raid 0 1 2 3 4 5 The following list explains the standard RAID levels 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 and popular non standard and hybrid options RAID 10 RAID 0 Striping RAID 0 also known as a striped set or a striped volume requires a minimum of two disks The disks are merged into a single large volume where data is stored evenly across the number of disks in
RAID levels 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 1 0 features explained in detail GoLinuxHub April 9 2014 by golinuxhub What is RAID RAID stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks which was later interpreted to Redundant Array of Independent Disks RAID 0 is based on data striping A stream of data is divided into multiple segments or blocks and each of those blocks is stored on different disks So when the system wants to read that data it can do so simultaneously from all the disks and join them together to reconstruct the entire data stream
raid 0 1 2 3 4 5

raid 0 1 2 3 4 5
https://4.bp.blogspot.com/-Fn37Q_osRYk/Va5GmmN5yTI/AAAAAAAABfs/bKONfiNKK3o/s1600/RAID_0.png
Best RAID Guide In 2020 RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 3 RAID 5 RAID 6 And
https://www.hifireport.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/raid10.png

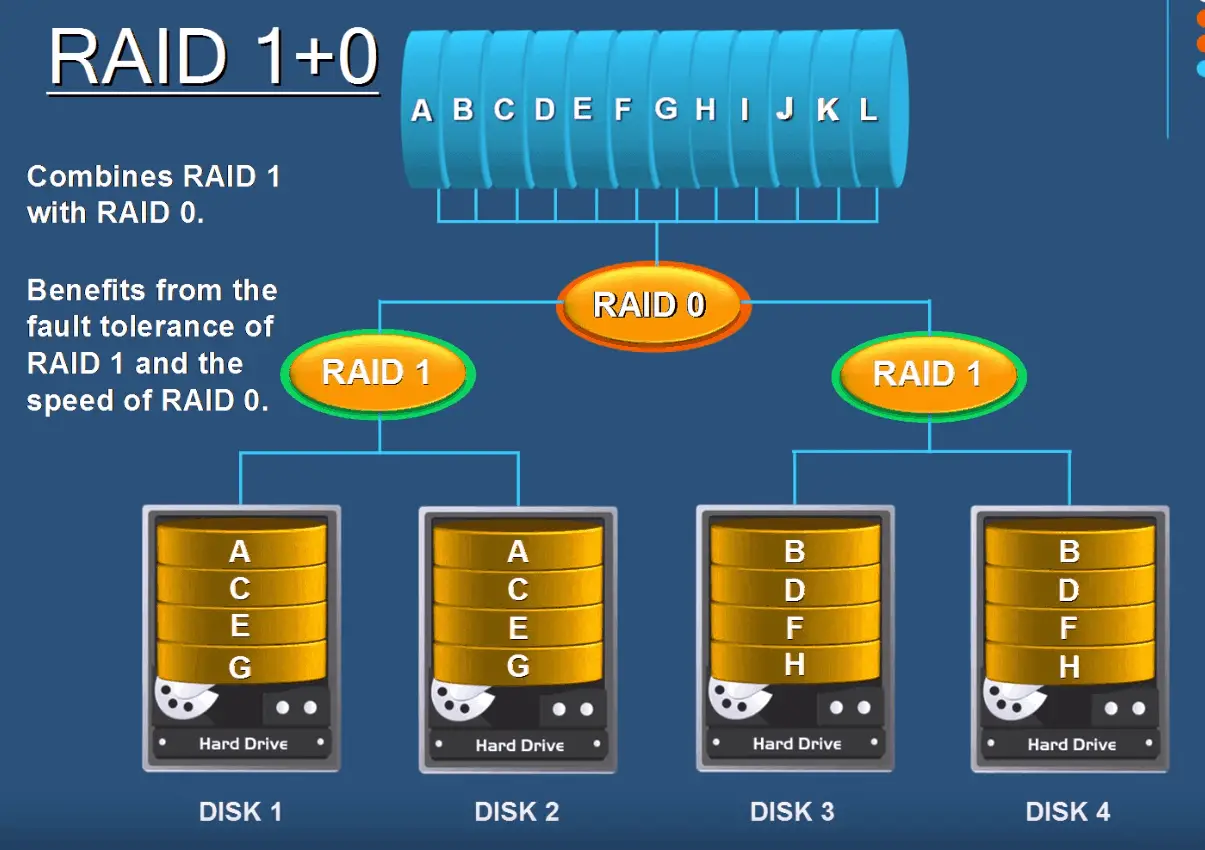
