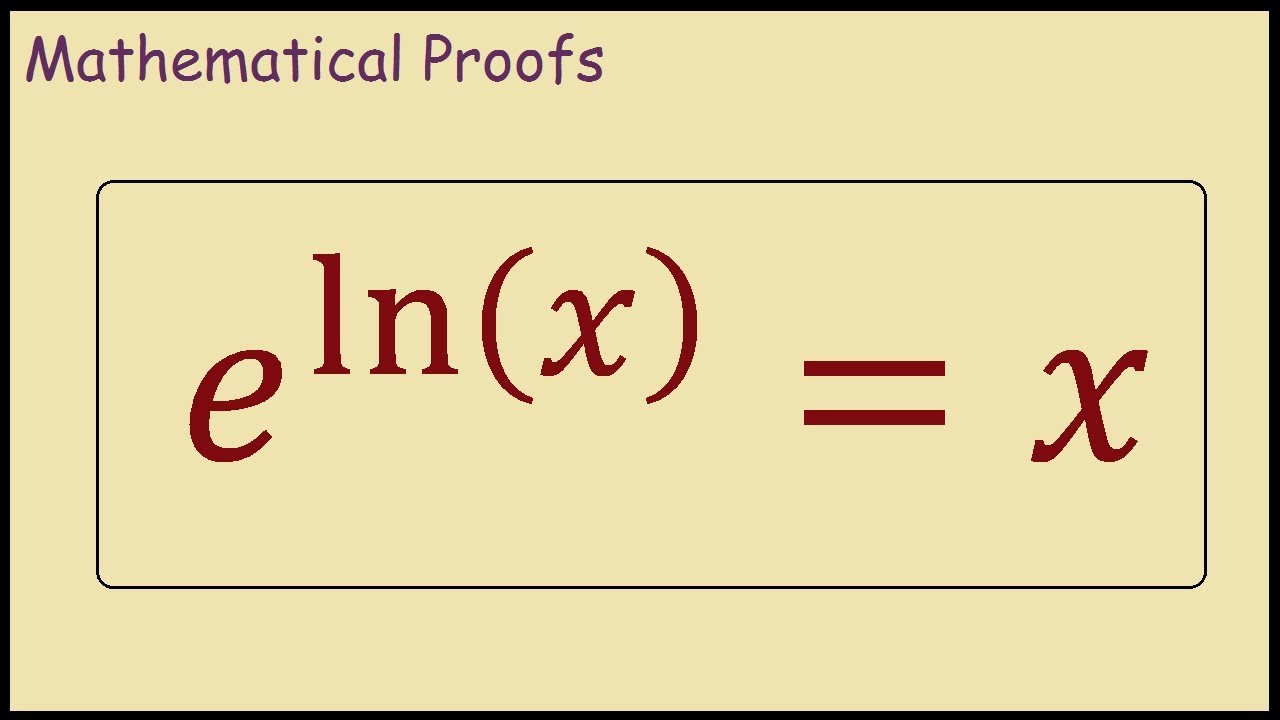
ln 1 equals Ln of 1 ln 1 0 ln of Infinity ln ln of e ln e 1 ln of e raised to the x power ln e x x e raised to the ln power e ln x x
The following are the rules of ln ln 1 0 ln e 1 ln m ln n ln mn ln m ln n ln m n ln a m m ln a e ln x x What are Log Derivative Rules Here are the derivatives of different types of logarithms The derivative of ln x is d dx ln x 1 x The derivative of log a x d dx log x 1 x ln a What are 4 Important Ln e 1 ln 1 1 As x approaches 0 ln x approaches As x approaches ln x approaches Natural logarithm rules properties Natural logarithms share the same basic logarithm rules as logarithms with other bases Product rule ln mn ln m ln n for x 0 and y 0 Quotient rule ln ln m ln n Power rule ln m n
ln 1 equals
ln 1 equals
