e ln x and ln e x are equal to The equivalent rule of ln is e ln x x Product Rule of Logarithms By the product rule of logarithms the log of a product of two terms is equal to the sum of logs of individual terms i e the rule says log b mn log b m log b n
The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant e which is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to 2 718281828459 The natural logarithm of x is generally written as ln x loge x or sometimes if the base e is implicit simply log x Parentheses are sometimes added for clarity giving ln x loge x or log x This is done partic Is it possible to prove e ln x x for a student or can you only say that exponentiation is defined to be the inverse of natural logarithm and stop there
e ln x and ln e x are equal to
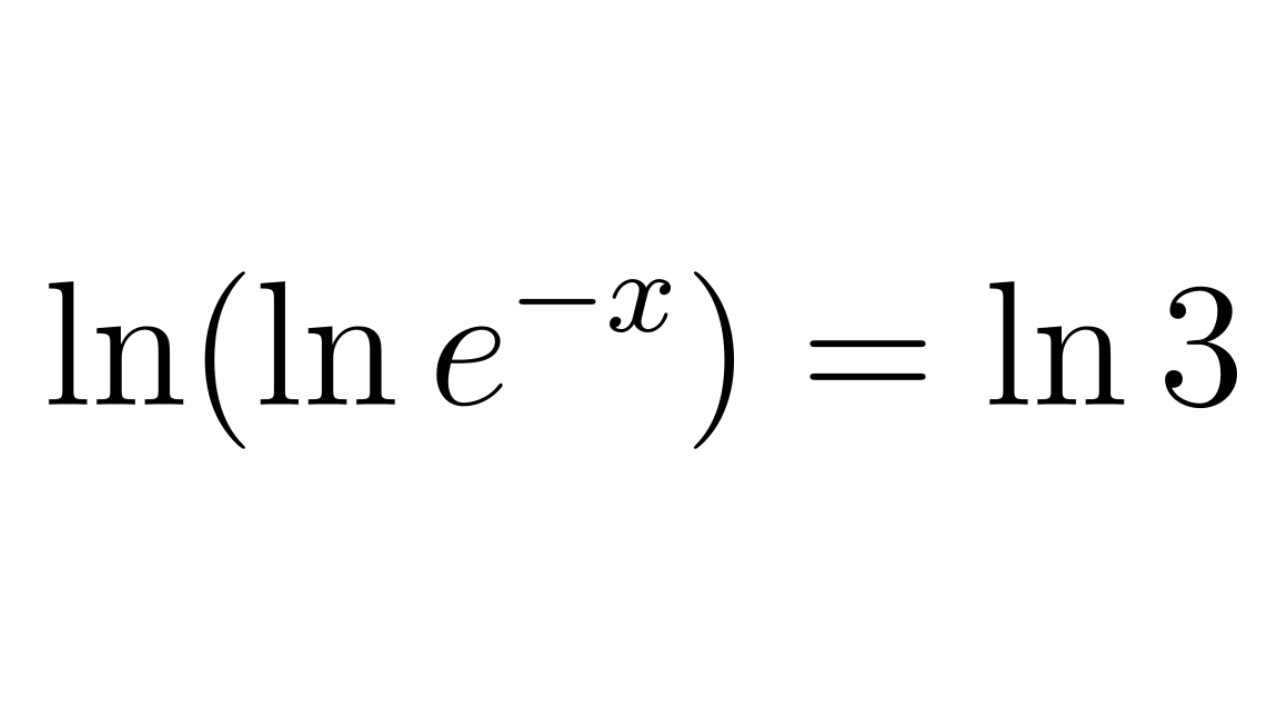
e ln x and ln e x are equal to
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/2ZgWQwZaHqs/maxresdefault.jpg
