diffusion coefficient explained The diffusion coefficient is a physical constant dependent on molecule size and other properties of the diffusing substance as well as on temperature and pressure Diffusion coefficients of one substance into the other are commonly determined experimentally and presented in reference tables
The diffusion flux has units of frac text amount text areaxtime or frac mathrm mol mathrm m 2 s mathrm D is the diffusion coefficient which is sometimes called diffusivity It depends on the specific circumstances the diffusion is occurring in including what materials are involved and the state of the Diffusion can be described as the random movement of particles through space usually due to a concentration gradient Diffusion is a spontaneous process and is a result of the random thermal motions between two particles The diffusion coefficient D can be solved for with Fick s laws of diffusion which are broken up into two laws
diffusion coefficient explained

diffusion coefficient explained
https://1.bp.blogspot.com/-6M7JLl1Mkyk/XS1ZKNo2SlI/AAAAAAAAAMQ/OhBuCWM7VjQfZd0Eu0uQPeIosdn4jBW_gCLcBGAs/w1200-h630-p-k-no-nu/Mto3.jpg
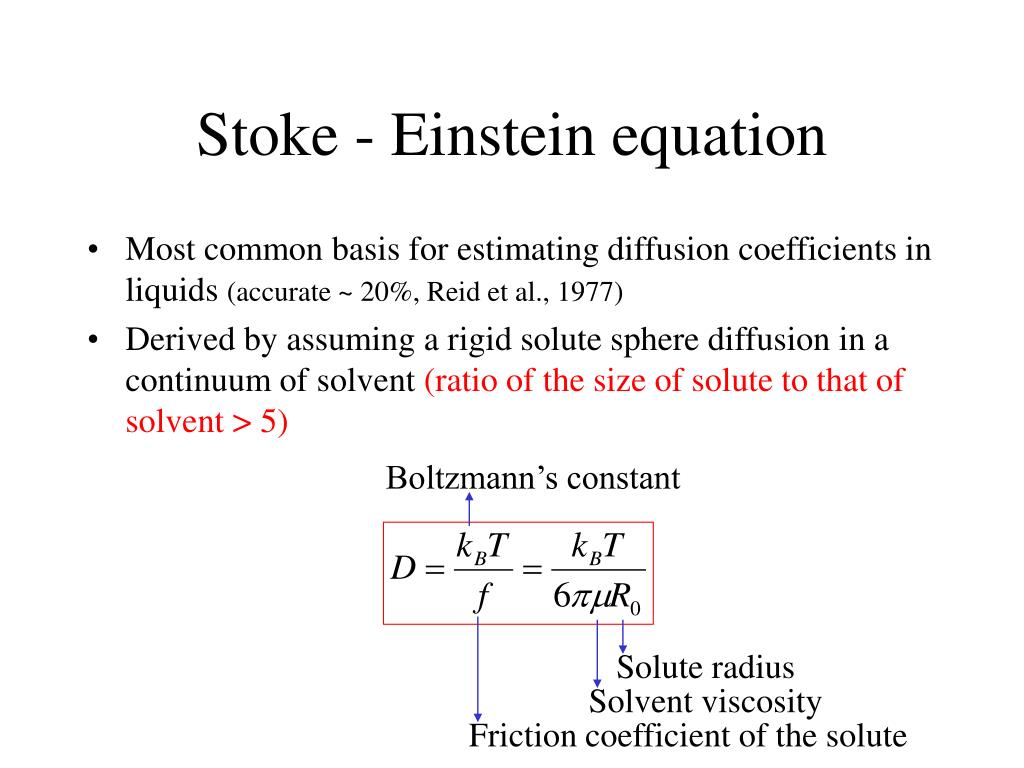
Einstein Diffusion Equation
https://image3.slideserve.com/6444263/stoke-einstein-equation-l.jpg

Experiment On Liquid Diffusion Coefficient UEMK2551 Process
https://www.thinkswap.com/sites/default/files/styles/document_full_view/public/pdf_thumbnails/1/docu_id175237_dd.jpg?3
Diffusion is a stochastic process where a single particle can move in each direction with the same probability Another description of the diffusion coefficient is the following equation D x 2 2t where t is the time and x 2 is the mean squared displacement of the particles at this time The diffusion flux J measures the amount of substance that flows through a unit area during a unit time interval measured in g m 2 The diffusion coefficient D measured in area per unit time m 2 s
Understand the general physical meaning of diffusion coefficient What is chemical diffusion coefficient DA C and tracer diffusion coefficient DA How are lng they inter related as DA C DA 1 A ln x lng Understand the meaning of the thermodynamic factor 1 A and the relationship ln x with the free energy gradient d lng Lecture Learn deduce the Fick s second law and understand the basic meaning in comparison the first law Learn apply the second law in several practical cases including homogenization carburization steel where diffusion plays dominant role
More picture related to diffusion coefficient explained

The Activation Volume For A The Diffusion Coefficient V D And B
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Zeke-Piskulich/publication/356022023/figure/fig1/AS:1094509232439296@1637962744746/a-Diffusion-coefficient-D-and-b-inverse-OH-reorientation-time-1-t-2-for-each-of_Q640.jpg
Diffusion Coefficients Passive Samplers
https://passivesamplers.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Diffusion-Coefficients-in-an-agarose.jpg

1 Diffusion Coefficient D 2 Download Scientific Diagram
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Malte-Siefert/publication/267259456/figure/fig1/AS:669420926029836@1536613794737/Diffusion-coefficient-D-2.png
Like chemical reactions diffusion is a thermally activated process and the temperature dependence of diffusion appears in the diffusivity as an Arrhenius type equation D D 0 e E a R T The diffusion coefficient or diffusivity is a measure of mobility of a species atom molecule or ion which depends on the frequency with which a species moves and the size of each movement The magnitude of diffusion coefficient is governed by the restricting forces of the medium in which diffusion takes place
The diffusion coefficient is the coefficient in the Fick s first law where J is the diffusion flux amount of substance per unit area per unit time n for ideal mixtures is the concentration x is the position length The diffusion coefficient of gases is important when comparing different gases in the lung Let s take CO2 and O2 They are similar in molecular weight but CO2 is about 20x more soluble than O2 in plasma and therefore diffuses faster

Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Equation
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yusuf_Bhagat/publication/291346848/figure/fig8/AS:670041561378835@1536761765707/2-Calculation-of-the-apparent-diffusion-coefficient-ADC-map-An-ADC-map-is-computed.png
Solved Example Calculate The Effective Diffusion Coefficient Chegg
https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/8a2/8a2eaec1-b131-4207-a263-2ee35c38d6e4/phpzeFqWV
diffusion coefficient explained - The diffusion coefficient is a parameter characteristic of particles in solution that describes the easiness with which they move from regions with higher concentration to regions with lower concentration due to random motion Brownian motion The diffusion coefficient depends on the solvent s temperature and viscosity and the shape and size