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/HL6AWNjVOnU/maxresdefault.jpg
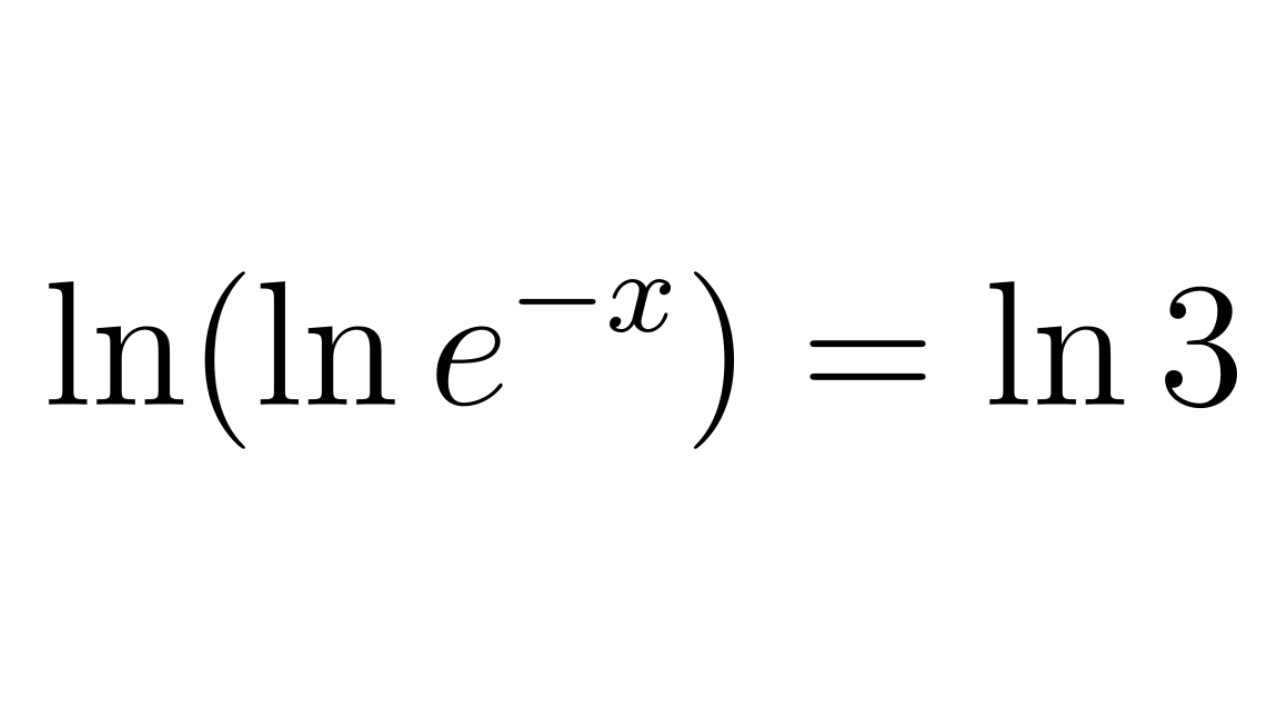
Solve The Logarithmic Equation Ln ln e x Ln 3 YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/2ZgWQwZaHqs/maxresdefault.jpg
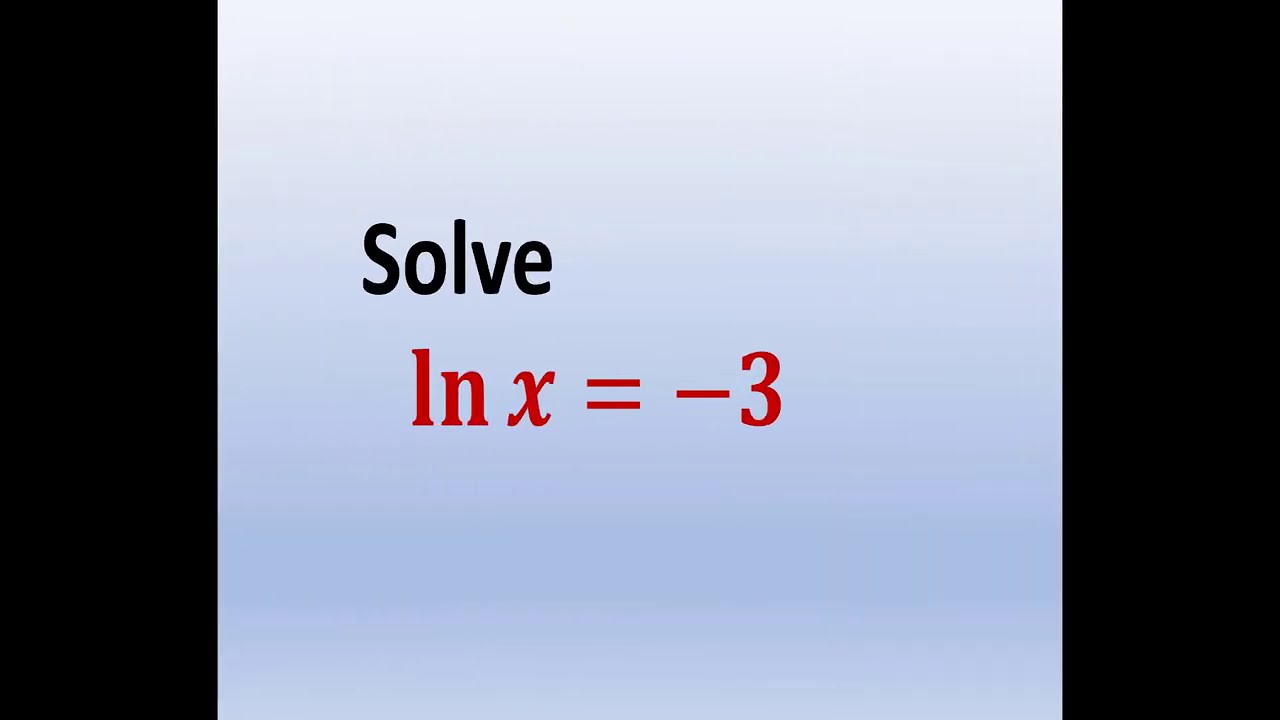
How Do You Solve Ln Equations For X How To Solve Ln X Is Equal To
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/KELVuurdy6o/maxresdefault.jpg
Natural Logarithm Calculator The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant e where e is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to 2 718281828459 The natural logarithm of x is the power to which e would have to be raised to equal x For example ln 7 5 is 2 0149 because e2 0149 7 5 The natural logarithm of e itself ln e is 1 because e1 e while the natural logarithm of 1 is 0 since e0 1