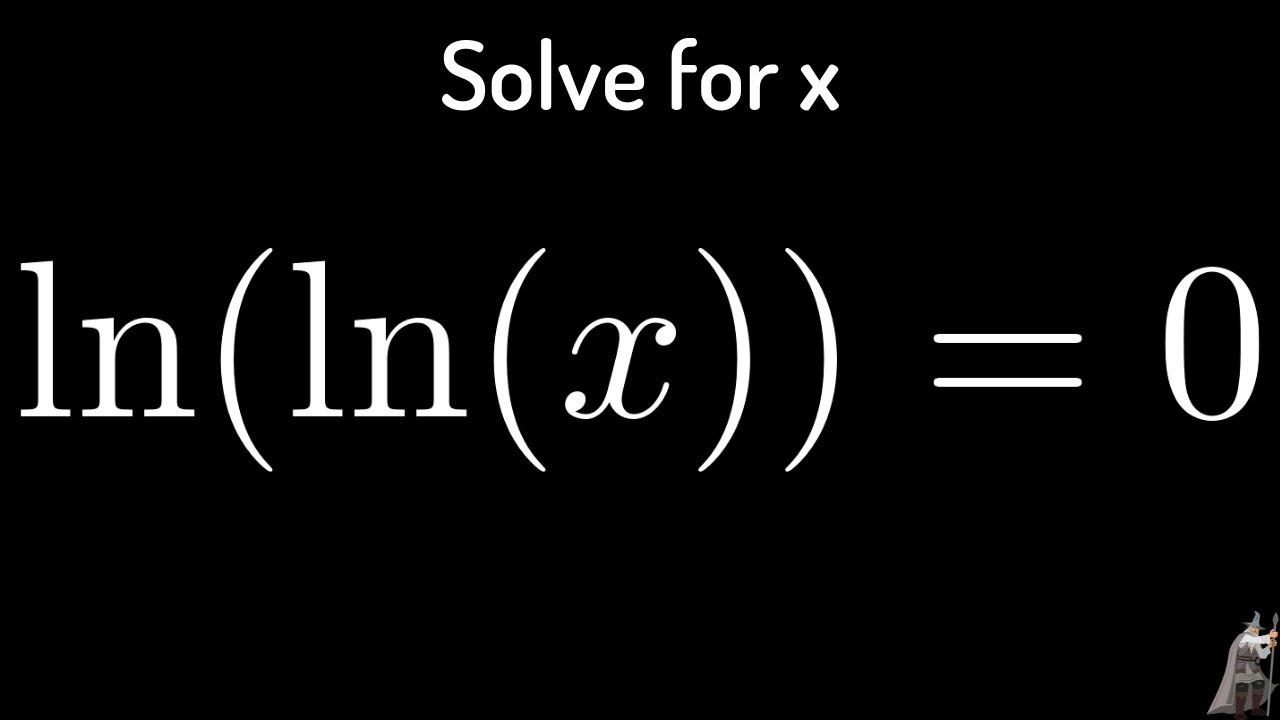
Solving The Logarithmic Equation Ln ln x 0 YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZDPNFJcBqnA/maxresdefault.jpg

Question Video Utilizando A Rela o Inversa Entre Fun es Exponenciais
https://media.nagwa.com/265131079460/en/thumbnail_l.jpeg
The equality x e ln x holds indeed only for x 0 The piecewise version could be for x 0 g x e ln x for x Like most functions you are likely to come across the exponential has an inverse function which is log e x often written ln x pronounced log x In the diagram e x is the red line lnx the green line and y x is the yellow line
The principal value of the natural logarithm is implemented in the Wolfram Language as Log x which is equivalent to Log E x This function is illustrated above in the complex plane You can change between exponential form and logarithmic form b stands for the base x represents the exponent log is short for logarithm means approximately equal to ln