RAID Levels 0 1 4 5 6 10 Explained Boolean World
https://www.booleanworld.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/raid-cover.jpg
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive or sometimes Independent Disks In general a RAID enabled system uses two or more hard disks to improve the performance or provide some level RAID 0 Disk striping RAID 1 Disk mirroring RAID 1 0 Disk mirroring and striping RAID 2 Striping and Hamming code parity RAID 3 Parity disk RAID 4 Parity disk and block level striping RAID 5 Disk striping with parity RAID 5 0 Disk striping and distributed parity RAID 6 Disk striping with double parity
Redundant Array of Independent Disks RAID is a storage technology that creates a data loss fail safe by merging two or more hard disk drives HDDs or solid state drives SSDs into one cohesive storage unit or array The most commonly used levels are RAID 0 1 5 6 and 10 RAID 0 1 and 5 work on both HDD and SSD media RAID levels 4 and 6 also work on both media but are rarely seen in practice RAID 4 has slow write speeds because of parity as does RAID 6 when performing intensive write operations
More picture related to raid 0 1 2 3 4 5
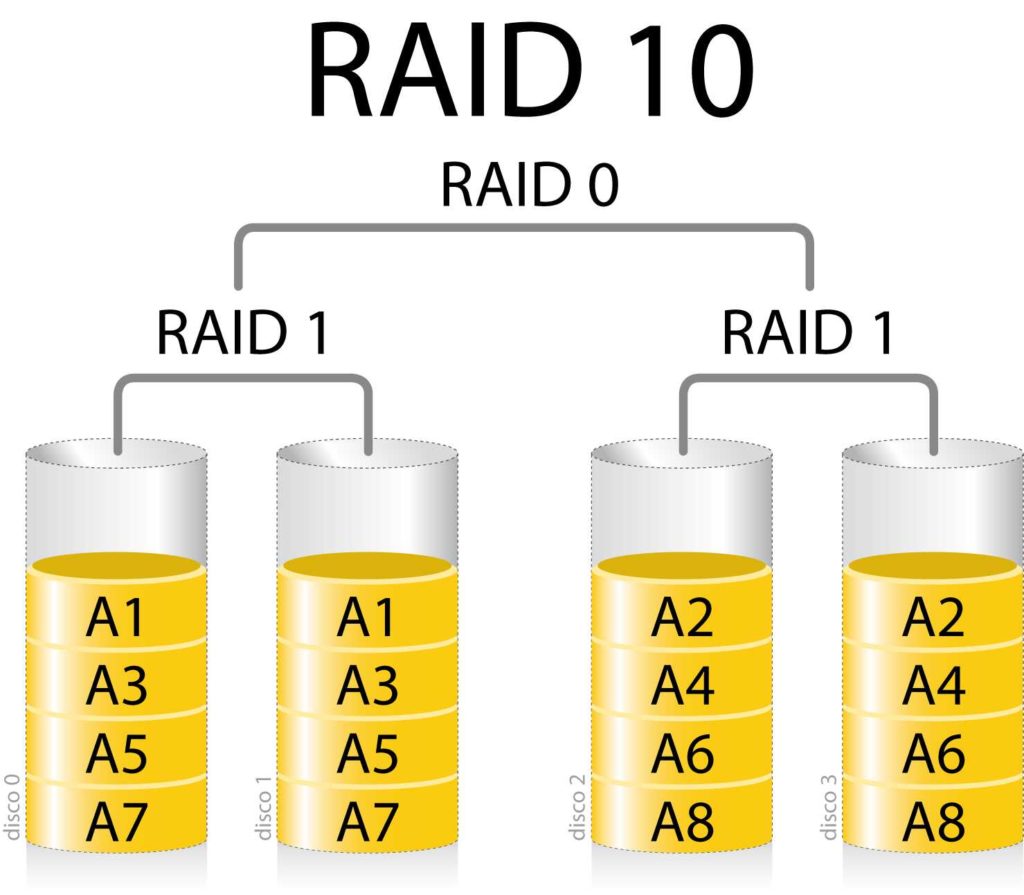
RAID 0 Vs RAID 1 Maximizing Performance Or Ensuring Data Safety
https://readus247.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Raid10.jpg
