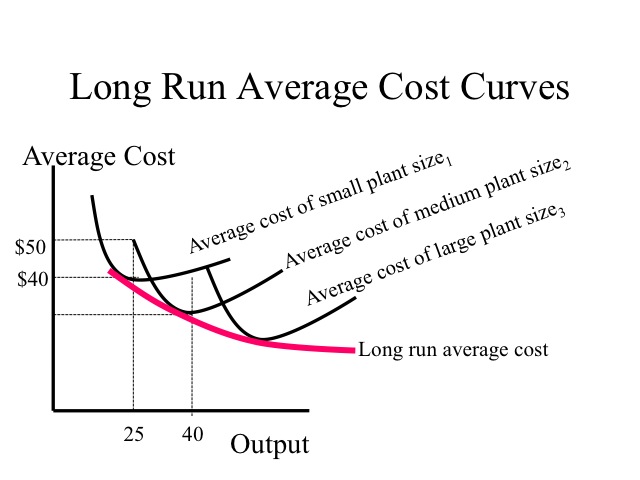
long run average cost curve for a natural monopoly Long run average costs in monopoly It is assumed monopolies have a degree of economies of scale which enables them to benefit from lower long run average costs In a competitive market firms
For a natural monopoly the long run average cost curve LRAC falls continuously over a large range of output The result may be that there is only room in a market for one firm to fully exploit the In a natural monopoly the LRAC of any one firm intersects the market demand curve where long run average costs are falling or are at a minimum If this is the case one firm in the industry will expand to
long run average cost curve for a natural monopoly

long run average cost curve for a natural monopoly
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vI1L5vV1aKQ/maxresdefault.jpg
ECON 150 Microeconomics
http://courses.byui.edu/ECON_150/ECON_150_Old_Site/images/6-3_LR_Costs_03.jpg

Economies Of Scale And Natural Monopoly In This Market The Demand
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344380378/figure/fig1/AS:939738085195777@1601062427534/Economies-of-Scale-and-Natural-Monopoly-In-this-market-the-demand-curve-intersects-the.jpg