More picture related to e ln x and ln e x are equal to
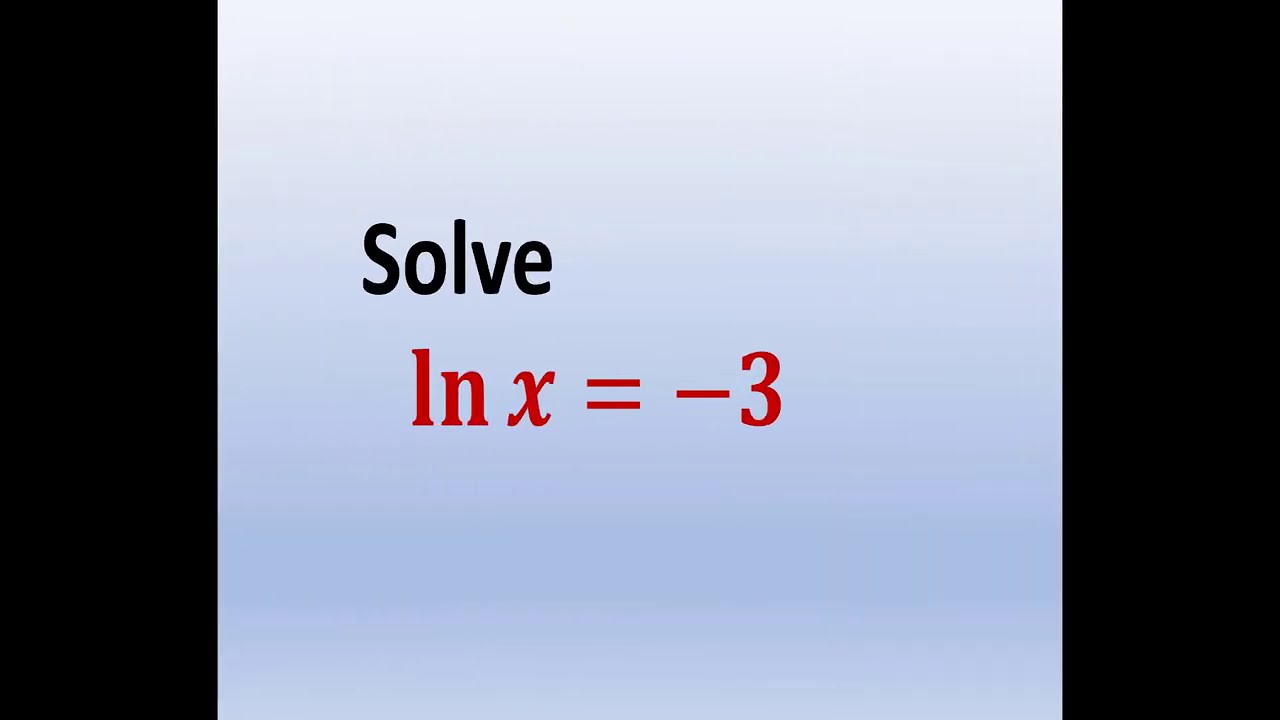
How Do You Solve Ln Equations For X How To Solve Ln X Is Equal To
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/KELVuurdy6o/maxresdefault.jpg

Find Power Series Representation For F x Ln 1 x And F x x Ln 1
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/lwiPioPt7Jc/maxresdefault.jpg

Solve x ln x e ln x 3 YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aXL_RmOky-Y/maxresdefault.jpg
Since the natural logarithm is a base e logarithm ln x log e x all of the properties of the logarithm apply to it We can use the properties of the logarithm to expand Ln e 1 These can be derived from the definition of ln x as the inverse of the function ex the definition of e and the rules of exponents we reviewed at the start of lecture We can also figure out what the graph of ln x must look like
