sin angle sum identity The sine and cosine angle addition identities can be compactly summarized by the matrix equation 7 These formulas can be simply derived using complex exponentials and the Euler formula as follows Equating real and imaginary parts then gives 1 and 3 and 2 and 4 follow immediately by substituting for
A2 c2 b2 c2 c2 c2 This can be simplified to a c 2 b c 2 1 a c is Opposite Hypotenuse which is sin b c is Adjacent Hypotenuse which is cos So a c 2 b c 2 1 can also be written sin 2 cos 2 1 Note sin2 means to find the sine of then square the result but We can use the sum and difference formulas to identify the sum or difference of angles when the ratio of sine cosine or tangent is provided for each of the individual angles To do so we construct what is called a reference triangle to help find each component of the sum and difference formulas
sin angle sum identity
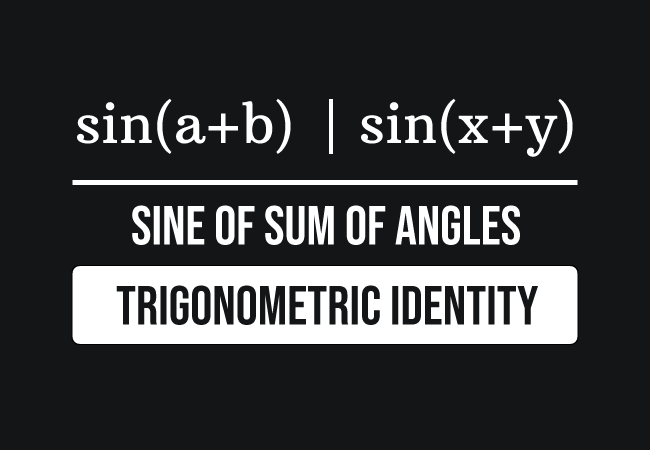
sin angle sum identity
https://www.mathdoubts.com/cimgs/trigonometry/identities/sin-angle-sum.png

Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
http://www2.clarku.edu/~djoyce/trig/sumformulas.jpg

Illustration Of Angle Addition Formulae For The Sine And Cosine
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/df/ef/41/dfef41af1a9a1672d22a370acfc42044.png
A cos b cos a sin b 2 sin x y sin x cos y cos x sin y 3 sin sin cos cos sin Constructing a Triangle with sum of Two angles D C E is a right triangle and its angle is divided as two angles to derive a trigonometric identity for the sine of sum of two angles 1 Basic and Pythagorean Identities csc x dfrac 1 sin x csc x sin x 1 sin x dfrac 1 csc x sin x csc x 1 sec x dfrac 1 cos x sec x cos x 1 cos x dfrac 1 sec x cos x sec x 1 cot x dfrac 1 tan x dfrac cos x sin x cot x tan x 1 sin x cos x
Define c a pi 2 and d b pi 2 c and d are acute angles Theorem sin c d sin c cos d cos c sin d angle addition formula for sin Substitute sin a pi 2 b pi 2 sin a pi 2 cos b pi 2 cos a pi 2 sin b pi 2 Simplify sin a pi 2 b pi 2 sin a b pi Sin 2 x cos 2 2 x cos x so sin 2 x cos x The two identities cos 2 x sin x and sin 2 x cos x are called cofunction identities These two cofunction identities show that the sine and cosine of the acute angles in a right triangle are related in a particular way
More picture related to sin angle sum identity
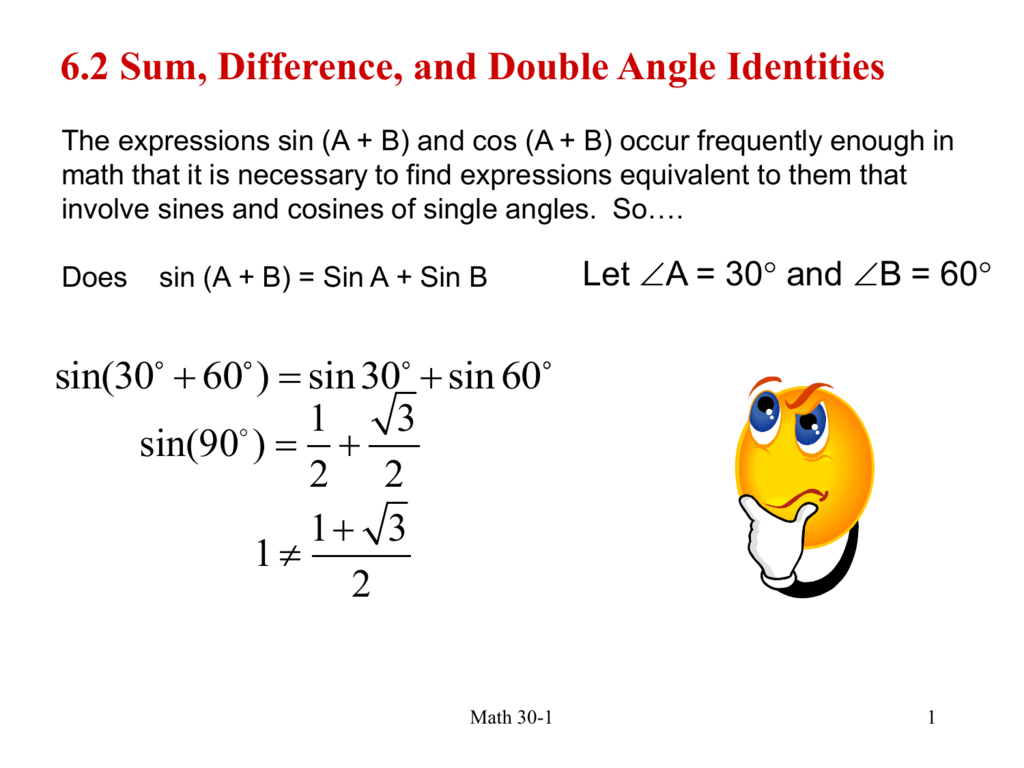
6 2 Sum Difference And Double Angle Identities
https://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009458429_1-ccf3691144124be9186c277e1733d726.png

Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
https://aleph0.clarku.edu/~djoyce/trig/complementary.jpg

Trigonometric Sum Identities Proof
https://i.stack.imgur.com/czRqF.png
You ll learn how to use trigonometric functions their inverses and various identities to solve and check equations and inequalities and to model and analyze problems involving periodic motion sound light and more Therefore the above formulas give us the sin and cos difference identities sin sin cos cos sin cos cos cos sin sin When we look at the sum or difference formulas we see that the only thing changing is the sign in one of the summands
Here is an example of using a sum identity Find sin15 If we can find think of two angles A and B whose sum or whose difference is 15 and whose sine and cosine we know sin A B sinAcosB cosAsinB We might notice that 75 60 15 so sin15 sin 75 60 sin75 cos60 cos75 sin60 BUT we don t know sine and cosine of 75 Sin sin cos cos sin sin sin cos cos sin sin sin cos cos sin sin sin cos cos sin We can rewrite each using the sum and difference formulas

Free Course Sum And Difference Identities And Formulas Sine Cosine
https://d3f1iyfxxz8i1e.cloudfront.net/courses/course_image/e4ce96a65e8a.jpg
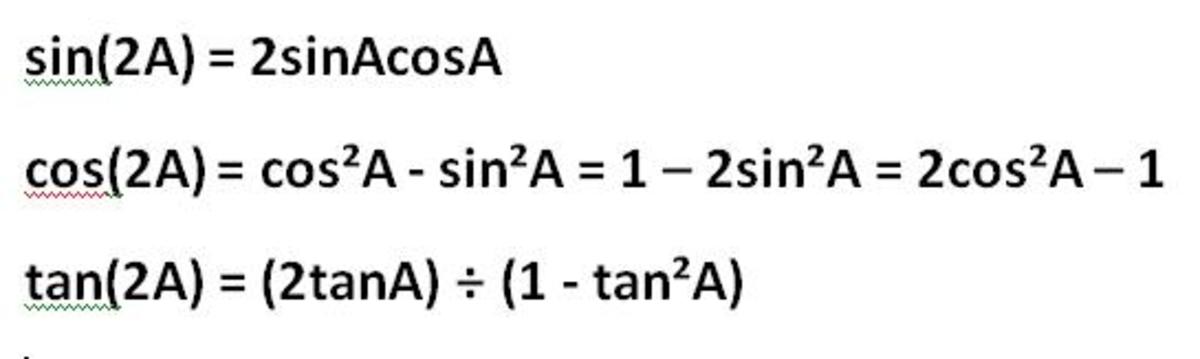
The Double Angle Identities Sin2A Cos2A And Tan 2A Derived From The
https://images.saymedia-content.com/.image/t_share/MTc2Mjg5NDEyNzM5NzAzOTgx/the-double-angle-identities-sin2a-cos2a-and-tan-2a-derived-from-the-trigonometric-addition-formulas.jpg
sin angle sum identity - A cos b cos a sin b 2 sin x y sin x cos y cos x sin y 3 sin sin cos cos sin Constructing a Triangle with sum of Two angles D C E is a right triangle and its angle is divided as two angles to derive a trigonometric identity for the sine of sum of two angles 1