A natural monopoly is a special case where one large business can supply the entire market at a lower long run average cost contrasted with multiple providers Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The figure below shows the demand curve and the long run average cost curve for an electric company
A natural monopoly will maximize profits by producing at the quantity where marginal revenue MR equals marginal costs MC and by then looking to the market demand curve to see what price to charge for this quantity In this short video we work through the shape of the long run average cost curve for a natural monopoly economics monopoly
More picture related to long run average cost curve for a natural monopoly
ECON 150 Microeconomics
https://courses.byui.edu/econ_150/econ_150_old_site/images/6-3_LR_Costs_05.jpg
Solved 3 Natural Monopoly Analysis The Following Graph Gives The
https://www.coursehero.com/qa/attachment/38118684/
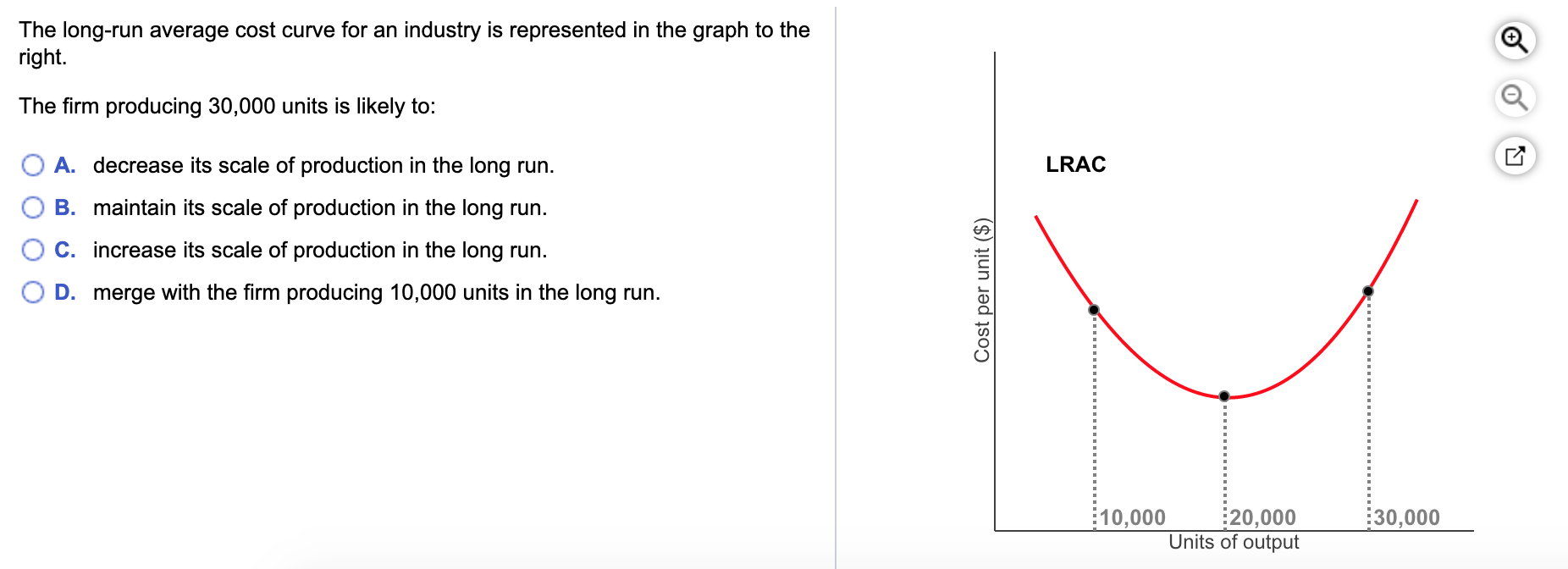
Solved The Long run Average Cost Curve For An Industry Is Chegg
https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/8ae/8ae0521a-264a-4363-b697-4ba7fa413495/phpAGh2GN.png
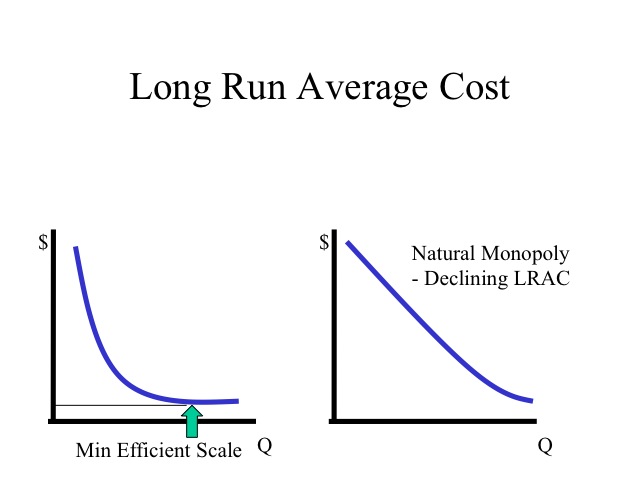