For problems that add subtract to from the x simply solve for the exponent by using ln In the example you gave e x 4 2 x 4 ln 2 x ln 2 4 An example for division e x 5 2 Same thing as before Use the ln x 5 ln 2 x 5 ln 2 For your last example let s equate it to some constant just for the sake of clarity Logarithms like exponents have many helpful properties that can be used to simplify logarithmic expressions and solve logarithmic equations This article explores three of those properties Let s take a look at each property individually The product rule log b M N log b M log b N
More picture related to ln 1 equals
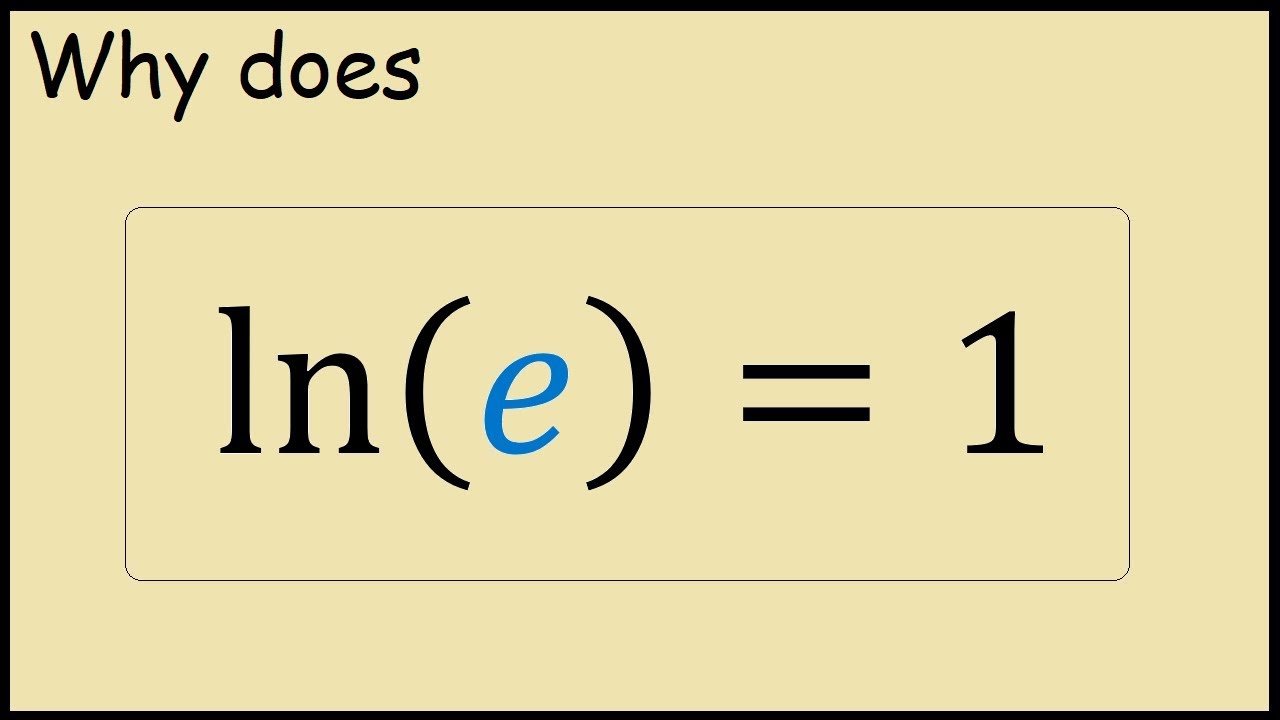
Ln E Hot Sex Picture