Suppose that there is y such that e y x Apply the natural logarithm on both sides of the equation You get ln e y ln x y ln e ln x y ln x That s it Ln x log e x where log e x is defined as the inverse function of e x just as x 2 2 is x so is log e e x It s just written as ln x as opposed to log e x for saving time and because the N means natural as in the natural log
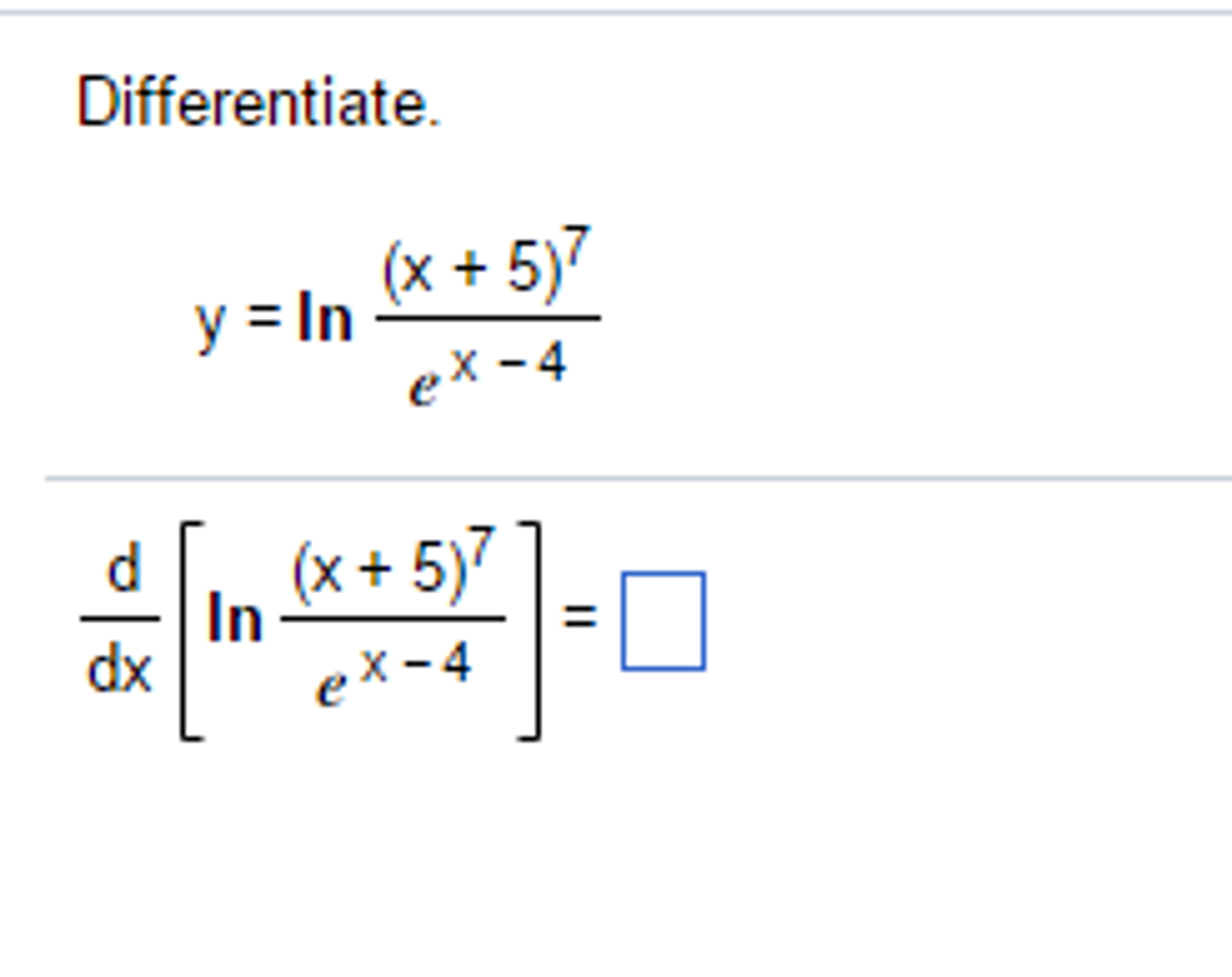
Solved Differentiate Y Ln x 5 7 e x 4 D dx ln x Chegg
https://d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media/bdd/bdd47e63-b7c5-47f4-9a11-9ae7d2251cf2/phpzHlqWF.png

E To The Power Of Ln x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/V553m9SAGgk/maxresdefault.jpg
e ln x and ln e x are equal to - The principal value of the natural logarithm is implemented in the Wolfram Language as Log x which is equivalent to Log E x This function is illustrated above in the complex plane