The long run average cost LRAC curve shows the lowest cost for producing each quantity of output when fixed costs can vary and so it is formed by the bottom edge of the family A natural monopoly occurs when the quantity demanded is less than the minimum quantity it takes to be at the bottom of the long run average cost curve Economists call this
Reason A natural monopoly occurs when the quantity demanded is less than the minimum quantity it takes to be at the bottom of the long run average cost curve Marginal revenue marginal cost average cost When a natural monopoly exists in a given industry the per unit costs of production will be lowest when a single firm generates the entire output of the industry The typical pattern
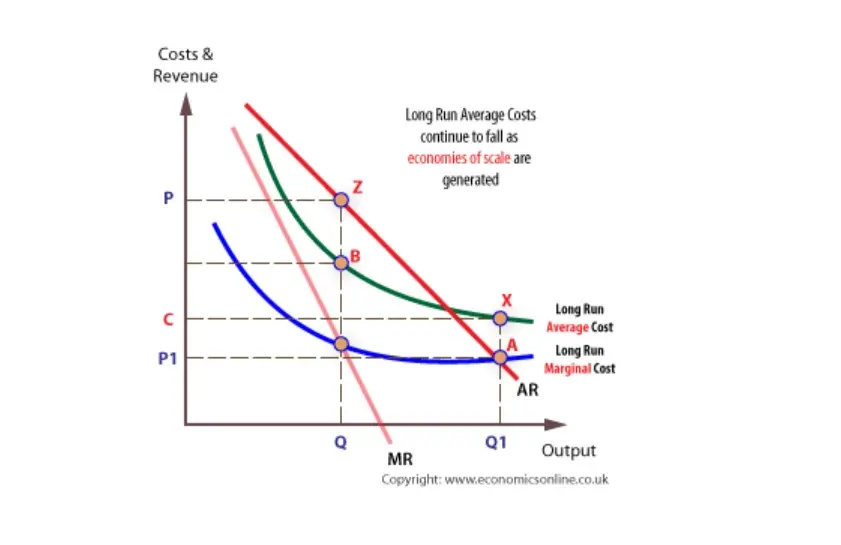
Natural Monopolies
https://www.economicsonline.co.uk/content/images/2021/10/20-2.webp
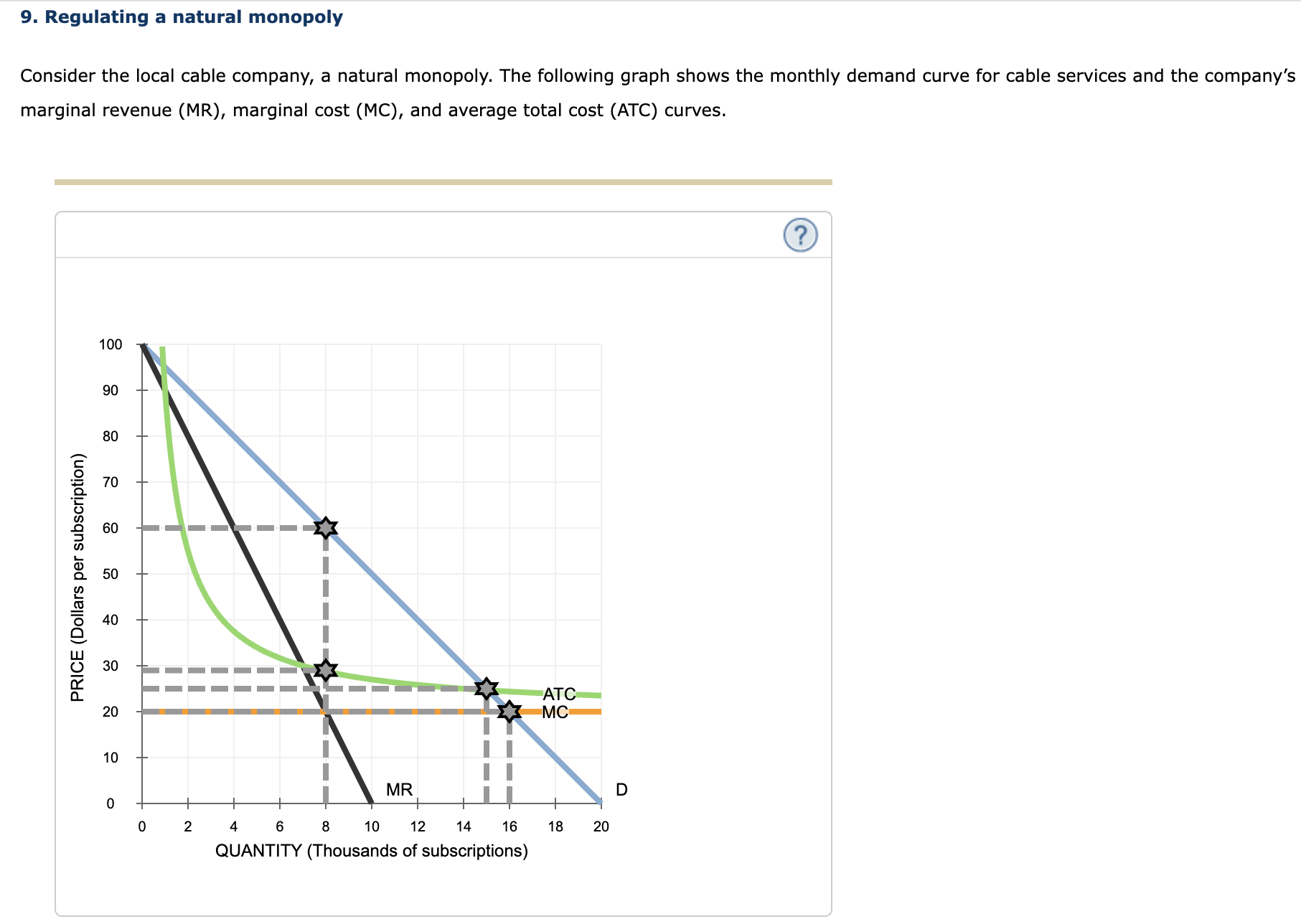
Solved 9 Regulating A Natural Monopoly Consider The Local Chegg
https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/23f/23f787f7-89c0-445d-988b-1f8a56405b55/php7dukZA
long run average cost curve for a natural monopoly - A natural monopoly is a special case where one large business can supply the entire market at a lower long run average cost contrasted with multiple providers