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ARXQQxlUAbs/maxresdefault.jpg
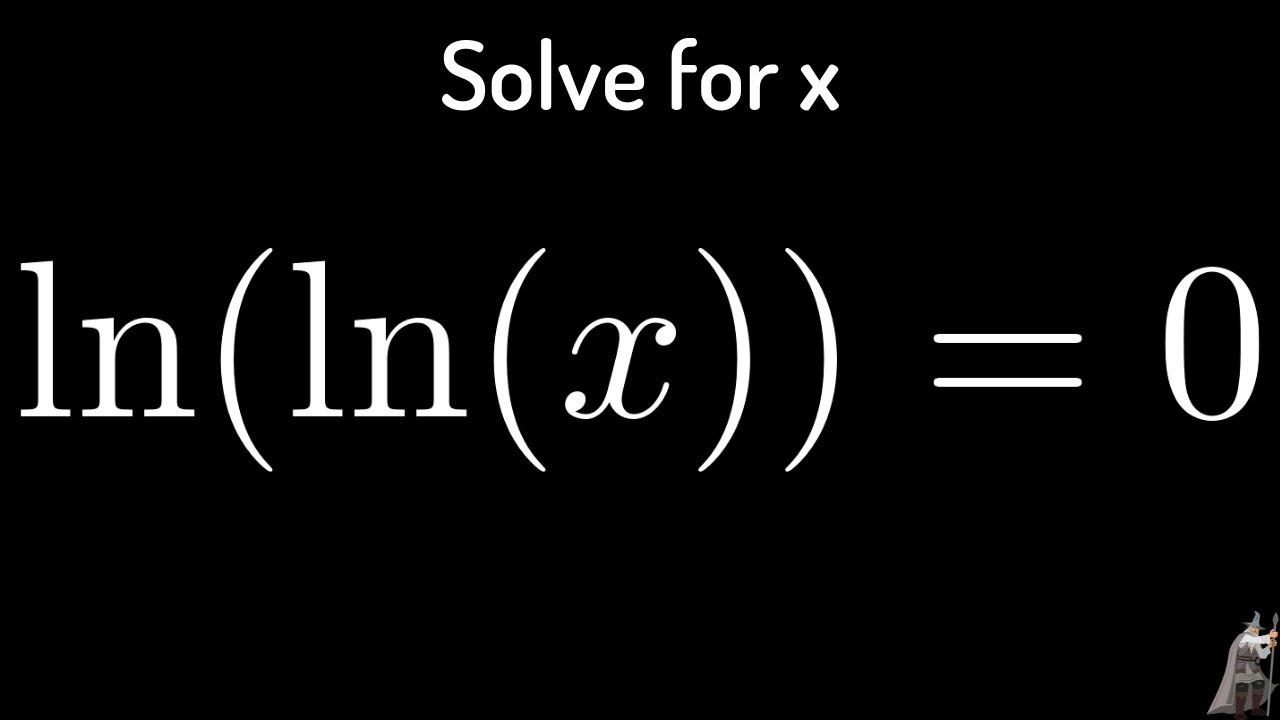
Solving The Logarithmic Equation Ln ln x 0 YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZDPNFJcBqnA/maxresdefault.jpg

Pin On Math Videos
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/50/43/2d/50432d3ca01ce25b180a1f01a9e91cc5.jpg
The natural logarithm is the logarithm having base e where 1 This function can be defined 2 for This definition means that e is the unique number with the property that the area of the region bounded by the hyperbola the x axis and the vertical lines and is 1 In other words 3 What is a logarithm Logarithms are another way of thinking about exponents For example we know that 2 raised to the 4 th power equals 16 This is expressed by the exponential