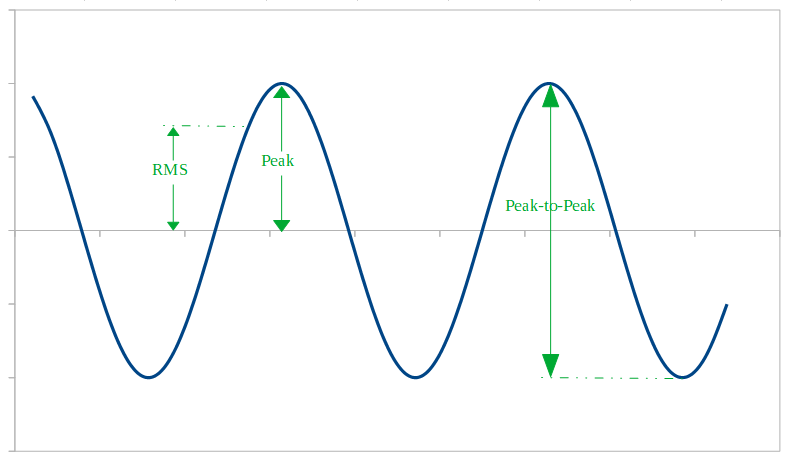
one cycle of a sine wave always has The peak value is 4 volts and the peak to peak value is 8 volts typically abbreviated as 8 V pp The period of one cycle is 0 2 seconds or T 200 milliseconds Further the frequency f 1 200 milliseconds or 5 Hz 5 cycles in one second AC waveforms may also be combined with a DC offset
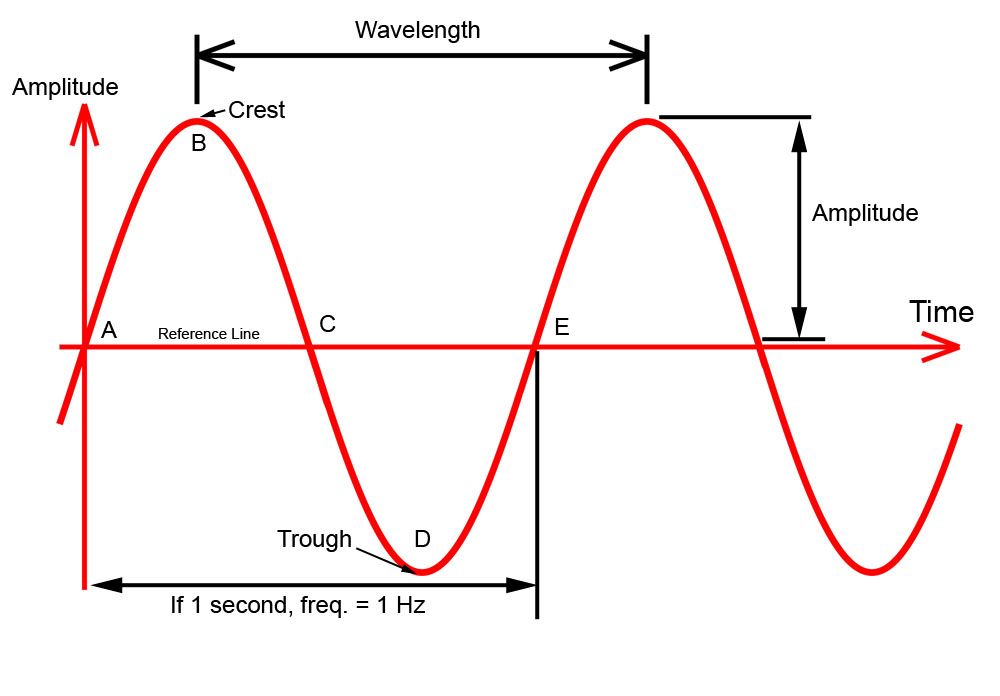
You are partially correct the period is the length on the x axis in one cycle However the amplitude does not refer to the highest point on the graph or the distance from the highest point to the x axis Notice that the wavelength is the distance through which the sine function completes one full cycle The crest and the trough of a wave are the locations of the maximum and minimum displacements as seen in figure 1 2
one cycle of a sine wave always has
one cycle of a sine wave always has
https://www.herramientasingenieria.com/onlinecalc/electronics/rms-value/curve_english.png

Is The Amplitude Of A Sine Wave Increasing Or Decreasing In This Phase
https://i.stack.imgur.com/TsppO.png
Sine Wave Mathematical Mysteries
https://mathematicalmysteries.files.wordpress.com/2021/11/sinewave.jpg
Sine cycles between 1 and 1 It starts at 0 grows to 1 0 max dives to 1 0 min and returns to neutral I also see sine like a percentage from 100 full steam ahead to 100 full retreat Sin w t In this formula the amplitude is A In electrical voltage measurements amplitude is sometimes used to mean the peak to peak voltage V pp This number will be twice the mathematical amplitude If this was a sound wave the higher the amplitude the louder the sound Frequency
