natural logarithm rules and examples Rules The natural logarithm follows all the properties of the logarithm Product Rule ln xy lnx lny Example ln 10 ln 5 ln 2 Quotient Rule ln left dfrac x y right ln x ln y Example ln left dfrac 42 5 right ln 42 ln 5 Power Rule ln x n n lnx Example ln 5z 7 7 ln 5z Change of Base Rule
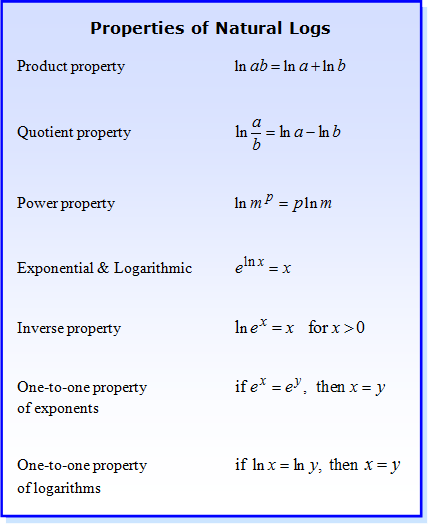
We have eleven main laws of natural logarithms With these eleven laws we can expand natural logarithms condense them and solve logarithmic equations Although these laws are specified for natural logarithms the laws of logarithms apply to logarithms of any base Natural logarithm is mostly used in pure mathematics such as calculus The basic properties of natural logarithms are same as the properties of all logarithms Product Rule ln ab ln a ln b Quotient Rule ln a b ln a ln b Reciprocal Rule ln 1 a ln a Power Rule ln a b b ln a
natural logarithm rules and examples

natural logarithm rules and examples
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/cd/dd/cc/cdddccd06a2a60c75a30b5a30a82bd50.gif

Integral Of Natural Log Logarithms Definition Calculus How To
https://www.calculushowto.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/natural-log.jpg

Logarithm Rules And Examples Physics Chemistry Math Biology
https://3.bp.blogspot.com/-75NssZ_yhKI/W9C8ERVwCtI/AAAAAAAACkM/s-8dsCfDldkrfCn_3RzCpgdWGd2pxG7_wCLcBGAs/s1600/Logarithm-Rules.png
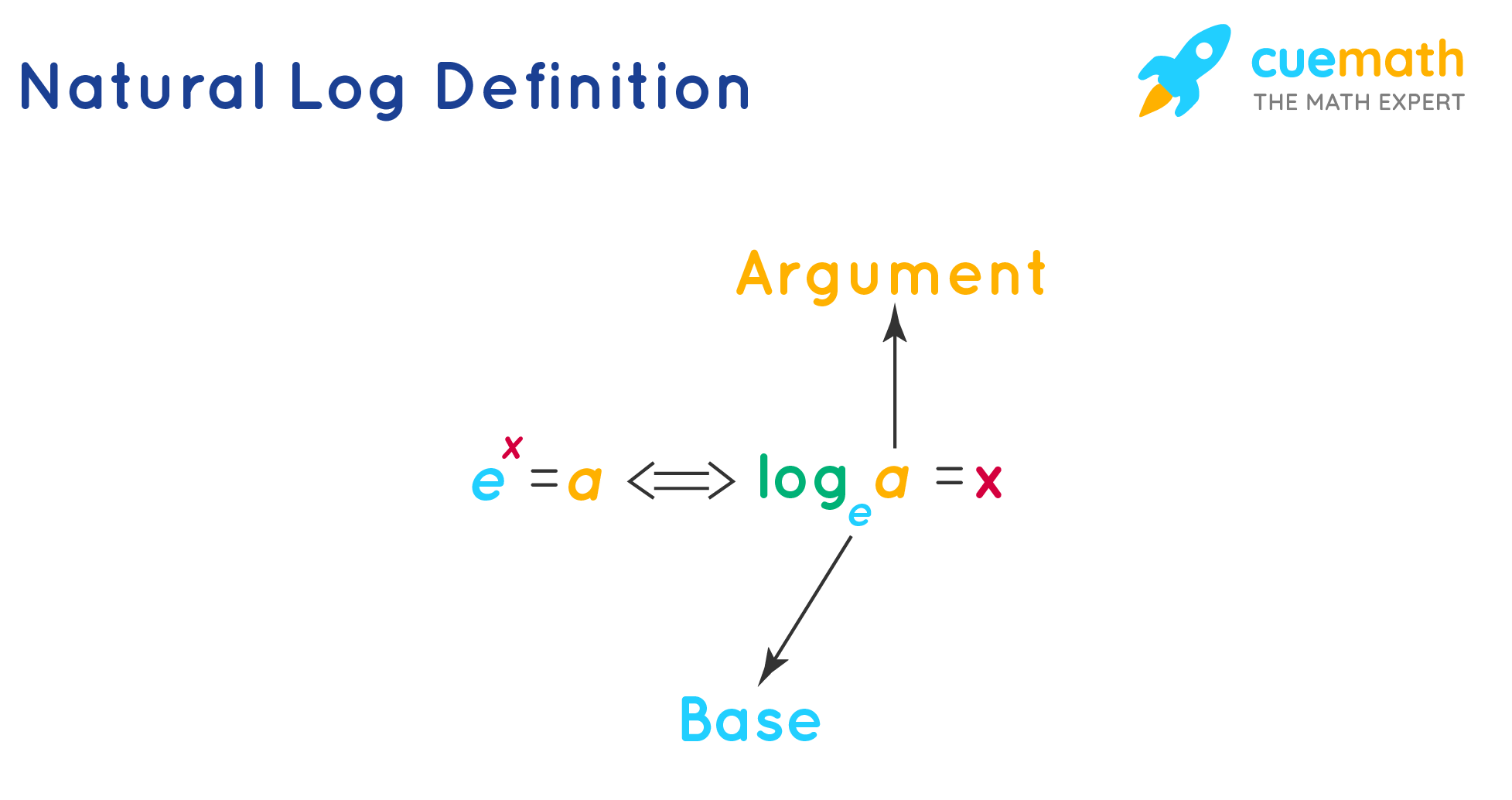
