terminology about graphs A graph G consists of a pair V E where V is the set of vertices and E the set of edges We write V G for the vertices of G and E G for the edges of G when necessary to avoid ambiguity as when more than one graph is under discussion This standard textbook of modern graph theory in its fifth edition combines the authority of a classic with the engaging freshness of style that is the hallmark of active mathematics It covers the core material of the subject with concise proofs
Given a graph G itsline graph or derivative L G is a graph such that i each vertex of L G represents an edge of G and ii two vertices of L G are adjacent if and only if their corresponding edges share a common endpoint are incident in G Fig Definition of a graph A graph G comprises a set V of vertices and a set E of edges Each edge in E is a pair a b of vertices in V If a b is an edge in E we connect a and b in the graph drawing of G Example 2 4 1 V 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 E 1 2 1 3 2 4 4 5 3 5 4 5 3
More picture related to w g graph theory
Introduction To Graph Theory
https://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009043224_1-1bd744dad1d52740120464f581bf98dd-768x994.png

Graph Theory A2LABS
https://codetechweb.files.wordpress.com/2016/09/untitled-design-2.jpg
GitHub Babiswas Graph Theory Des
https://opengraph.githubassets.com/57e7d95527cb830894f863c24c329f6c36744fa31a134d0ddff1e6581522d556/babiswas/Graph-Theory
Theorem In any graph with at least two nodes there are at least two nodes of the same degree Proof 1 Let G be a graph with n 2 nodes There are n possible choices for the degrees of nodes in G namely 0 1 2 and n 1 We claim that G cannot simultaneously have a node u of degree 0 and a node v of degree n 1 if there were Graph Theory 1 Introduction Graphs are an incredibly useful structure in Computer Science They arise in all sorts of applications including scheduling optimization communications and the design and analysis of algorithms In the next few lectures we ll even show how two Stanford stu dents used graph theory to become multibillionaires
Suppose W is a walk from vertex a to vertex b and that W minimises over all walks from a to b Then W is a path Proof Suppose W a a0 a1 ak b and ai aj where 0 i j k Then W a0 a1 ai aj 1 ak is also a walk from a to b and W W j i W contradiction Find an original example of a graph whose chromatic number does not equal its clique number yet whose clique partition number equals its independence number Chromatic number chi G is the m
Graph Chart Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
https://www.publicdomainpictures.net/pictures/140000/velka/graph-chart-1447781098d6A.jpg

Graph Theory Concepts
https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:2400/1*G5P1Vl5Y33iogqErs0JMmg.jpeg
w g graph theory - Given a graph G itsline graph or derivative L G is a graph such that i each vertex of L G represents an edge of G and ii two vertices of L G are adjacent if and only if their corresponding edges share a common endpoint are incident in G Fig