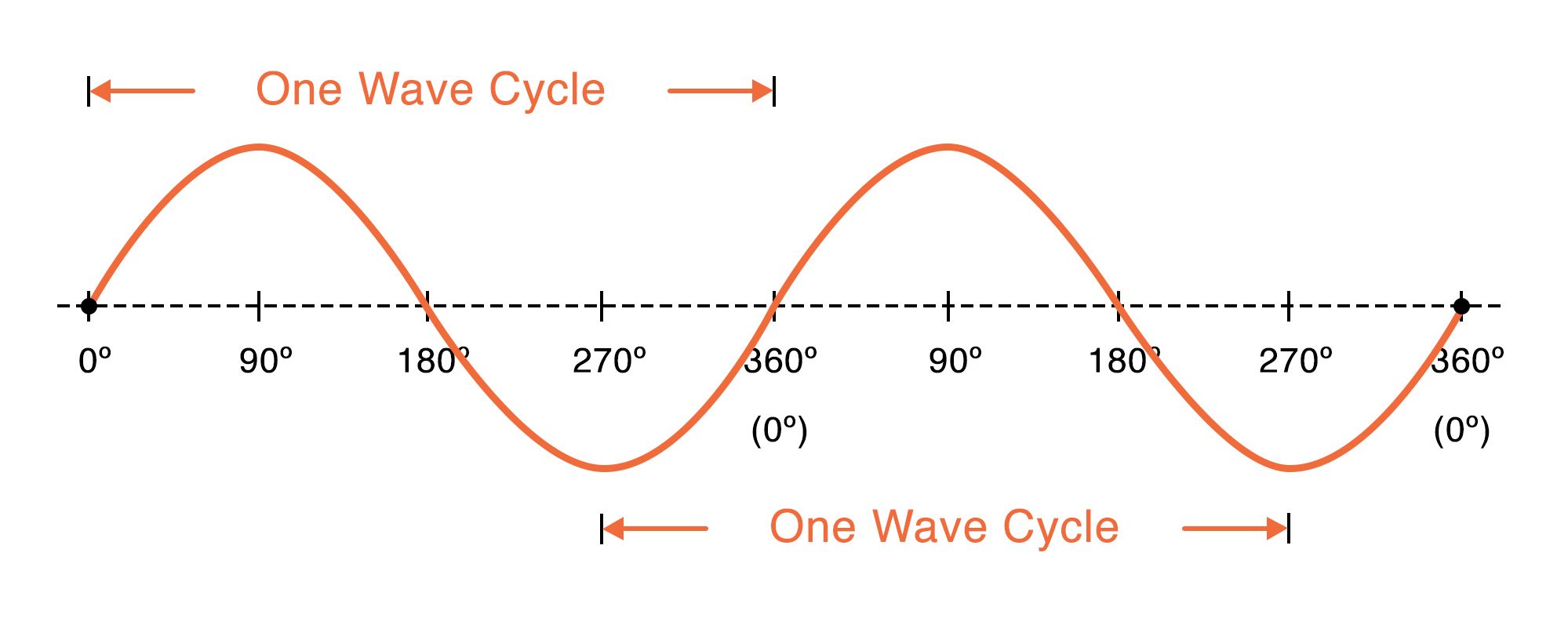
The complete positive and negative portion of the wave is one cycle of the sine wave Time is designated by t The time taken for any wave to complete one full cycle is called the period T In general any periodic wave constitutes a number of such cycles In sinusoidal waves the period represents the duration it takes for one complete cycle of the wave to occur The period cannot be negative because it is a measure of time and time cannot be negative in the physical sense
More picture related to one cycle of a sine wave always has
Sine Sin And Medi sin
https://d10j3mvrs1suex.cloudfront.net/u/473653/d1b5647566c3f55a7194776e2ebf5d8ba02c0552/original/3-3-characteristics-of-sinusoidal-signals1.jpg/!!/meta:eyJzcmNCdWNrZXQiOiJiemdsZmlsZXMifQ==/b:W10=.jpg

Sinusoidal Waveform Or Sine Wave In Electricity Electrical Academia
https://electricalacademia.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/2-5.gif
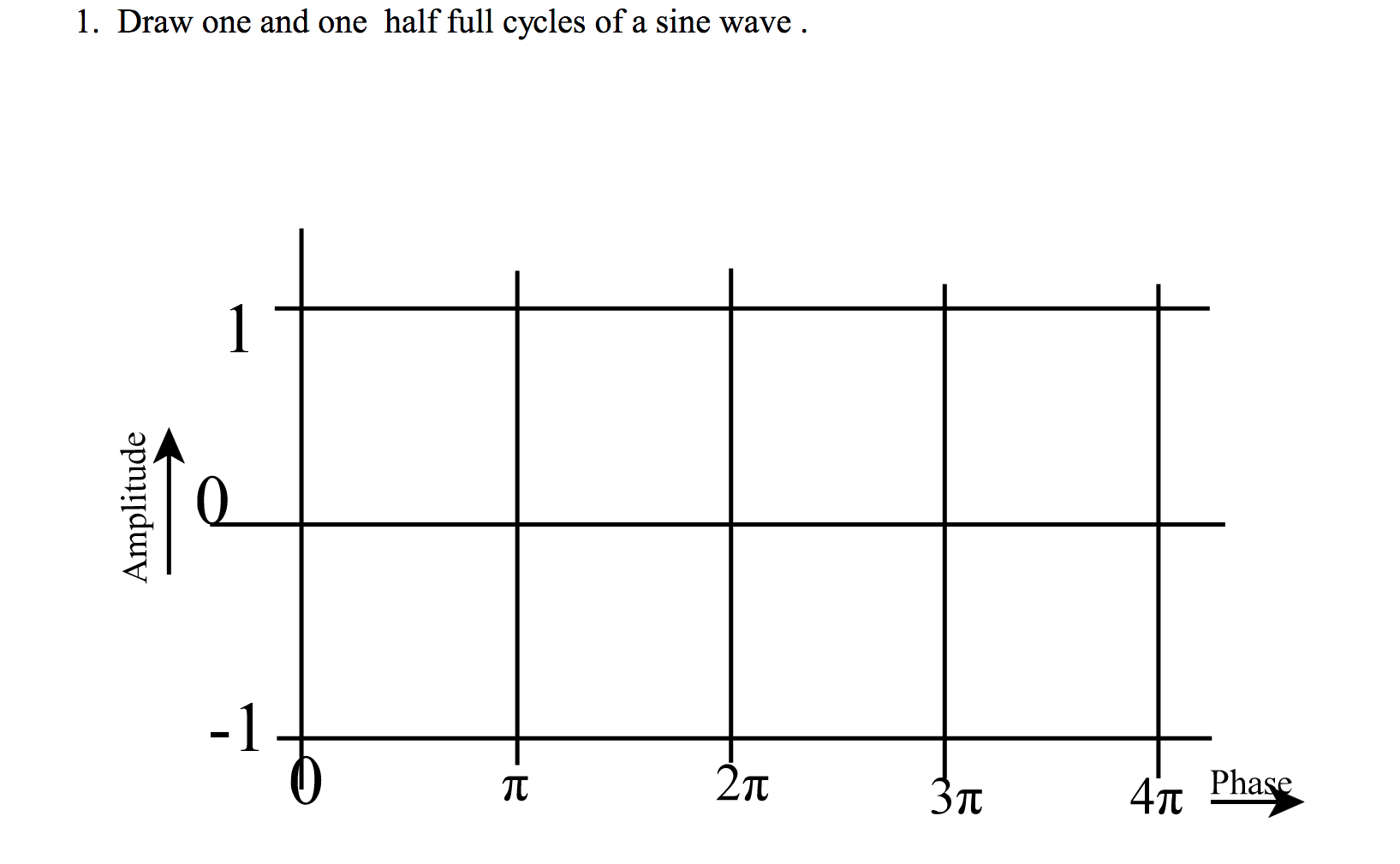
Solved 1 Draw One And One Half Full Cycles Of A Sine Wave Chegg
https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/354/35494da9-6d26-4c90-a6f2-2400c105f52f/phpKCudFi.png