Logb x n or bn x Where b is the base of the logarithmic function This can be read as Logarithm of x to the base b is equal to n In this article we are going to learn the definition of logarithms two types of logarithms such as common logarithm and natural logarithm and different properties of logarithms with many solved examples The natural logarithm of x is the power to which e would have to be raised to equal x For example ln 7 5 is 2 0149 because e 2 0149 7 5 The natural logarithm of e itself ln e is 1 because e 1 e while the natural logarithm of 1 is 0 since e 0 1
Natural Logarithm Natural logarithm is nothing but log with base e That is a natural log means log e But it is not usually represented as log e Instead it is represented as ln i e log e ln Examples e x 2 log e 2 x or ln 2 x e x 7 log e 7 x or ln 7 x Common Logarithm Common logarithm is nothing but log 16 4 Both equations describe the same relationship between the numbers 2 4 and 16 where 2 is the base and 4 is the exponent The difference is that while the exponential form isolates the power 16 the logarithmic form isolates the exponent 4 Here are more examples of equivalent logarithmic and exponential equations
More picture related to natural logarithm rules and examples

Logarithm Rules video Lessons Examples And Solutions
https://www.onlinemathlearning.com/image-files/logarithm-rules.png
200 Y e x Inverse Function 192539 Inverse Function Of Y E X
https://virtuallearningacademy.net/VLA/LessonDisplay/Lesson6230/def1.png
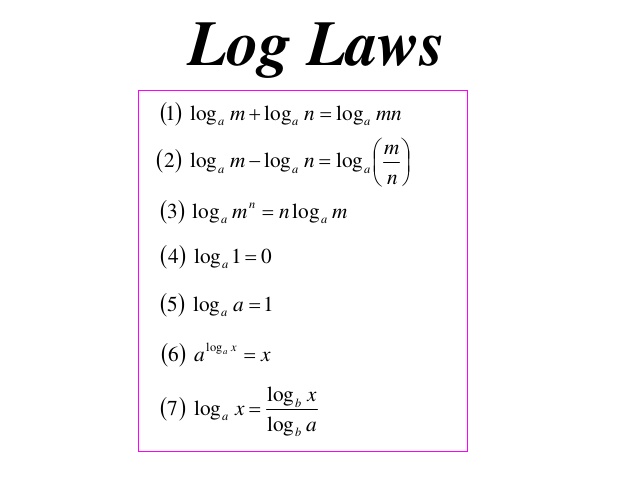
Exercise 3BLogarithms And Laws Of Logarithms Mathematics Tutorial
http://doylemaths.weebly.com/uploads/4/7/0/6/47063657/4908269_orig.jpg
