if f x 0 then a possible function is Many functions actually uncountably many exists which satisfy f 0 0 For an example just take the functions f 1 equiv 0 f 2 x x forall x in mathbb R and
Let f be n times differentiable at x and suppose f x f x dots f n 1 x 0 Then if f n x 0 there is a local minimum at x and if f n x Free functions calculator explore function domain range intercepts extreme points and asymptotes step by step
if f x 0 then a possible function is

if f x 0 then a possible function is
https://d1hj4to4g9ba46.cloudfront.net/questions/1112274_1208170_ans_c65fd5655aa34b4dbd9c9917b8875e61.jpg

Show That The Function F R R f x X 2 Is Neither One One Nor Onto
https://d1hj4to4g9ba46.cloudfront.net/questions/1544528_1705707_ans_6037ff93a8f74b2cb17368e0c88472da.jpg

Let F x Be A Function Defined By F x 3x x 2x X 0 0 X
https://d1hj4to4g9ba46.cloudfront.net/questions/1410427_1667527_ans_808ac0a063f24c108340275d48104e5a.jpg
The Derivative tells us the slope of a function at any point There are rules we can follow to find many derivatives For example The slope of a constant value like 3 is always 0 The slope A If f x 0 on an interval then f is increasing on that interval b If f x 0 on an interval then f is concave upward on that
A function cannot cross a vertical asymptote because the graph must approach infinity or from at least one direction as x approaches the vertical asymptote However a When f x 0 it only implies that there is a horizontal tangent at that point An example of the case when a function has a horizontal tangent at a point that is not a local extremum is given
More picture related to if f x 0 then a possible function is
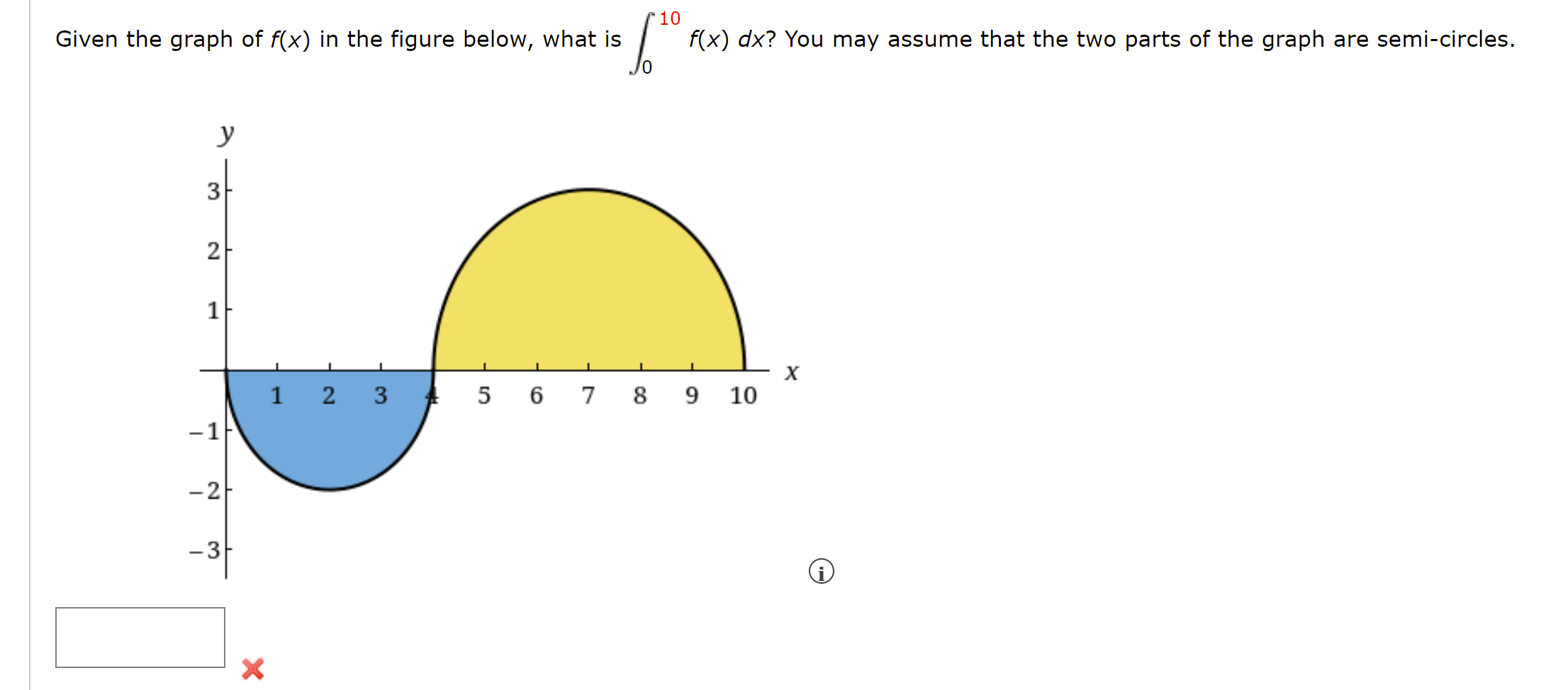