equation 2 4 16 Now suppose someone asked us 2 raised to which power equals 16 The answer would be 4 This is expressed by the logarithmic equation log 2
[desc-10] [desc-11]
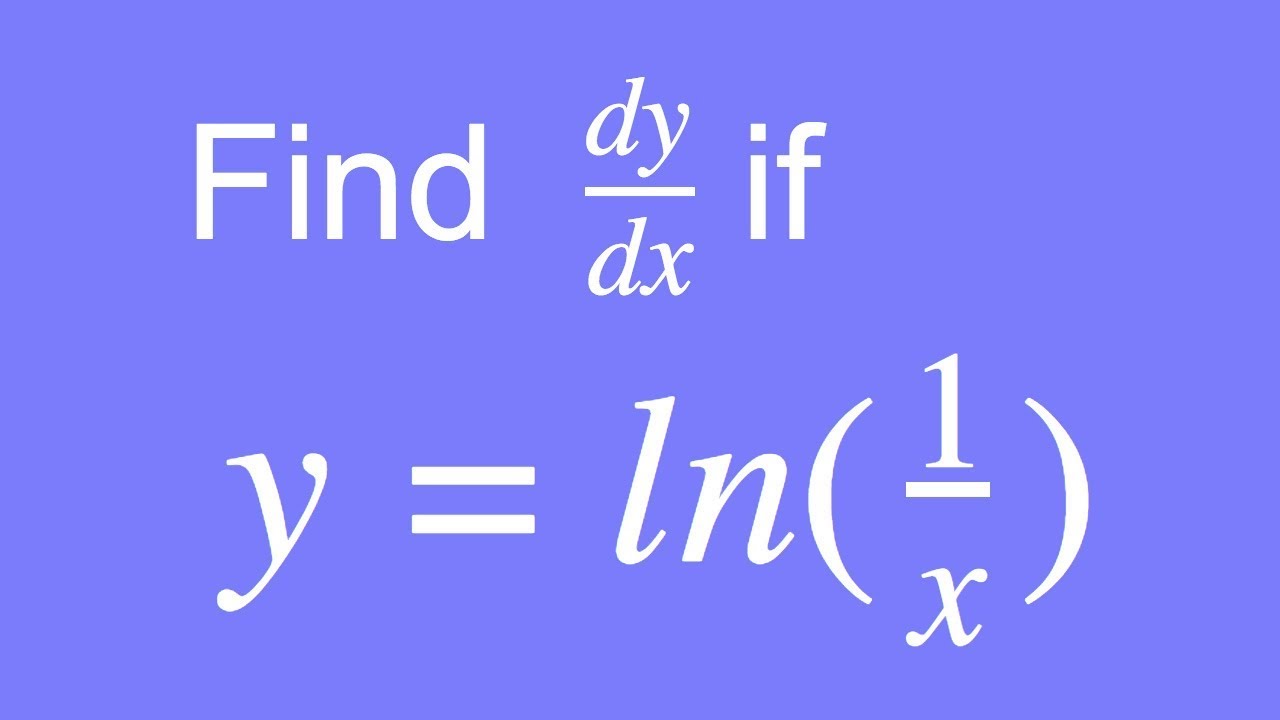
How To Differentiate Y ln 1 x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Aip9MGtP0Y4/maxresdefault.jpg
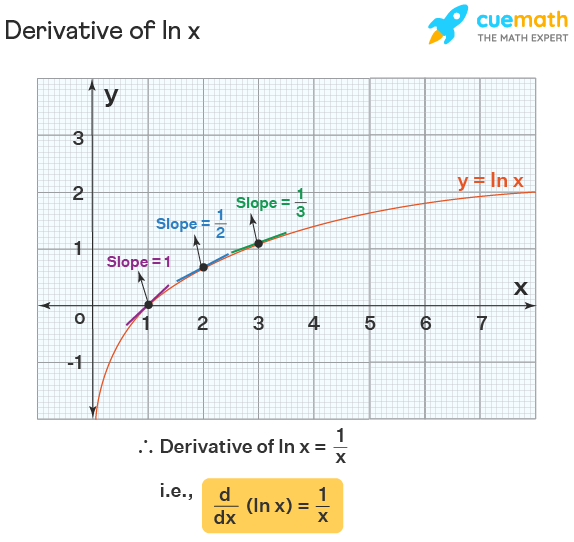
Derivative Of Ln X Natural Log Formula Differentiation Of Ln X
https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/ln-x-derivative-proof-by-graph-1629215157.png
ln 1 equals - The natural logarithm of x is the power to which e would have to be raised to equal x For example ln 7 5 is 2 0149 because e2 0149 7 5 The natural logarithm of e itself ln e is 1 because e1 e while the natural logarithm of 1 is 0 since e0 1