The natural logarithm function is defined by ln x Integral on the interval 1 x of 1 x dt t for x 0 therefore the derivative of the natural logarithm is d dx ln x 1 x The natural logarithm is one of the most useful functions in mathematics with applications throughout the physical and biological sciences Natural logarithms can also be evaluated using a scientific calculator By definition ln Y X Y e X Using a calculator we can use common and natural logarithms to solve equations of the form a x b especially when b cannot be expressed as a n Example Solve the equations a 6 x 2 21 b e 2x 9 Solution a 6 x 2 21
Rule 1 Product Rule The logarithm of the product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors Rule 2 Quotient Rule The logarithm of the ratio of two quantities is the logarithm of the numerator minus the logarithm of the denominator Rule 3 Power Rule The logarithm of an exponential number is the exponent times the logarithm of the base All logarithm rules are mentioned below Going forward we will see how each of these rules is derived using the exponent rules Natural Log Rules A natural log is a logarithm with the base e It is denoted by ln i e log e ln i e we do NOT write a base for the natural logarithm
What Is Natural Log Formula Examples
https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/natural-log-definition-1618943966.png
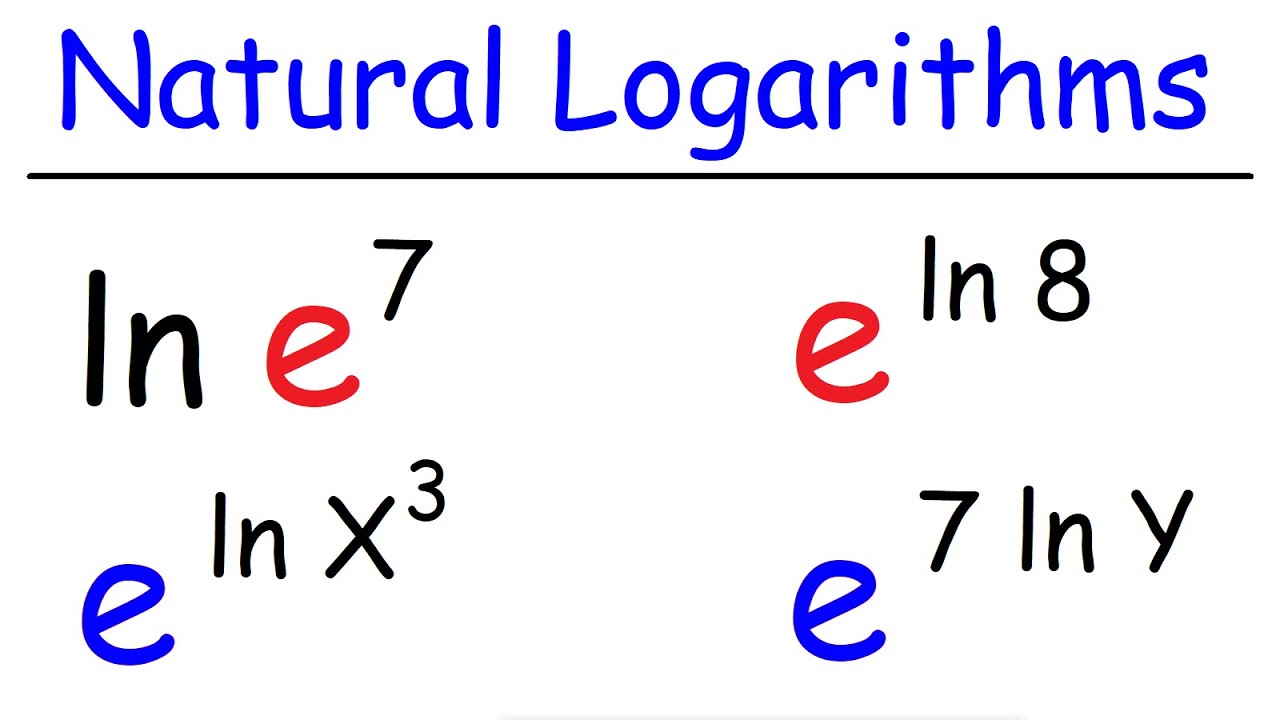
Natural Logarithms YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/daUlTsnCNRQ/maxresdefault.jpg
natural logarithm rules and examples - Logb x n or bn x Where b is the base of the logarithmic function This can be read as Logarithm of x to the base b is equal to n In this article we are going to learn the definition of logarithms two types of logarithms such as common logarithm and natural logarithm and different properties of logarithms with many solved examples