The time it takes to complete on cycle is called the Period and is denoted with the symbol T T for Time In the example above the Period is 10 milliseconds or T 10 ms The reciprocal of the Period is the Frequency f Thus f 1 T The frequency indicates how many cycles exist in one second Period of tan and cot occurs twice as frequently as sin cos because tan is slope and when you travel halfway pi radians around the unit circle you encounter another point on the same line same slope
The graph of y sin color Cerulean 2 t has one complete cycle over the interval 0 pi and so its period is P pi dfrac 2 pi color Cerulean 2 Some functions like Sine and Cosine repeat forever and are called Periodic Functions The Period goes from one peak to the next or from any point to the next matching point The Amplitude is the height from the center line to the peak or to the trough Or we can measure the height from highest to lowest points and divide that by 2
Symmetry Free Full Text Nonlinear Transformation Of Sine Wave
https://pub.mdpi-res.com/symmetry/symmetry-14-00668/article_deploy/html/images/symmetry-14-00668-g006.png?1648128028

Inverters For Green Energy Systems Power Electronic Tips
https://www.powerelectronictips.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Waveform-comparison-1.jpg
one cycle of a sine wave always has - The complete positive and negative portion of the wave is one cycle of the sine wave Time is designated by t The time taken for any wave to complete one full cycle is called the period T In general any periodic wave constitutes a number of such cycles