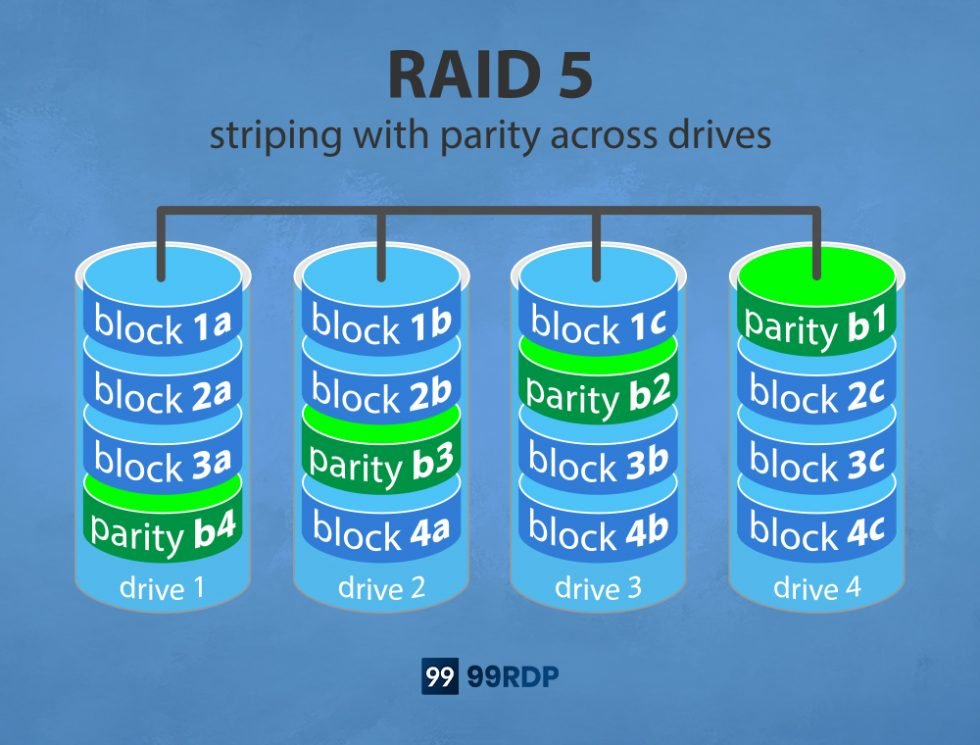
Quick Guide To RAID And Distinct Types RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 5 RAID 6
https://99rdp.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Raid-5-980x745.jpg

Data Recovery From RAID 5 Alandata Data Recovery
http://alandata.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/Raid5.jpg
The original paper that put together this term defined six levels starting from 0 to 5 Over the years other RAID levels such as RAID 6 and RAID 10 have been added and some organizations even prefer to combine the role of two or more RAID levels to get the functionality they want 3 1 Level 0 Stripping In a RAID 0 system data is split up into blocks These blocks are written across all of the drives simultaneously By using multiple disks at least two at the same time this offers better I O performance Furthermore it uses all the disks storage and is easy to implement due to its simplicity
[desc-10] [desc-11]

Hardware RAID Vs Software RAID Pros And Cons For Each
https://techgenix.com/tgwordpress/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/raid-0-vs-raid-1-1024x681.png

AHCI Vs RAID Storage Types Differences And Comparison
https://cdn.appuals.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/raid-5-volume.png
raid 0 1 2 3 4 5 - [desc-14]