Solved Given The Graph Of F x In The Figure Below What Is Chegg
https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/18f/18f4577e-3423-4919-927e-0bd55abce2b4/php6olHoJ
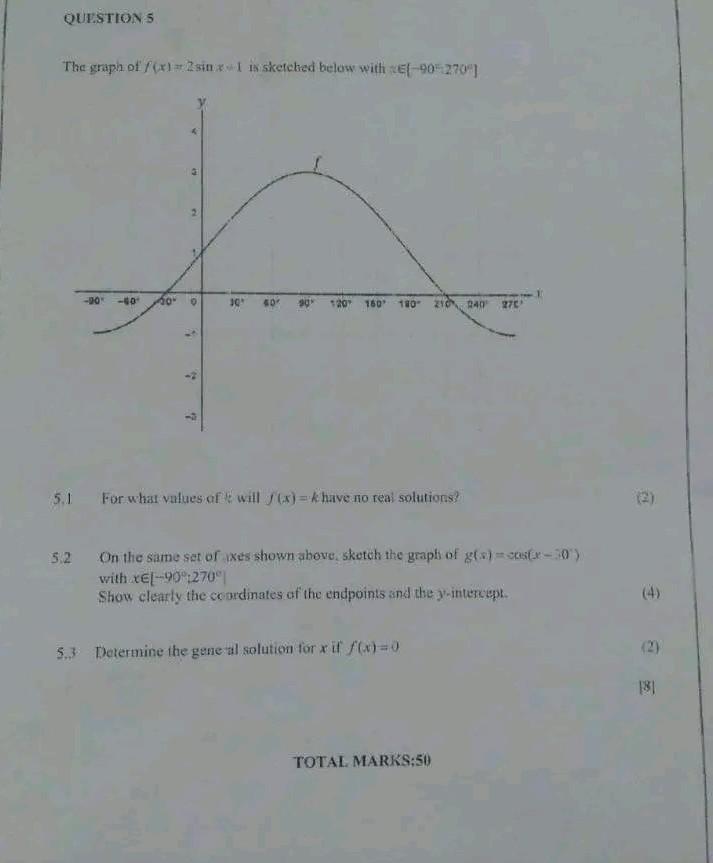
Solved The Graph Of F x 2 Sin X 1 Is Skelched Below With T Chegg
https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/49c/49cd1885-d625-48ab-b88e-89cf72849653/image.jpg

The Graph Of The Function F x x 4 x 1 Is Shown Below On A
https://media.brainly.com/image/rs:fill/w:828/q:75/plain/https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d16/02312343957b568811e1dd3f9641d71d.png
A one sided limit only considers values of a function that approaches a value from either above or below The right side limit of a function f as it approaches a is the limit lim x to I m trying to prove that if f 0 then is f is constant WITHOUT using the Mean Value Theorem My attempt sketch of proof Assume that f is not constant Identify interval I 1 such that
z dz Exdx Eydy fx x0 y0 dx fy x0 y0 dy Exdx Eydy If the approximation of z by dz is good then as dx and dy get small so does Exdx Eydy The Let f x be a function defined at all values in an open interval containing a with the possible exception of a itself and let L be a real number If all values of the function f x approach the

SOLVED True Or False If F Is A One to one Differentiable Function And
https://cdn.numerade.com/previews/ee773a43-3d4d-4f01-abce-a42cfd6abc54_large.jpg
Solved F x x 2if X 3 4x 7if X 3 Let F Be The Function Course Hero
https://www.coursehero.com/qa/attachment/15005986/
if f x 0 then a possible function is - A If f x 0 on an interval then f is increasing on that interval b If f x 0 on an interval then f is concave upward on that